上篇文章介绍了Pandas的基础操作,包括文件读写、Series和DataFrame数据结构、一些常用基本函数、数据排序等。
今天我们来学习一下Pandas的索引。
(超详细!一文搞定!)
Pandas单级索引
1. loc、iloc、[]操作符
这三类最常用的索引方法,其中iloc表示位置索引,loc表示标签索引,[]也具有很大的便利性,各有特点。
总结来说就是:
- loc只能传布尔列表或索引列表
- iloc只能传整数列表
1.1 loc方法
- 本质上来说,loc中能传入的只有布尔列表和索引子集构成的列表。
- loc方法包含切片右端点。
# 单行索引
dataframe.loc[index]
# 多行索引
dataframe.loc[index1, index2]
dataframe.loc[index: ]
dataframe.loc[开始:结束:步长]
# 多列索引
dataframe[:, '列索引名']
# 函数式索引(传入的参数是dataframe)
dataframe.loc[lambda x:x['Gender']=='M']
def f(x):
return [1101,1103]
df.loc[f]
1.2 iloc方法
- iloc中接收的参数只能为整数或整数列表,不能使用布尔索引
- iloc方法不包含切片右端点。
# 单行索引
df.iloc[3]
#多行索引
df.iloc[3:5]
# 单列索引
df.iloc[:,3]
# 多列索引
df.iloc[:,7::-2]
# 函数式索引
df.iloc[lambda x:[3]]
1.3 []操作符
- 在Series中的浮点[]并不是进行位置比较,而是值比较,因此不要在行索引为浮点时使用[]操作符。
- []操作符常用于列选择或布尔选择,尽量避免行的选择
(1) Series的[]操作符
s = pd.Series(df['Math'],index=df.index)
# 单元素索引
s[1101]
# 多行索引
s[0:4]
# 函数式索引
s[lambda x: x.index[16::-6]]
# 布尔索引
s[s>80]
(2) DataFrame的[]操作符
# 单行索引
df[1:2]
row = df.index.get_loc(1102) # get_loc()返回索引值(所在的行号)
df[row:row+1]
# 多行操作
df[3:5] # 切片
# 单列索引
df['School']
# 多列索引
df[['School','Math']]
# 函数式索引
df[lambda x:['Math','Physics']]
2. 布尔索引
2.1 布尔符号:'&', '|', '~',分别代表 和and,或or,非not
df[(df['Gender']=='F')&(df['Address']=='street_2')]
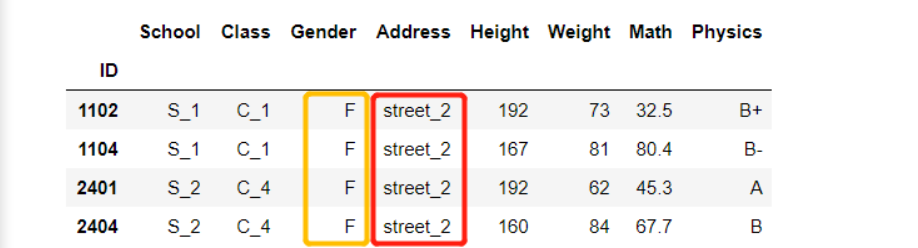
df[(df['Math']>85)|(df['Address']=='street_7')].head()

df[~((df['Math']>75)|(df['Address']=='street_1'))]
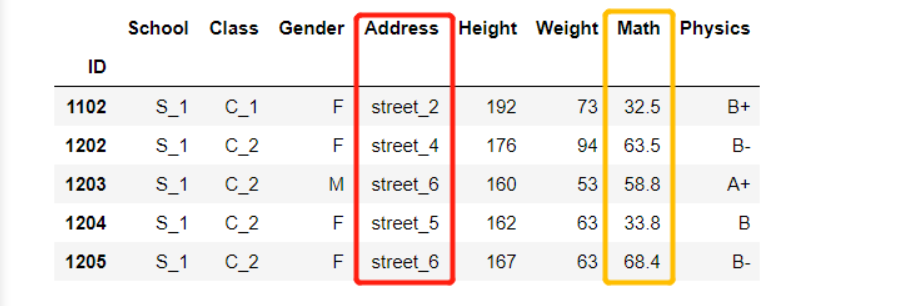
2.2 isin方法
df[df['Address'].isin(['street_1','street_4'])&df['Physics'].isin(['A','A+'])]
# 字典方式
df[df[['Address','Physics']].isin({'Address':['street_1','street_4'],'Physics':['A','A+']}).all(1)]
#all与&的思路是类似的,其中的1代表按照跨列方向判断是否全为True
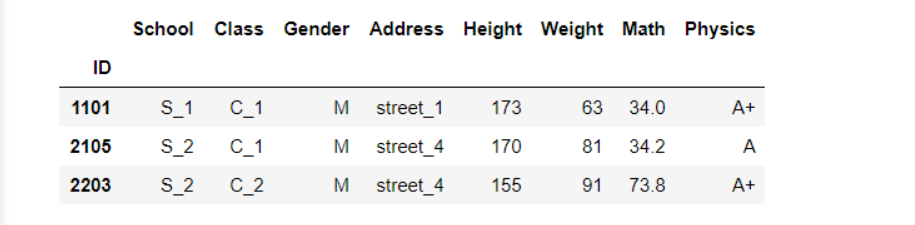
3 标量索引
at和iat方法,适用于只取一个元素的情况。
同样,at只能传布尔列表或索引列表,iat只能传整数列表
df.at[1101,'School']
df.iat[0,0]
4 区间索引
(1) interval_range方法:
#closed参数可选'left''right''both''neither',默认左开右闭
pd.interval_range(start=0,end=5)
# periods参数控制区间个数,freq控制步长
pd.interval_range(start=0,periods=8,freq=5)
下面用一个具体的例子——统计数学成绩的区间情况,来说明区间索引。
math_interval = pd.cut(df['Math'],bins=[0,40,60,80,100])
df_i = df.join(math_interval,rsuffix='_interval')[['Math','Math_interval']].reset_index().set_index('Math_interval')
df_i.head()

df_i.loc[90] # 会选中该值的区间
如果想要选取某个区间,先要把分类变量转为区间变量,再使用overlap方法:
df_i[df_i.index.astype('interval').overlaps(pd.Interval(70, 85))].head()

Pandas多级索引
1 多层索引的创建
多层索引的创建主要有三类方法:
- from_tuple或from_arrays
- from_product
- 指定dataframe的列创建(set_index方法)
下面分别举例说明。
1.1 from_tuple或from_arrays
# 直接创建
tuples = [('A','a'),('A','b'),('B','a'),('B','b')]
mul_index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples(tuples, names=('Upper', 'Lower'))
pd.DataFrame({'Score':['perfect','good','fair','bad']},index=mul_index)
# 利用zip
L1 = list('AABB')
L2 = list('abab')
tuples = list(zip(L1,L2))
mul_index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples(tuples, names=('Upper', 'Lower'))
pd.DataFrame({'Score':['perfect','good','fair','bad']},index=mul_index)
# 通过array
arrays = [['A','a'],['A','b'],['B','a'],['B','b']]
mul_index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples(arrays, names=('Upper', 'Lower'))
pd.DataFrame({'Score':['perfect','good','fair','bad']},index=mul_index)

通过打印mul_index可以看出,上述三种方式都是通过内部自动转换成元组来创建的。
1.2 from_product
L1和L2两两相乘
L1 = ['A','B']
L2 = ['a','b']
pd.MultiIndex.from_product([L1,L2],names=('Upper', 'Lower'))
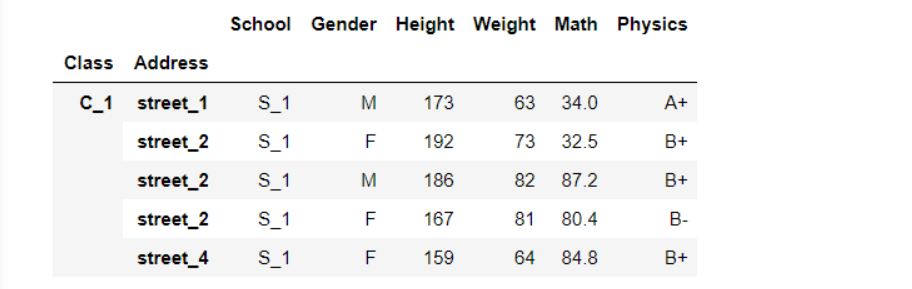
1.3 指定dataframe的列(set_index方法)
df_using_mul = df.set_index(['Class','Address'])
df_using_mul.head()
2 多层索引切片
这里举例都是用上一小节的df_using_mul做演示。
(1)一般切片
# 当索引不排序时,不能使用多层切片
df_using_mul.sort_index().loc['C_2','street_5']
df_using_mul.sort_index().loc[('C_2','street_6'):('C_3','street_4')]
df_using_mul.sort_index().loc[('C_2','street_7'):'C_3'].head()
(2)第一类特殊情况:由元组构成列表
df_using_mul.sort_index().loc[[('C_2','street_7'),('C_3','street_2')]]
# 表示选出某几个元素,精确到最内层索引
第二类特殊情况:由列表构成元组
df_using_mul.sort_index().loc[(['C_2','C_3'],['street_4','street_7']),:]
# 选出第一层在‘C_2’和'C_3'中且第二层在'street_4'和'street_7'中的行
3 多层索引的slice对象
L1,L2 = ['A','B','C'],['a','b','c']
mul_index1 = pd.MultiIndex.from_product([L1,L2],names=('Upper', 'Lower'))
L3,L4 = ['D','E','F'],['d','e','f']
mul_index2 = pd.MultiIndex.from_product([L3,L4],names=('Big', 'Small'))
df_s = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(9,9),index=mul_index1,columns=mul_index2)
idx=pd.IndexSlice
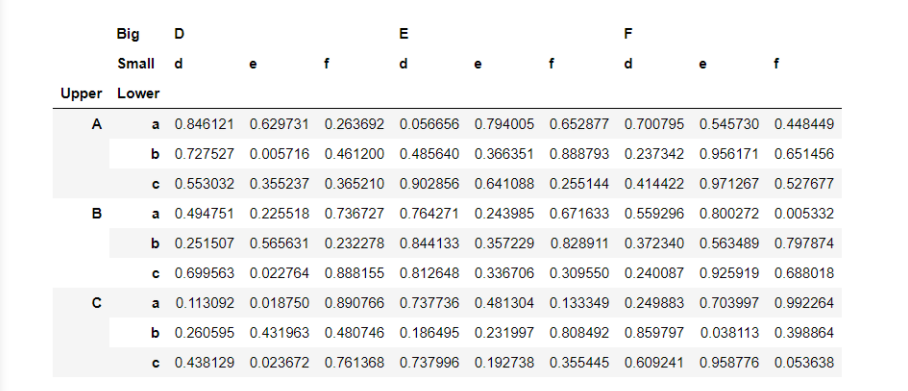
索引Slice的使用非常灵活,可以很方便地对索引进行操作。
结果如下:索引取了B后面的、D d>0.3的、纵向求和>4的部分。
df_s.loc[idx['B':,df_s['D']['d']>0.3],idx[df_s.sum()>4]]

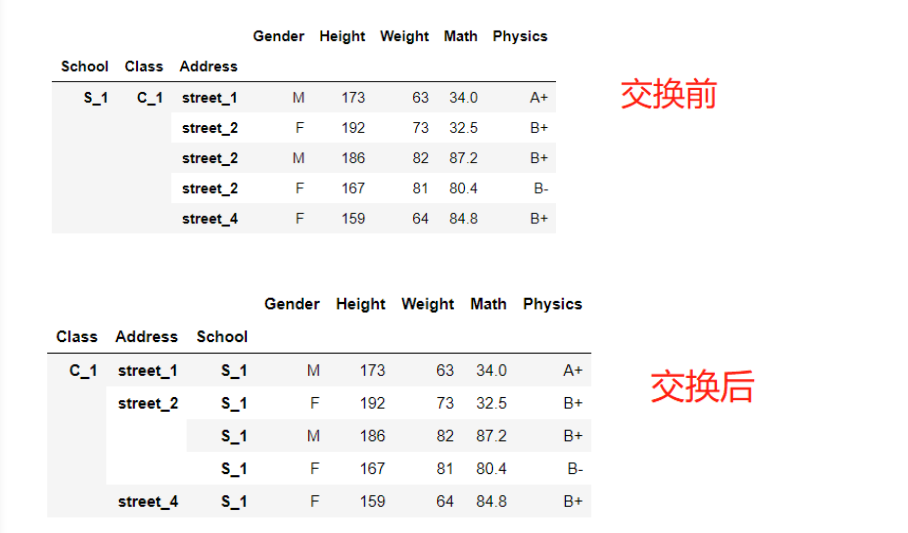
4 索引层交换
主要有两个方法:
- swaplevel方法:用于两层交换
- recorder_levels方法:用于多层交换
# swaplevel方法
df_using_mul.swaplevel(i=1,j=0,axis=0).sort_index()
# recorder_levels方法
df_muls = df.set_index(['School','Class','Address'])
df_muls.reorder_levels([1,2,0],axis=0).sort_index()
#如果索引有name,可以直接使用name
df_muls.reorder_levels(['Class','Address','School'],axis=0).sort_index()
索引设定
这部分所讲的是索引设定的一些操作。
(1)index_col参数
在使用read_csv函数时,通过index_col可以设定索引。
(2)reindex和reindex_like
- reindex是指重新排序。重要特性在于索引对齐,很多时候用于重新排序。
#bfill表示用所在索引的后一个有效行填充,ffill为前一个有效行,nearest是指最近的
df.reindex(index=[1101,1203,1206,2402], columns=['Height','Gender','Average'], method='bfill')
- reindex_like的作用为生成一个横纵索引完全与参数列表一致的DataFrame,数据使用被调用的表。如果表是单调的还可以使用method参数。
df_temp = pd.DataFrame({'Weight':range(5),
'Height':range(5),
'ID':[1101,1104,1103,1106,1102]}).set_index('ID').sort_index()
df_temp.reindex_like(df[0:5][['Weight','Height']],method='bfill')
#可以自行检验这里的1105的值是否是由bfill规则填充

(3)set_index和reset_index
- 使用set_index时,将某些列作为索引。指定参数
append=True可以维持当前索引不变 - reset_index将索引重置。默认状态直接恢复到自然数索引
(4)rename_axis和rename
- rename_axis是针对多级索引的方法,作用是修改某一层的索引名,而不是索引标签。
- rename方法用于修改列或者行索引标签,而不是索引名。
df_temp.rename_axis(index={'Lower':'LowerLower'},columns={'Big':'BigBig'})
df_temp.rename(index={'A':'T'},columns={'e':'changed_e'})
常用索引型函数
1 where()和mask()
- where()函数对条件为False的单元进行填充,第一个参数为布尔条件,第二个参数为填充值。
- mask()函数对条件为True的单元进行填充,其余完全一致。
# where
df.where(df['Gender']=='M',np.random.rand(df.shape[0],df.shape[1]))
# mask
df.mask(df['Gender']=='M',np.random.rand(df.shape[0],df.shape[1]))
2 query()函数
query函数中的布尔表达式中,行列索引名、字符串、and/not/or/&/|/~/not in/in/==/!=、四则运算符等都是合法的
df.query('(Address in ["street_6","street_7"])&(Weight>(70+10))&(ID in [1303,2304,2402])')
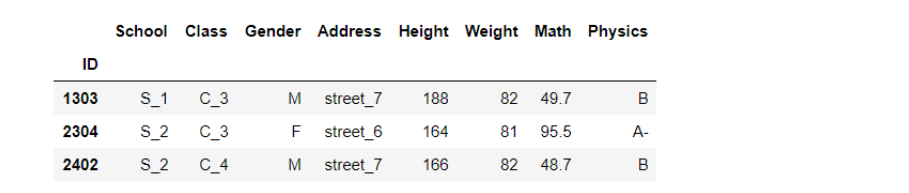
重复元素处理(duplicated和drop_duplicates)
- duplicated方法:
- 返回是否重复的布尔列表。
- 可选参数
keep默认为first,即首次出现设为不重复; - 若为
last,则最后一次设为不重复; - 若为
False,则所有重复项为False。
- drop_duplicates方法:
- 参数与duplicated方法类似。
- 在传入多列时等价于将多列共同视作一个多级索引,比较重复项。
df.duplicated('Class',keep='last')
df.drop_duplicates('Class',keep='last')
df.drop_duplicates(['School','Class'])
抽样函数(sample)
- n:样本量
- frace为抽样比
- replace为是否放回,
True或者False - axis为抽样维度,默认为0,即抽行
- weights为样本权重,自动归一化。也可以以某一列为权重。
如什么问题,欢迎留言交流,觉得有用的小伙伴顺手点个赞吧。
你的肯定是我的最大动力!