给出一个n,求1-n这n个数,同n的最大公约数的和。比如:n = 6时,1,2,3,4,5,6 同6的最大公约数分别为1,2,3,2,1,6,加在一起 = 15
看起来很简单对吧,但是n<=1e9,所以暴力是不行的,所以要把公式进行推导。
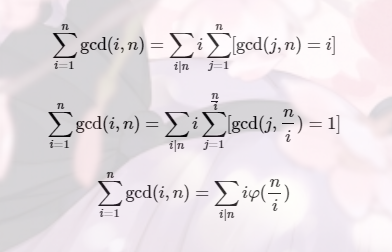
这个自己上手推一下也很好推的,不过没推过公式的可能不太懂。

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cmath> 3 typedef long long ll; 4 const int N=52118; 5 bool nop[N]={false}; 6 int pn,pri[N]; 7 void init() 8 { 9 pn=0; 10 for(int i=2;i<N;i++) 11 { 12 if(!nop[i]) 13 pri[pn++]=i; 14 for(int j=0;j<pn&&1ll*i*pri[j]<N;j++) 15 { 16 nop[i*pri[j]]=true; 17 if(i%pri[j]==0) 18 break; 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 int phi(int x) 23 { 24 int ans=x; 25 for(int i=0;i<pn&&pri[i]*pri[i]<=x;i++) 26 if(x%pri[i]==0) 27 { 28 ans=ans-ans/pri[i]; 29 while(x%pri[i]==0) 30 x/=pri[i]; 31 } 32 if(x>1) 33 ans=ans-ans/x; 34 return ans; 35 } 36 ll solve(int x) 37 { 38 ll ans=0; 39 int xx=sqrt(x); 40 for(int i=1;i<=xx;i++) 41 { 42 if(x%i==0) 43 { 44 ans+=i*phi(x/i); 45 if(x/i!=i) 46 ans+=x/i*phi(i); 47 } 48 } 49 return ans; 50 } 51 int main() 52 { 53 int n; 54 init(); 55 while(~scanf("%d",&n)) 56 printf("%lld ",solve(n)); 57 return 0; 58 }
另一个方法就是首先可以观察看出f(n)=∑gcd(i,n)是积性函数的性质(不懂证明),然后借用积性函数的性质
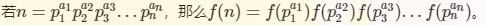
这样要求f(n),我们只需要知道f(pk)等于多少就行了,而f(pk)的话
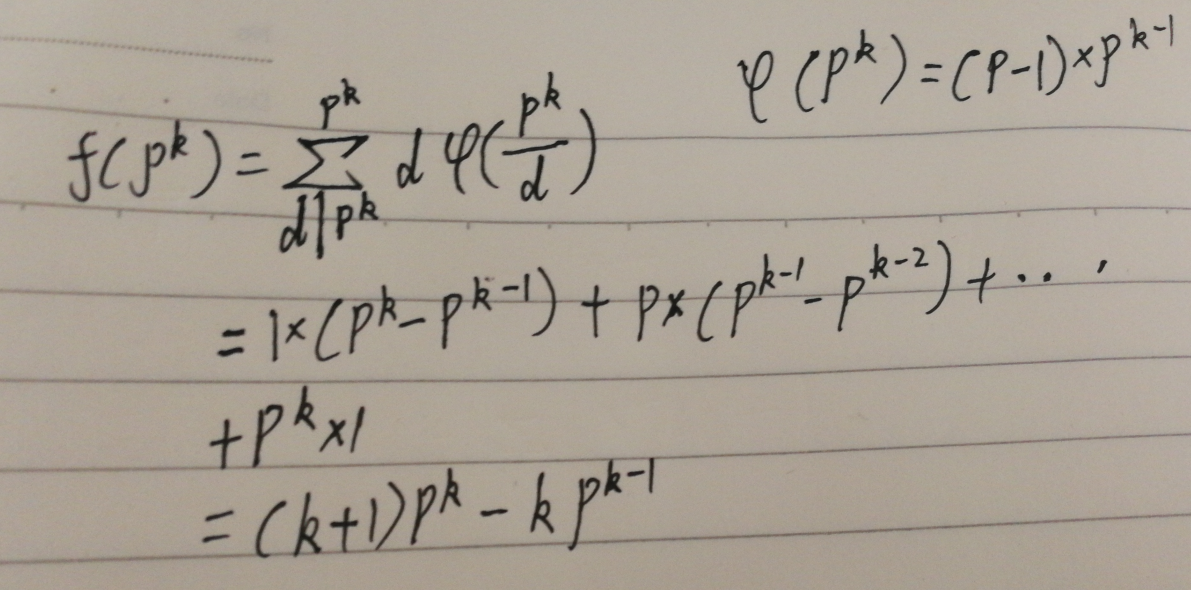
而不懂怎么化简成最后一步的话,直接跑第一步的式子也行,因为pk它的因子也不会有多少个

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cmath> 3 typedef long long ll; 4 const int N=52118; 5 bool nop[N]={false}; 6 int pn,pri[N]; 7 void init() 8 { 9 pn=0; 10 for(int i=2;i<N;i++) 11 { 12 if(!nop[i]) 13 pri[pn++]=i; 14 for(int j=0;j<pn&&1ll*i*pri[j]<N;j++) 15 { 16 nop[i*pri[j]]=true; 17 if(i%pri[j]==0) 18 break; 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 int phi(int x) 23 { 24 int ans=x; 25 for(int i=0;i<pn&&pri[i]*pri[i]<=x;i++) 26 if(x%pri[i]==0) 27 { 28 ans=ans-ans/pri[i]; 29 while(x%pri[i]==0) 30 x/=pri[i]; 31 } 32 if(x>1) 33 ans=ans-ans/x; 34 return ans; 35 } 36 //不化简 37 //ll solve(int x) 38 //{ 39 // ll ans=1,res; 40 // for(int i=0;i<pn&&pri[i]<=x;i++) 41 // { 42 // if(x%pri[i]==0) 43 // { 44 // int y=1,z,num=0; 45 // res=0; 46 // while(x%pri[i]==0) 47 // { 48 // x/=pri[i]; 49 // y*=pri[i]; 50 // } 51 // z=y; 52 // while(z) 53 // { 54 // res+=1ll*(y/z-num)*z; 55 // num=y/z; 56 // z/=pri[i]; 57 // } 58 // ans*=res; 59 // } 60 // } 61 // if(x>1) 62 // ans*=2ll*x-1; 63 // return ans; 64 //} 65 ll solve(int x) 66 { 67 ll ans=0; 68 int xx=sqrt(x); 69 for(int i=1;i<=xx;i++) 70 { 71 if(x%i==0) 72 { 73 ans+=i*phi(x/i); 74 if(x/i!=i) 75 ans+=x/i*phi(i); 76 } 77 } 78 return ans; 79 } 80 int main() 81 { 82 int n; 83 init(); 84 while(~scanf("%d",&n)) 85 printf("%lld ",solve(n)); 86 return 0; 87 }
