Vladik was bored on his way home and decided to play the following game. He took n cards and put them in a row in front of himself. Every card has a positive integer number not exceeding 8 written on it. He decided to find the longest subsequence of cards which satisfies the following conditions:
- the number of occurrences of each number from 1 to 8 in the subsequence doesn't differ by more then 1 from the number of occurrences of any other number. Formally, if there are ck cards with number k on them in the subsequence, than for all pairs of integers
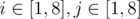 the condition |ci - cj| ≤ 1 must hold.
the condition |ci - cj| ≤ 1 must hold. - if there is at least one card with number x on it in the subsequence, then all cards with number x in this subsequence must form a continuous segment in it (but not necessarily a continuous segment in the original sequence). For example, the subsequence [1, 1, 2, 2] satisfies this condition while the subsequence [1, 2, 2, 1] doesn't. Note that [1, 1, 2, 2] doesn't satisfy the first condition.
Please help Vladik to find the length of the longest subsequence that satisfies both conditions.
The first line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000) — the number of cards in Vladik's sequence.
The second line contains the sequence of n positive integers not exceeding 8 — the description of Vladik's sequence.
Print single integer — the length of the longest subsequence of Vladik's sequence that satisfies both conditions.
3
1 1 1
1
8
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
8
24
1 8 1 2 8 2 3 8 3 4 8 4 5 8 5 6 8 6 7 8 7 8 8 8
17
In the first sample all the numbers written on the cards are equal, so you can't take more than one card, otherwise you'll violate the first condition.
题解:
先简单翻译一下,给一个序列,求最长的满足下面条件的子序列:
第一,相同数字连续;第二,每种数字出现次数之差不超过1
我们来考虑,由于每种数字出现都是连续的,因此一种数字一旦出现过,就不能再出现第二次。
所以我们可以用二进制来压每种数字是否出现过。
那么,每种数字出现次数的限制怎么处理?
这个东西不好说,所以我们考虑,如果有一种选择,使得每种数字都出现了至少a次,
那么一定会有其他选择,使得每种数字都出现了至少a-1次,a-2次……1次。
因此,我们就可以二分了!二分枚举每种数字至少出现的次数len,那么每种数字要么出现len次,要么出现len+1次。
对于某个len,定义状态数组f[i][j]为前i位中,数字出现状态为j时出现len+1次的数的最大种数
设tmp=max{f[i][(1<<8)-1}},那么显然,ans=tmp*(len+1)+(8-tmp)*len
在选取新的数字时,新数字要么出现len次,要么出现len+1次,
那么状态方程也显而易见了(刷表),更新对应位置的f值即可
最后注意特判:如果二分得到len=0,那么ans=出现的数的种数
代码见下:

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<vector> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 const int N=1010; 7 const int K=(1<<8)+10; 8 int n,a[N],f[N][K],now[10],bit[15];//now数组用来记录转移位置 9 inline int max(int a,int b){return a>b?a:b;} 10 vector<int> loc[10]; 11 inline int judge(int len) 12 { 13 for(int i=1;i<=8;i++)now[i]=0; 14 memset(f,0xaf,sizeof(f)); 15 int inf=f[0][0]; 16 f[0][0]=0; 17 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 18 { 19 for(int j=0;j<bit[8];j++) 20 { 21 if(f[i][j]==inf)continue; 22 for(int k=0;k<8;k++) 23 { 24 if(j&bit[k])continue; 25 int pos=now[k+1]+len-1; 26 if(pos>=loc[k+1].size())continue; 27 f[loc[k+1][pos]][j|bit[k]]=max(f[loc[k+1][pos]][j|bit[k]],f[i][j]); 28 pos++; 29 if(pos>=loc[k+1].size())continue; 30 f[loc[k+1][pos]][j|bit[k]]=max(f[loc[k+1][pos]][j|bit[k]],f[i][j]+1); 31 } 32 } 33 now[a[i]]++; 34 } 35 int ans=inf; 36 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) 37 ans=max(ans,f[i][bit[8]-1]); 38 if(ans==inf)return -1; 39 return ans*(len+1)+(8-ans)*len; 40 } 41 int main() 42 { 43 bit[0]=1;for(int i=1;i<=10;i++)bit[i]=bit[i-1]<<1; 44 scanf("%d",&n); 45 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 46 scanf("%d",&a[i]),loc[a[i]].push_back(i); 47 int l=0,r=n/8+1,ans=2333; 48 while(l<=r) 49 { 50 int mi=(l+r)>>1; 51 if(judge(mi)!=-1)ans=judge(mi),l=mi+1; 52 else r=mi-1; 53 } 54 if(ans==2333) 55 { 56 ans=0; 57 for(int i=1;i<=8;i++) 58 if(!loc[i].empty())ans++; 59 } 60 printf("%d",ans); 61 }
