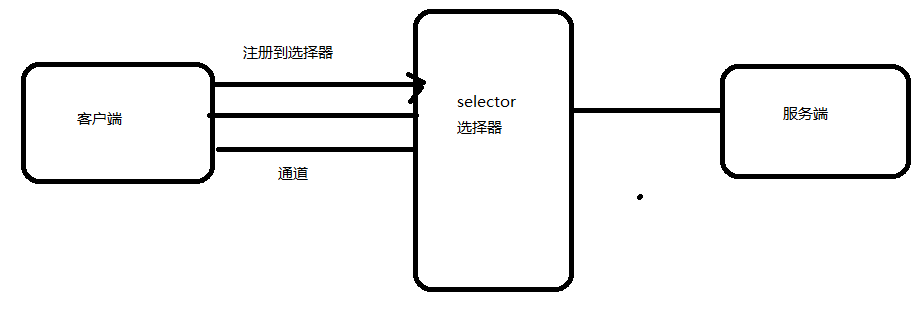
Buffer的数据存取
一个用于特定基本数据类行的容器。有java.nio包定义的,所有缓冲区都是抽象类Buffer的子类。
Java NIO中的Buffer主要用于与NIO通道进行交互,数据是从通道读入到缓冲区,从缓冲区写入通道中的。
Buffer就像一个数组,可以保存多个相同类型的数据。根据类型不同(boolean除外),有以下Buffer常用子类:ByteBuffer、CharBuffer、ShortBuffer、IntBuffer、LongBuffer、FloatBuffer、DoubleBuffer
Buffer的概述
1)容量(capacity):表示Buffer最大数据容量,缓冲区容量不能为负,并且建立后不能修改。
2)限制(limit):第一个不应该读取或者写入的数据的索引,即位于limit后的数据不可以读写。缓冲区的限制不能为负,并且不能大于其容量(capacity)。
3)位置(position):下一个要读取或写入的数据的索引。缓冲区的位置不能为负,并且不能大于其限制(limit)。
4)标记(mark)与重置(reset):标记是一个索引,通过Buffer中的mark()方法指定Buffer中一个特定的position,之后可以通过调用reset()方法恢复到这个position。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.指定缓冲区大小1024
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
// 2.向缓冲区存放5个数据
buf.put("abcd1".getBytes());
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
// 3.开启读模式
buf.flip();
System.out.println("----------开启读模式...----------");
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
byte[] bytes = new byte[buf.limit()];
buf.get(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, bytes.length));
System.out.println("----------重复读模式...----------");
// 4.开启重复读模式
buf.rewind();
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
byte[] bytes2 = new byte[buf.limit()];
buf.get(bytes2);
System.out.println(new String(bytes2, 0, bytes2.length));
// 5.clean 清空缓冲区 数据依然存在,只不过数据被遗忘
System.out.println("----------清空缓冲区...----------");
buf.clear();
System.out.println(buf.position());
System.out.println(buf.limit());
System.out.println(buf.capacity());
System.out.println((char)buf.get());
}
}
- make与rest用法
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
String str = "abcd1";
buf.put(str.getBytes());
// 开启读取模式
buf.flip();
byte[] dst = new byte[buf.limit()];
buf.get(dst, 0, 2);
buf.mark();
System.out.println(new String(dst, 0, 2));
System.out.println(buf.position());
buf.get(dst, 2, 2);
System.out.println(new String(dst, 2, 2));
System.out.println(buf.position());
buf.reset();
System.out.println("重置恢复到mark位置..");
System.out.println(buf.position());
}
}
通道Channel
-
通道可以同时进行读写,而流只能读或者只能写
-
通道可以实现异步读写数据
-
通道可以从缓冲读数据,也可以写数据到缓冲:
- 分散读取与聚集写入
分散读取:将通道中的数据分散到多个缓冲区中

聚集写入:将多个缓冲区的数据聚集到通道中
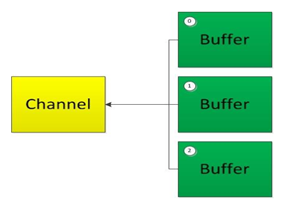
直接缓冲区与非直接缓冲区别
- 非直接缓冲区:通过 allocate() 方法分配缓冲区,将缓冲区建立在 JVM 的内存中
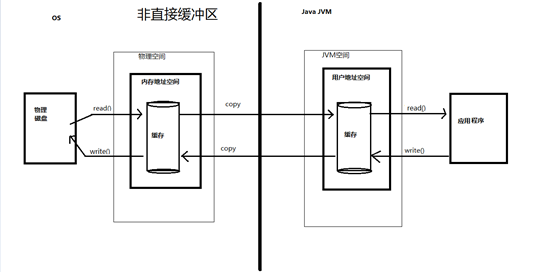
// 1.利用通道完成文件的复制(非直接缓冲区)
static public void test1() throws IOException { // 4400
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("e://1.jpg");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("e://2.jpg");
// ①获取通道
FileChannel inChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel outChannel = fos.getChannel();
// ②分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (inChannel.read(buf) != -1) {
buf.flip();// 切换为读取数据
// ③将缓冲区中的数据写入通道中
outChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
outChannel.close();
inChannel.close();
fos.close();
fis.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
- 直接缓冲区:通过 allocateDirect() 方法分配直接缓冲区,将缓冲区建立在物理内存中。可以提高效率
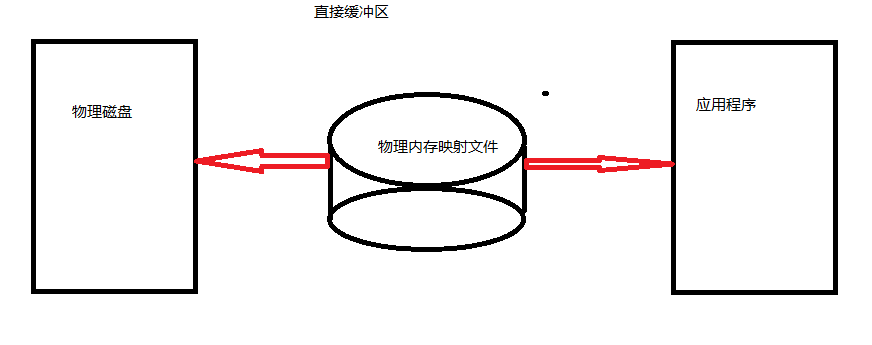
// 使用直接缓冲区完成文件的复制(内存映射文件)
static public void test2() throws IOException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("e://1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("e://2.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,
StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
// 内存映射文件
MappedByteBuffer inMappedByteBuf = inChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outMappedByteBuffer = outChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size());
// 直接对缓冲区进行数据的读写操作
byte[] dsf = new byte[inMappedByteBuf.limit()];
inMappedByteBuf.get(dsf);
outMappedByteBuffer.put(dsf);
inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
Selector
一个组件,可以检测多个NIO channel,看看读或者写事件是否就绪。
多个Channel以事件的方式可以注册到同一个Selector,从而达到用一个线程处理多个请求成为可能。
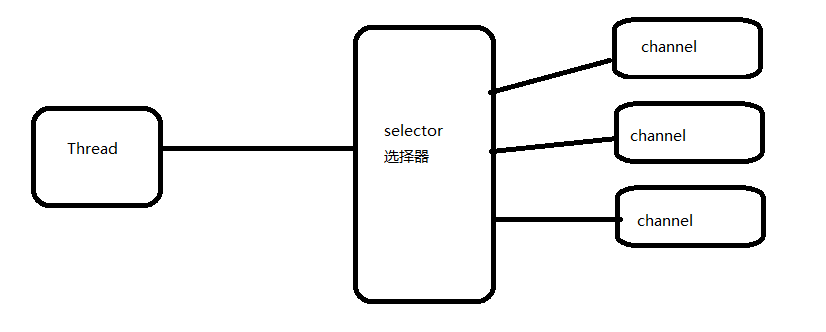
非阻塞IO数据准备就绪之后,由选择器发通知给服务器端,数据在准备之前服务器无需等待