Fire Net
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 8338 Accepted Submission(s): 4796
Problem Description
Suppose that we have a square city with straight streets. A map of a city is a square board with n rows and n columns, each representing a street or a piece of wall.
A blockhouse is a small castle that has four openings through which to shoot. The four openings are facing North, East, South, and West, respectively. There will be one machine gun shooting through each opening.
Here we assume that a bullet is so powerful that it can run across any distance and destroy a blockhouse on its way. On the other hand, a wall is so strongly built that can stop the bullets.
The goal is to place as many blockhouses in a city as possible so that no two can destroy each other. A configuration of blockhouses is legal provided that no two blockhouses are on the same horizontal row or vertical column in a map unless there is at least one wall separating them. In this problem we will consider small square cities (at most 4x4) that contain walls through which bullets cannot run through.
The following image shows five pictures of the same board. The first picture is the empty board, the second and third pictures show legal configurations, and the fourth and fifth pictures show illegal configurations. For this board, the maximum number of blockhouses in a legal configuration is 5; the second picture shows one way to do it, but there are several other ways.
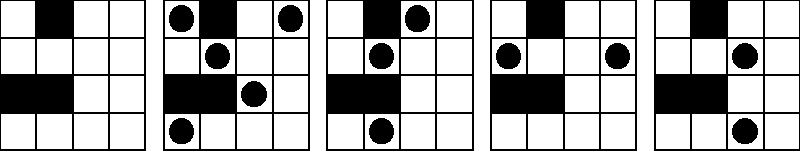
Your task is to write a program that, given a description of a map, calculates the maximum number of blockhouses that can be placed in the city in a legal configuration.
A blockhouse is a small castle that has four openings through which to shoot. The four openings are facing North, East, South, and West, respectively. There will be one machine gun shooting through each opening.
Here we assume that a bullet is so powerful that it can run across any distance and destroy a blockhouse on its way. On the other hand, a wall is so strongly built that can stop the bullets.
The goal is to place as many blockhouses in a city as possible so that no two can destroy each other. A configuration of blockhouses is legal provided that no two blockhouses are on the same horizontal row or vertical column in a map unless there is at least one wall separating them. In this problem we will consider small square cities (at most 4x4) that contain walls through which bullets cannot run through.
The following image shows five pictures of the same board. The first picture is the empty board, the second and third pictures show legal configurations, and the fourth and fifth pictures show illegal configurations. For this board, the maximum number of blockhouses in a legal configuration is 5; the second picture shows one way to do it, but there are several other ways.

Your task is to write a program that, given a description of a map, calculates the maximum number of blockhouses that can be placed in the city in a legal configuration.
Input
The input file contains one or more map descriptions, followed by a line containing the number 0 that signals the end of the file. Each map description begins with a line containing a positive integer n that is the size of the city; n will be at most 4. The next n lines each describe one row of the map, with a '.' indicating an open space and an uppercase 'X' indicating a wall. There are no spaces in the input file.
Output
For each test case, output one line containing the maximum number of blockhouses that can be placed in the city in a legal configuration.
Sample Input
4
.X..
....
XX..
....
2
XX
.X
3
.X.
X.X
.X.
3
...
.XX
.XX
4
....
....
....
....
0
Sample Output
5
1
5
2
4
Source
/* ID: LinKArftc PROG: 1045.cpp LANG: C++ */ #include <map> #include <set> #include <cmath> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <vector> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <utility> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; #define eps 1e-8 #define randin srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)) #define input freopen("input.txt","r",stdin) #define debug(s) cout << "s = " << s << endl; #define outstars cout << "*************" << endl; const double PI = acos(-1.0); const double e = exp(1.0); const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int INF = 0x7fffffff; typedef long long ll; const int maxn = 20; struct Node { char cha; int idx, idy; } node[maxn][maxn]; int mp[maxn][maxn]; int n, uN, vN; int linker[maxn]; bool vis[maxn]; bool dfs(int u) { for (int v = 1; v <= vN; v ++) { if (!vis[v] && mp[u][v]) { vis[v] = true; if (linker[v] == -1 || dfs(linker[v])) { linker[v] = u; return true; } } } return false; } int hungry() { memset(linker, -1, sizeof(linker)); int ret = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= uN; i ++) { memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); if (dfs(i)) ret ++; } return ret; } int main() { while (~scanf("%d", &n) && n) { for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) scanf(" %c", &node[i][j].cha); } uN = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) { if (node[i][j].cha == 'X') continue; if (j == 1 && node[i][j].cha == '.') uN ++; else if (node[i][j].cha == '.' && node[i][j-1].cha == 'X') uN ++; node[i][j].idx = uN; } } vN = 0; for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) { for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { if (node[i][j].cha == 'X') continue; if (i == 1 && node[i][j].cha == '.') vN ++; else if (node[i][j].cha == '.' &&node[i-1][j].cha == 'X') vN ++; node[i][j].idy = vN; } } memset(mp, 0, sizeof(mp)); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) { if (node[i][j].cha == 'X') continue; mp[node[i][j].idx][node[i][j].idy] = 1; } } printf("%d ", hungry()); } return 0; }