Octopus 源码阅读——fs部分
bitmap.cpp
bitmap中的代码基本上没啥好说的,比较清楚。不过不解的是为什么在初始化的时候要统计freecount,理论上buffer不是应该可以直接初始化成全零吗?
Bitmap::Bitmap(uint64_t count, char *buffer) /* Constructor of bitmap. */
{
if (count % 8 == 0) {
if (buffer != NULL) { /* Judge if buffer is null or not. */
bytes = (uint8_t *)buffer; /* Assign byte array of bitmap. */
varCountTotal = count; /* Initialize count of total bits. */
varCountFree = 0; /* Initialize count of free bits. */
for (unsigned int index = 0; index < varCountTotal / 8; index++) { /* Search in all bytes in array. */
for (int offset = 0; offset <= 7; offset++) { /* Search in all offsets in byte. */
if ((bytes[index] & (1 << (7 - offset))) == 0) { /* Judge if bit is cleared. */
varCountFree++; /* Increment of free bit. */
}
}
}
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Bitmap: buffer pointer is null.
");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); /* Fail due to null buffer pointer. */
}
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Bitmap: count should be times of eight.
");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); /* Fail due to count alignment. */
}
}
dmfs.cpp
入口
filesystem.cpp
这个2k+的代码量看着就刺激。。。正式开始:
分布式事务实现
这部分相关的函数是Tx开头的一些,具体的实现在RPCServer中实现(因为要先找到TxManager),这个实现主要是因为要保证metadata的一致性,所以在mknod之类的时候需要分布式事务的支持。
FileSystem
首先比较建议和RPCServer的代码一起看,会比较清晰。
有些比较直观的函数就不贴出来了。
updateRemoteMeta
更新remote Metadata,分为两种情况:
-
需要更新的metadata的存储位置在本地:直接在本地memcpy即可
-
需要更新的metadata的存储位置不在本地:使用RDMA的write_with_imm来进行处理,RDMA write + read
void FileSystem::updateRemoteMeta(uint16_t parentNodeID, DirectoryMeta *meta, uint64_t parentMetaAddress, uint64_t parentHashAddress) {
Debug::debugTitle("updateRemoteMeta");
/* Prepare imm data. */
uint32_t imm, temp;
/*
| 12b | 20b |
+-------+------------+
| 0XFFF | HashAdress |
+-------+------------+
*/
temp = 0XFFF;
imm = (temp << 20);
imm += (uint32_t)parentHashAddress;
/* Remote write with imm. */
uint64_t SendBuffer;
/* 得到发送端的buffer地址(根据NodeID) */
server->getMemoryManagerInstance()->getServerSendAddress(parentNodeID, &SendBuffer);
uint64_t RemoteBuffer = parentMetaAddress;
Debug::debugItem("imm = %x, SendBuffer = %lx, RemoteBuffer = %lx", imm, SendBuffer, RemoteBuffer);
if (parentNodeID == server->getRdmaSocketInstance()->getNodeID()) {
/* 如果在本地,那么从参数meta的地址直接memcpy到RemoteBuffer为基址的相应位置即可 */
memcpy((void *)(RemoteBuffer + server->getMemoryManagerInstance()->getDmfsBaseAddress()), (void *)meta, sizeof(DirectoryMeta));
//unlockWriteHashItem(0, parentNodeID, parentHashAddress);
return;
}
/* 如果更新的双方不在一台机器上,先把meta中的数据复制到sendbuffer */
uint64_t size = sizeof(DirectoryMeta) - sizeof(DirectoryMetaTuple) * (MAX_DIRECTORY_COUNT - meta->count);
memcpy((void *)SendBuffer, (void *)meta, size);
server->getRdmaSocketInstance()->RdmaWrite(parentNodeID, SendBuffer, RemoteBuffer, size, -1, 1);
server->getRdmaSocketInstance()->RdmaRead(parentNodeID, SendBuffer, RemoteBuffer, size, 1);
/* Data will be written to the remote address, and lock will be released with the assist of imm data. */
/* WRITE READ will be send after that, flushing remote data. */
}
RDMA call
server得到client,执行RDMACall(细节待补充)
getParentDirectory
/* Get parent directory.
Examples: "/parent/file" -> "/parent" return true
"/file" -> "/" return true
"/" -> return false
@param path Path.
@param parent Buffer to hold parent path.
@return If succeed return true, otherwise return false. */
getNameFromPath
/* Get file name from path.
Examples: '/parent/file' -> 'file' return true
'/file' -> 'file' return true
'/' -> return false
@param path Path.
@param name Buffer to hold file name.
@return If succeed return true, otherwise return false. */
parseMessage
根据sendMessage的不同执行不同的动作,所以会看到主体结构是一个switch case。代码里接下来对这些用到的功能函数进行了实现。
addMetaToDirectory
根据hashUnique来进行区分,如果hashNode在本地,那么直接更新本地的DirectoryTable,然后再更新分布式事务即可。
如果hashNode不在本地,那么需要给对应的Node发送一个ADDMETATODIRECTORY类型的message。
removeMetaToDirectory
同样的,remove也需要分成本地和远端,如果是本地,就直接重新整理chainItems,把需要remove的Meta覆盖掉,之后更新分布式事务log即可。
如果是远端,那么就需要给对应的hashNode发送一个REMOVEMETATODIRECTORY类型的message。
updateDirectoryMeta
本地:直接memcpy对应的metadata即可。
远端:发送一个对应类型的message
mknodWithMeta
创建实际的文件时使用。
实际上mknod只有本地方式,Octopus保证了一个file的data block和inode在一个机器上,用户可以在机器A上创建文件a,但是文件a实际存储在机器B上,而且文件a的data blocks和inode都存储在机器B上,并不会说inode存在A上,data blocks存在B上这种情况。(个人理解:这是比较显然的,不然还会需要不止一次hash)。
(个人理解:也就是说,实际上分布式文件系统并不能做到把整个集群看作一个机器,其中还是存在一定的限制)
直接通过实例化的storage在inode table中创建一个inode即可,具体的create操作在template table中实现。
mknod(WithoutMeta)
创建空文件时使用。
如标题所示,实际上这里的mknod是没有添加有效的metadata的,我们可以暂时理解为一个空的inode。
分成2pc和collect-dispatch两种方式,分别对应mknod2pc和mknodcd两个函数。
mknod2pc:
(这个暂时不是我们研究的重点,暂且跳过)
mknodcd:
我们其实会发现,Octopus中并没有用到太多的VFS层面类似inode,dentry之类的说法,因为目前的实现中,并没有类似VFS的思想(个人理解本文中实现的FileMeta有点类似于inode加dentry结构的混合体)。但是实际上代码中的parentHashAddress和parentMetaAddress就类似于dentry的作用,就是先找到这个inode的父目录,把父目录的inode对应的孩子数加一,之后更新到本地的分布式事务中,更新结束后调用updateRemoteData即可。因为updateRemoteData区分本地和远端,所以这里并不用判断parentNodeID是否在本地。update之后就正常的在本地create inode然后把这个inode放到hashTable中即可。
需要注意的是这里是先更新分布式事务,再update parent-inode的Data,之后在本地创建inode,并放到hashTable中,最后提交本地事务。
getattr
从FileMeta的Table中得到对应的FileMeta。(根据path得到hash值)。
access
注释给的比较明确,就是根据path判断一下这个file或者dir是否存在。
mkdir
同样的也分成了mkdircd和mkdir2pc,我们依旧不关注2pc的实现,来看mkdircd的实现:
会发现mkdircd和mknodcd的代码基本一致,除了使用的结构体不同,所以也侧面反映出,实际上创建文件和创建目录实际上区别不大。
readdir
得到某一个目录下面的文件以及目录的名字,类似的,根据path得到metadata,之后遍历metadata中的name,复制到一个list中,在函数体外可以通过list指针访问。
recursivereaddir
递归读取,读取当前目录下的全部目录以及文件名。
具体实现就是在readdir的时候,根据name和parentDirectory拼接成的新path继续readdir。
readDirectoryMeta
就像我们之前分析的,directory的meta可以在不同的机器上访问,因此这里也需要区分本地和远端。
Lock相关
lockWriteHashItem
unlockWriteHashItem
lockReadHashItem
unlockReadHashItem
基本是用到lock.cpp中的函数(不过那个读写锁我是真的理解不了)
构造函数
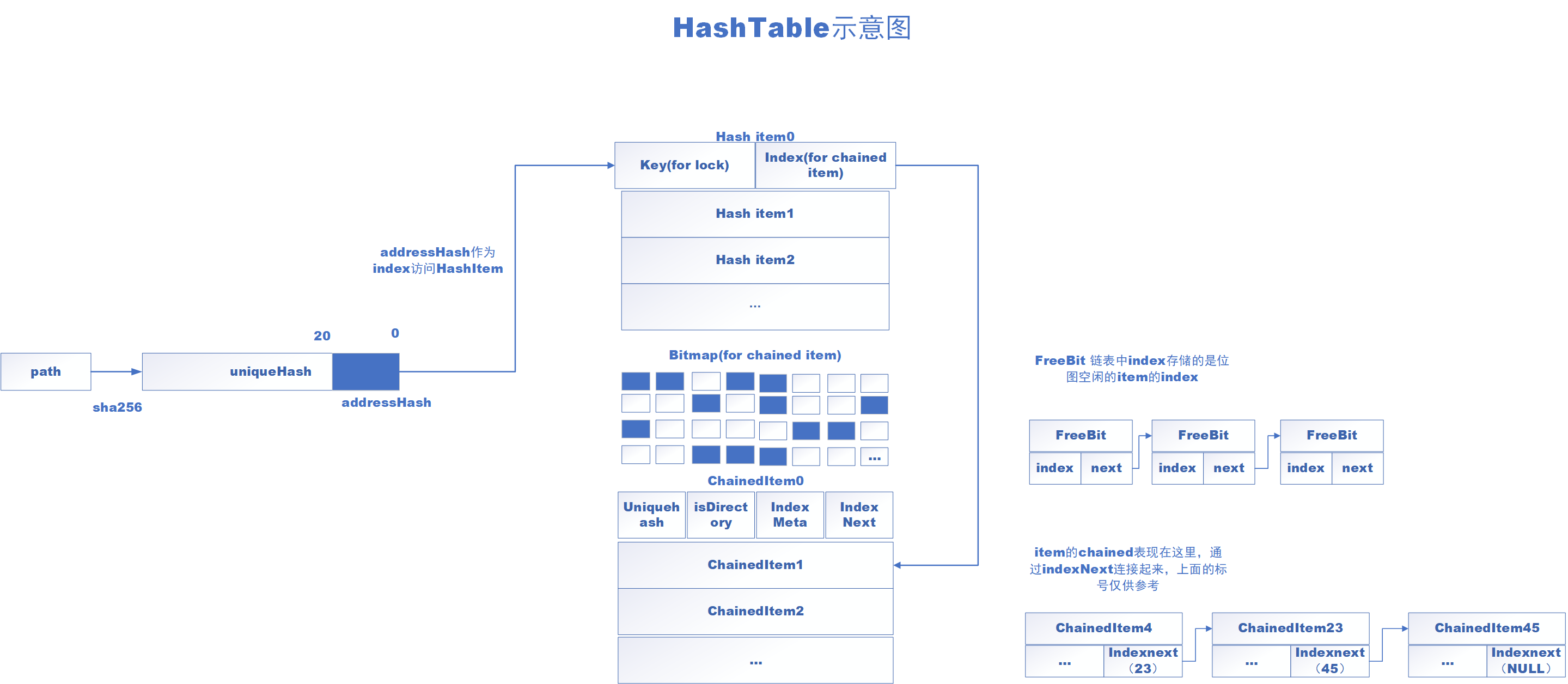
hashtable.cpp
构造函数
构造函数没啥可说的,就是初始化一些items的地址等。最后可以发现使用链表来保存bitmap中的freebit,避免了遍历的开销。
FreeBit *currentFreeBit;
for (uint64_t i = 1; i < bitmapChainedItems->countTotal(); i++) {
currentFreeBit = (FreeBit *)malloc(sizeof(FreeBit));
currentFreeBit->position = i;
currentFreeBit->nextFreeBit = headFreeBit;
headFreeBit = currentFreeBit;
}
(这里使用头插法构造链表,自己写代码从来没写过这种,记录一下。)
HashTable::get
步骤:
- 通过path得到一个 unique hash
- unique hash 的后20位作为 address hash
- 使用 address hash 作为 hash items 的索引,找到合适的item;
- 之后从hash item 中拿出chained item 的 index,因为可能出现hash冲突,所以从index开始向下依次遍历,直到找到相同的unique hash
其实就是开放链地址法解决hash冲突。(所以有一个do while)
bool HashTable::get(const char *path, uint64_t *indexMeta, bool *isDirectory)
{
if ((path == NULL) || (indexMeta == NULL) || (isDirectory == NULL)) {
return false; /* Fail due to null parameters. */
} else {
UniqueHash hashUnique;
HashTable::getUniqueHash(path, strlen(path), &hashUnique); /* Get unique hash. */
// printf("%016x%016x%016x%016x
", hashUnique.value[3], hashUnique.value[2], hashUnique.value[1], hashUnique.value[0]);
AddressHash hashAddress = HashTable::getAddressHash(&hashUnique); /* Get address hash by unique hash. */
// getAddressHash(path, strlen(path), &hashAddress); /* Get address hash. */
bool result;
mutexBitmapChainedItems.lock(); /* Though currently there is no bitmap reading or writing, other operations such as delete might affect hash item reading. */
{
uint64_t indexHead = itemsHash[hashAddress].indexHead;
if (indexHead == 0) {
result = false; /* Fail due to no hash item. */
} else {
// UniqueHash hashUnique;
// getUniqueHash(path, strlen(path), &hashUnique); /* Get unique hash. */
uint64_t indexCurrent = indexHead; /* Index of current chained item. */
bool found = false;
do { /* Traverse every chained item. */
if (memcmp(&(itemsChained[indexCurrent].hashUnique), &(hashUnique), sizeof(UniqueHash)) == 0) {
*indexMeta = itemsChained[indexCurrent].indexMeta; /* Save meta index. */
*isDirectory = itemsChained[indexCurrent].isDirectory; /* Save state of directory. */
found = true; /* Found one matched. */
break; /* Jump out. */
} else {
indexCurrent = itemsChained[indexCurrent].indexNext; /* Move to next chained item. */
}
} while (indexCurrent != 0); /* If current item is over last chained item then jump out. */
if (found == true) {
result = true; /* Succeed. Find one matched. */
} else {
result = false; /* Fail due to no chained item matched. */
}
}
}
mutexBitmapChainedItems.unlock(); /* Unlock hash table bitmap. */
return result; /* Return specific result. */
}
}
HashTable::put
基本的hash开放链地址法实现(跟我们用数组模拟的方式有些不同,使用FreeBit来维护空闲item,但是本质上还是开放链地址法)。
HashTable::del
删除一个hash item 和 chained item,与链表中删除节点非常类似。
剩下的方法基本是统计hash item 和 chained item等这些item的数量长度等。没什么需要专门分析的。总结一下hashtable的基本数据结构和操作:
lock.cpp
读写锁的原理比较容易懂,但是代码中存在着一堆magic number,比如LockAddress + 4的4之类,猜测可能和metadata的结构有关,这里暂时跳过。
这里是一个读写锁实现,在另一篇文章中实现了一个python版本的,这里的实现基本一致。
但是代码里还是存在一些问题:
uint64_t LockService::WriteLock(uint16_t NodeID, uint64_t Address) {
/* Address是相对地址,相对 hash item table 基址的位移 */
int workerid = server->getIDbyTID();
uint16_t ID = __sync_fetch_and_add(&WriteID, 1ULL);
uint64_t key = (uint64_t)NodeID;
uint64_t LockAddress = MetaDataBaseAddress + Address;
key = key << 16;
key += ID;
key = key << 32;
while (true) {
if (__sync_bool_compare_and_swap((uint64_t *)LockAddress, 0ULL, key))
break;
//if (workerid == 0) {
server->RequestPoller(workerid);
//}
}
return key;
}
bool LockService::WriteUnlock(uint64_t key, uint16_t NodeID, uint64_t Address) {
uint64_t LockAddress = MetaDataBaseAddress + Address;
uint32_t *p = (uint32_t *)(LockAddress + 4);
*p = 0;
return true;
}
这个写解锁的操作为什么要加4呢?理论上这里执行完,写加锁这里__sync_bool_compare_and_swap((uint64_t *)LockAddress, 0ULL, key)LockAddress的内容完全没变啊,解完锁之后依旧无法执行新的写操作。
storage.cpp
storage.cpp的构造函数主要是进行内存分配的工作(count是自己输入的,所以个人感觉sizeBufferUsed中的Used可能不太准确。。。),分别是Hashtable,file metadata的table,file block的table,directory metadata的table。
Storage::Storage(char *buffer, char* bufferBlock, uint64_t countFile, uint64_t countDirectory, uint64_t countBlock, uint64_t countNode)
{
if ((buffer == NULL) || (bufferBlock == NULL) || (countFile == 0) || (countDirectory == 0) ||
(countBlock == 0) || (countNode == 0)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Storage::Storage: parameter error.
");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); /* Exit due to parameter error. */
} else {
hashtable = new HashTable(buffer, countDirectory + countFile); /* Initialize hash table. */
Debug::notifyInfo("sizeof Hash Table = %d MB", hashtable->sizeBufferUsed / 1024 / 1024);
tableFileMeta = new Table<FileMeta>(buffer + hashtable->sizeBufferUsed, countFile); /* Initialize file meta table. */
Debug::notifyInfo("sizeof File Meta Size = %d MB", tableFileMeta->sizeBufferUsed / 1024 / 1024);
tableDirectoryMeta = new Table<DirectoryMeta>(buffer + hashtable->sizeBufferUsed + tableFileMeta->sizeBufferUsed, countDirectory); /* Initialize directory meta table. */
Debug::notifyInfo("sizeof Directory Meta Size = %d MB", tableDirectoryMeta->sizeBufferUsed / 1024 / 1024);
tableBlock = new Table<Block>(bufferBlock, countBlock); /* Initialize block table. */
this->countNode = countNode; /* Assign count of nodes. */
sizeBufferUsed = hashtable->sizeBufferUsed + tableFileMeta->sizeBufferUsed + tableDirectoryMeta->sizeBufferUsed + tableBlock->sizeBufferUsed; /* Size of used bytes in buffer. */
}
}
还有一个getNodeHash函数,应该是得到server node的编号,等到遇到的时候再详细看。
TxManager.cpp
最关键的函数是:
void TxManager::TxDistributedPrepare(uint64_t TxID, bool action) {
DistributedLogEntry *log = (DistributedLogEntry *)DistributedLogAddress;
log[TxID].prepare = action;
FlushData((uint64_t)&log[TxID].prepare, CACHELINE_SIZE);
}
emmm,我是没看出来这里涉及了什么collect-dispatch操作。。。