1、网络模型
1)OSI参考模型
2)TCP/IP协议
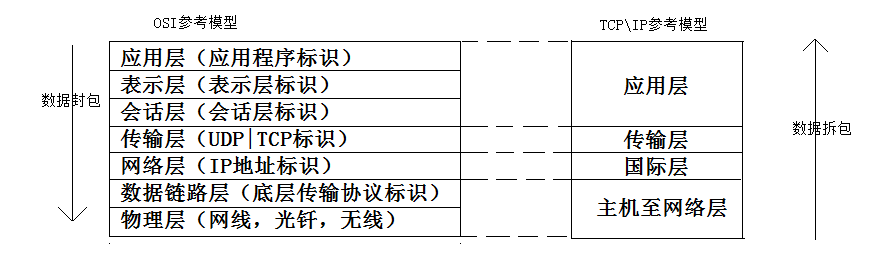
2.网络通讯要素
1)IP地址(IntAddress已经封装成了对象)
1.网络中设备的标识
2.不易记忆,可用主机名
3.本地IP地址:127.0.01 主机 名:localhost
2)端口号(数字标识,没有必要封装成对象)
1.用于标识进程的逻辑地址,不同进程的标识。
2.有效端口:0~65535,其中0~1024系统使用或保留端口
3)传输协议
1.通讯的规则
2.常见协议:TCP, UDP
3.网络通讯过程
1)找到对方IP.
2)数据要发到对方指定的应用程序上,为了标识这些应用程序,所以这些网络应用程序都用数字进行了标识。为了方便称呼这个数字,叫做端口。
IntAddress
1 package com.lovo.chat; 2 3 import java.net.InetAddress; 4 5 public class IntAddressTest { 6 7 public static void main(String[]args) throws Exception { 8 //获取IntAddress对象 9 InetAddress i = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); 10 //获取IP地址 11 String ip = i.getHostAddress(); 12 //获取主机的名称 13 String hostName = i.getHostName(); 14 15 System.out.println("IP地址" + ip); 16 17 System.out.println("主机名" + hostName); 18 19 InetAddress inetAddress = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com"); 20 21 System.out.println(inetAddress.getHostAddress()); 22 23 System.out.println(inetAddress.getHostName()); 24 25 } 26 27 }
(网络编程-UDP-TCP)
UDP特点:(面向无连接)(聊天)
1.将数据及源和目的封装成数据包中,不需要建立连接。(封包,无连接)
2.每个数据包的大小限制在64K内。(小数据)
3.因无连接,是不可靠协议。
4.不需要建立连接,速度快。
TCP特点:(面向连接)(下载)
1.建立连接,形成传输数据的通道。(传输,连接)
2.在连接中进行大数据量传输。(大数据)
3.是可靠的协议
(网络编程-Socket)(Socket也称套接字)
1.Socket就是为网络服务提供的一种机制。
2.通信的两端都有Socket
3.网络通信其实就是Socket间的通信
4.数据在两个Socket间通过IO传输
UDP
1 package com.lovo.UDP; 2 3 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 4 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 5 import java.net.InetAddress; 6 7 /** 8 * 发送 9 * @author Mine 10 * 11 */ 12 /* 13 * 思路: 14 * 1.建立UDP Socket服务 15 * 2.提供数据,并将数据封装到数据包中 16 * 3.通过Socket服务的发送功能,将数据包发送出去 17 * 4.关闭资源 18 * */ 19 public class Send { 20 21 public static void main(String[ ] args) throws Exception { 22 23 // 1.创建UDP服务,通过DatagramSocket对象。 24 25 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(888); 26 27 // 2.确定数据,并封装成数据包。 28 29 // DatagramPacket(byte[] buf, int length, InetAddress address, int port) 30 31 byte[] buf = "Hello World!".getBytes(); 32 33 DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length,InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"),10000); 34 35 // 3.通过socket服务,将已有的数据包发送出去,通过Send方法。 36 37 ds.send(dp); 38 39 // 4.关闭资源。 40 41 ds.close(); 42 43 } 44 45 }
1 package com.lovo.UDP; 2 3 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 4 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 5 6 /** 7 * 接收 8 * 9 * @author Mine 10 * 11 */ 12 /* 13 * 思路: 14 * 1.建立UDP Socket服务 15 * 2.建立一个数据包,用于存储监听到的端口的数据把接收到的数据封装的数据包,就可以操作数据包对象
16 * 17 * 3.通过Socket服务的监听功能,将接收到的数据存入到已经定义好的数据包中 18 * 4.通过数据包对象的特有功能,讲这些不同的数据取出,打印在控制台上 19 * 5.关闭资源 20 * 21 * */ 22 public class Receive { 23 24 public static void main(String... args) throws Exception { 25 26 // 1.创建udp的Socket服务,建立端点。 27 28 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10000); 29 30 // 2.预定义数据包,用于存储接收数据。 31 32 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 33 34 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length); 35 36 // 3.通过服务的receive方法,将收到的数据存入到定义好的数据包中。 37 38 ds.receive(dp); 39 40 // 4.通过数据包中的方法获取其中的数据。 41 42 String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); 43 44 int port = dp.getPort(); 45 46 String data = new String(dp.getData(), 0, dp.getLength()); 47 48 System.out.println("IP地址:" + ip + "..." + data + "...端口:" + port); 49 50 // 5.关闭资源。 51 52 ds.close(); 53 54 } 55 56 }
TCP
1 package com.lovo.TCP; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 7 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 8 import java.net.ServerSocket; 9 import java.net.Socket; 10 /** 11 * 服务器 12 * @author Mine 13 * 14 */ 15 public class ServerTest { 16 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ 17 /*创建ServerSocket对象 参数为指定的端口服务器*/ 18 ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(31223); 19 /*设置超时的时间 才能连接到客户端上*/ 20 server.setSoTimeout(10000); 21 /*等待客户端连接*/ 22 Socket socket=server.accept(); 23 //处理客户端数据 24 /*从客户端读取数据 用缓冲区,把从客户端得到的字节的输入流 用转换流 转换成字符流*/ 25 BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); 26 char [] ch=new char[100]; 27 int len=reader.read(ch); 28 System.out.println("(服务器发送)客户端接受到的消息是:severTest"); 29 System.out.println(new String(ch,0,len)); 30 31 /*向客户端写入数据 */ 32 BufferedWriter writer=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream())); 33 writer.write("你好,客户端,服务器已接受到了你的消息 serverTest"); 34 writer.flush(); 35 //释放资源 36 writer.close(); 37 reader.close(); 38 socket.close(); 39 server.close(); 40 } 41 }
1 package com.lovo.TCP; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 7 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 8 import java.net.Socket; 9 10 /** 11 * 客户端 12 * @author Mine 13 * 14 */ 15 public class SocketTest { 16 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ 17 /*创建Socket对象*/ 18 Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",31223); 19 /*利用已创建的socket创建输入输出流,处理与服务器的连接*/ 20 //向服务器写入数据 21 BufferedWriter writer=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream())); 22 writer.write("你好,服务器,客户端已接收到你的消息 socketTest"); 23 writer.flush(); 24 25 //向服务器读取消息 26 BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); 27 char [] ch=new char[100]; 28 int len=reader.read(ch); 29 System.out.println("(客户端发送)服务器接收到的消息"); 30 System.out.println(new String(ch,0,len)); 31 //释放资源 32 writer.close(); 33 reader.close(); 34 socket.close(); 35 } 36 }