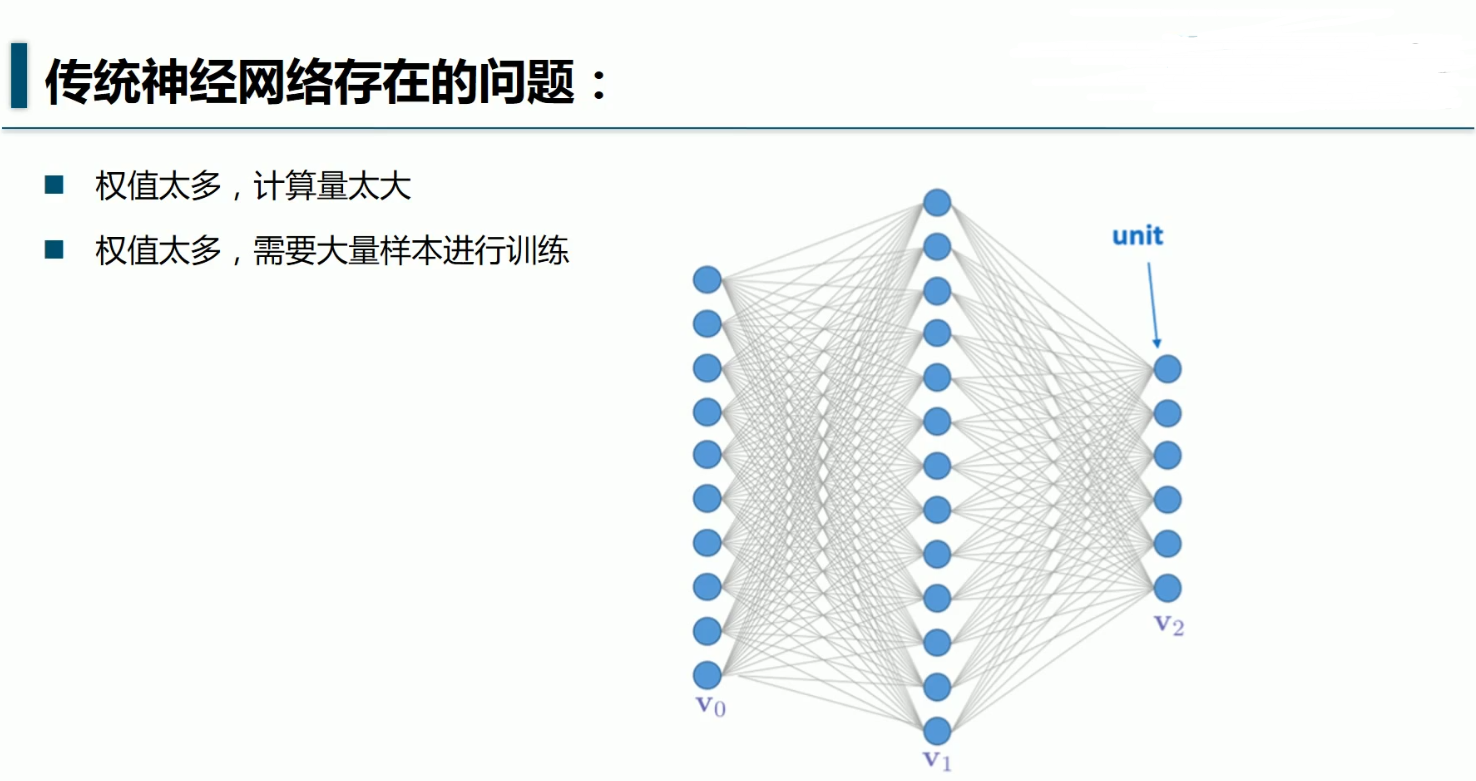
经验之谈:
一般样本的大小是权值的5~10倍

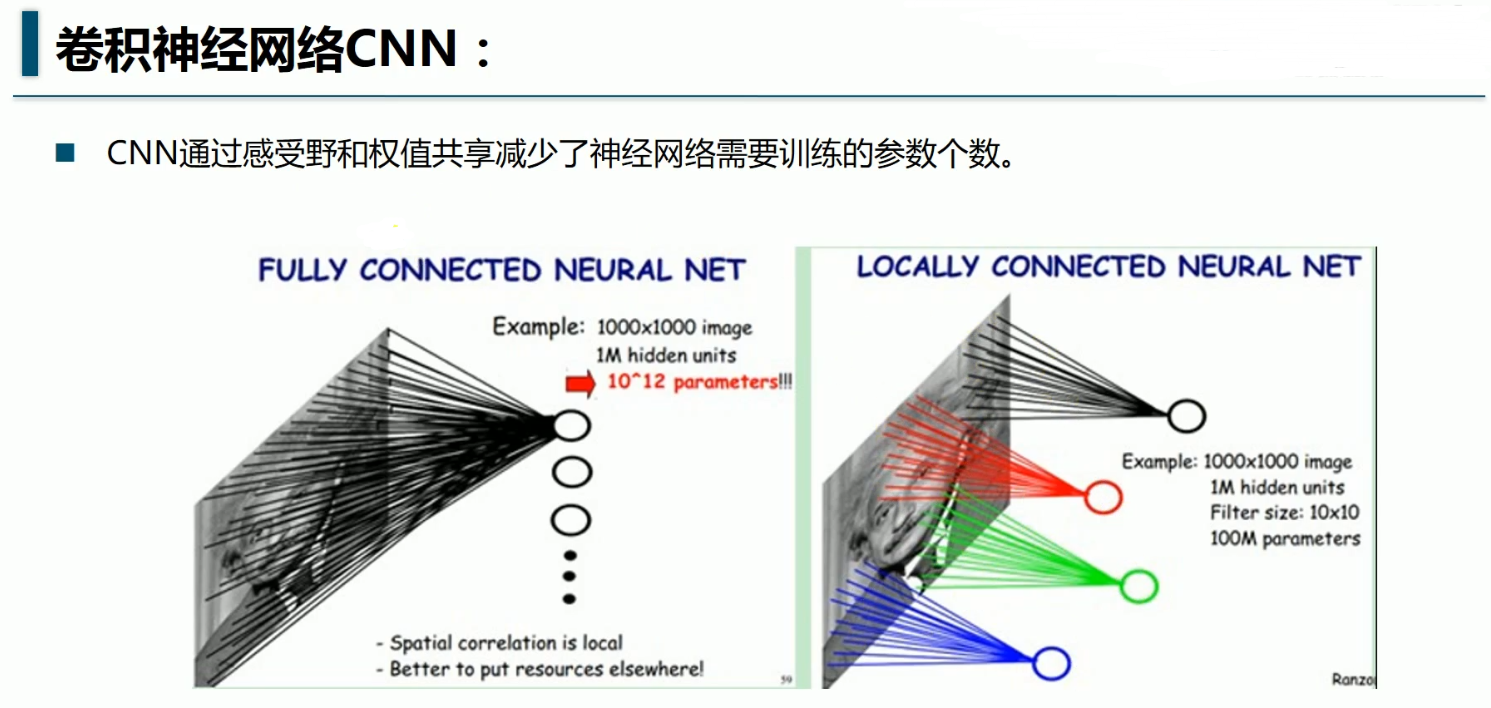
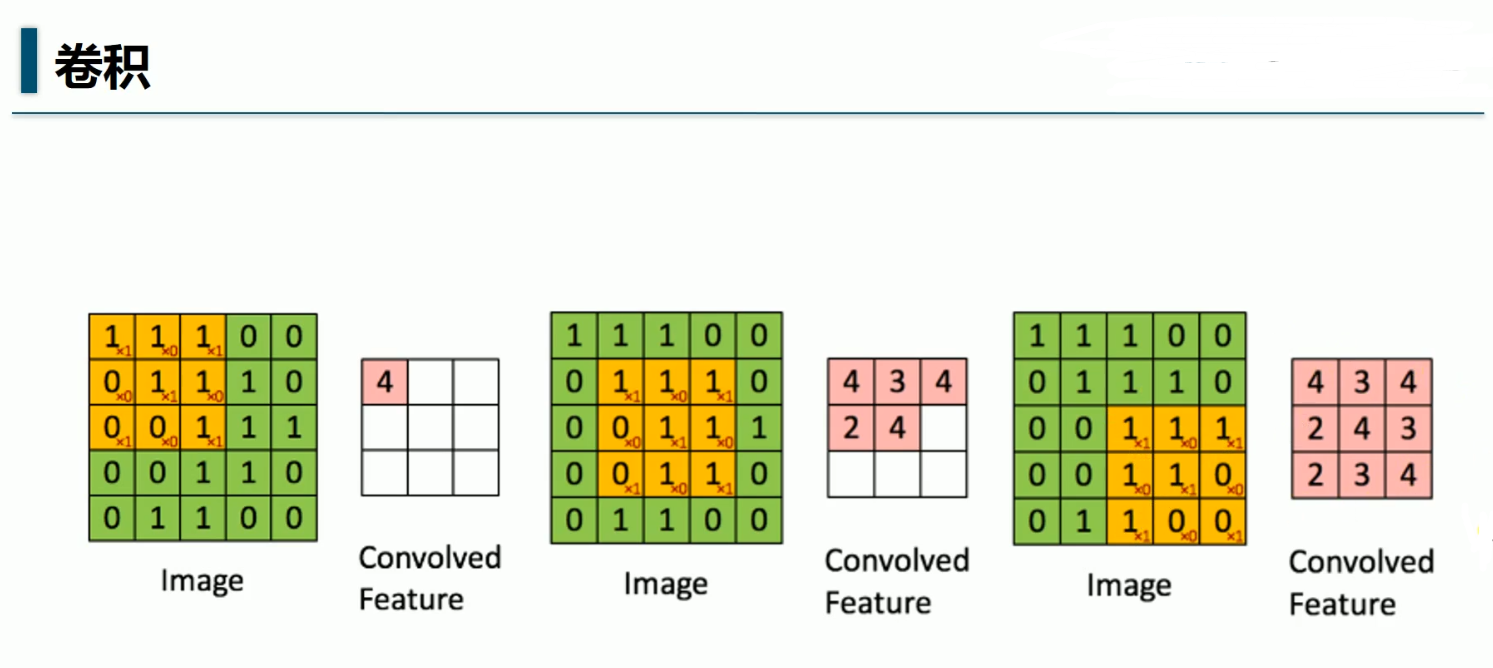
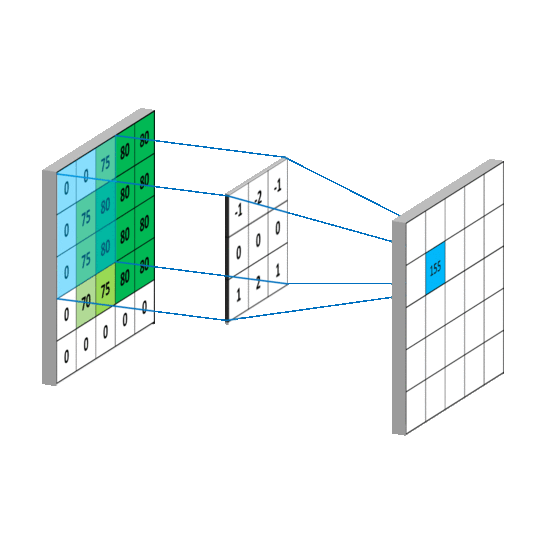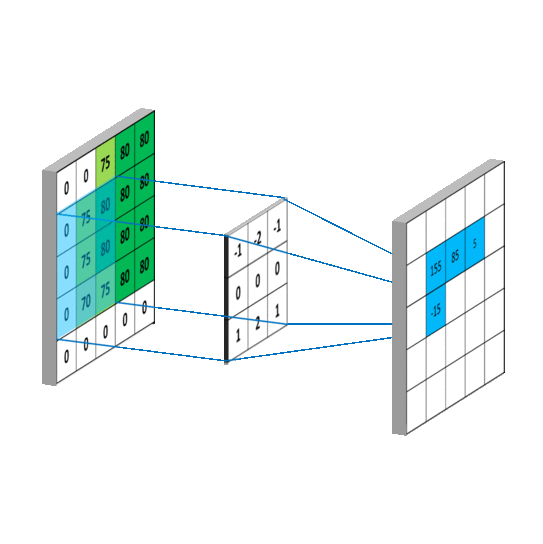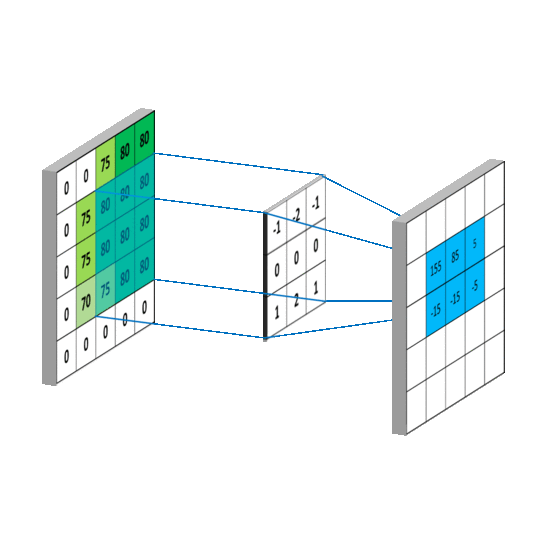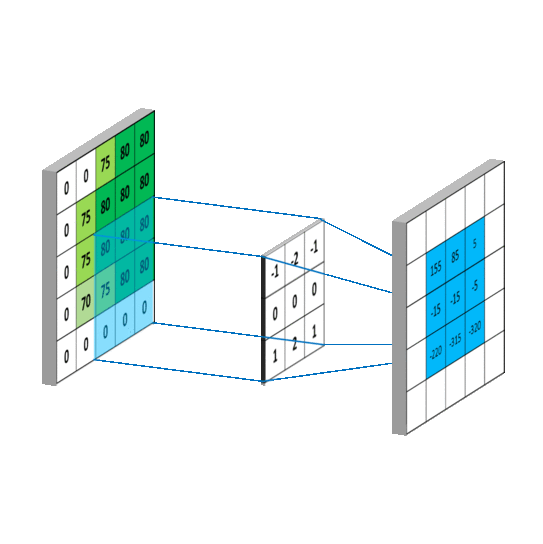

import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data/',one_hot= True)
#每个批次的大小:
batch_size = 128
#计算一共有多少批次
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples//batch_size
#初始化权重值W:
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape=shape,stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
#初始化偏置值b
def biases_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1,shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
#卷积层
def conv2d(x,W):
''' x-input tensor of shape [batch,in_height,in_weight,in_channels]
W-filter/kernel tensor of shape [filter_height,filter_weight,
in_channels,out_channels]
stride[0]=stride[3]=1,
stride[1]-x步长
stride[2]-y步长
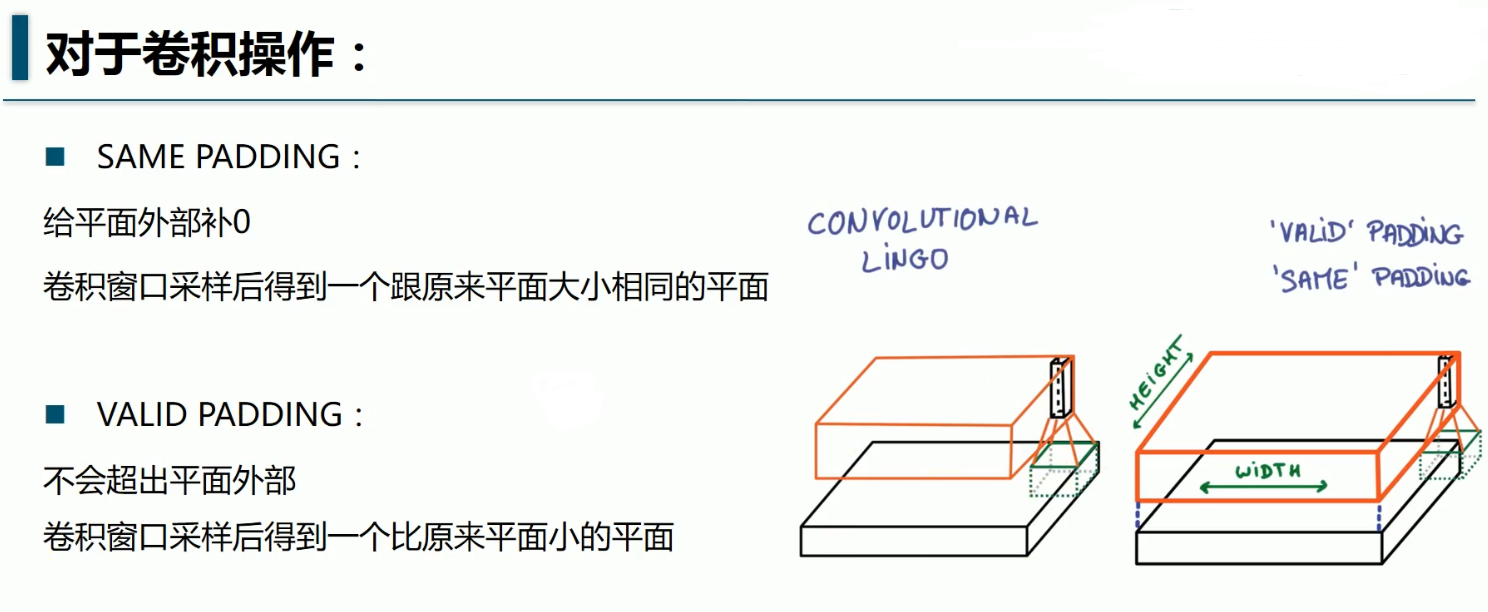
padding-SAME如果不够则补零(卷积后图像大小与输入一致),VALID-不补(多余的舍弃)
'''
return tf.nn.conv2d(x,W,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
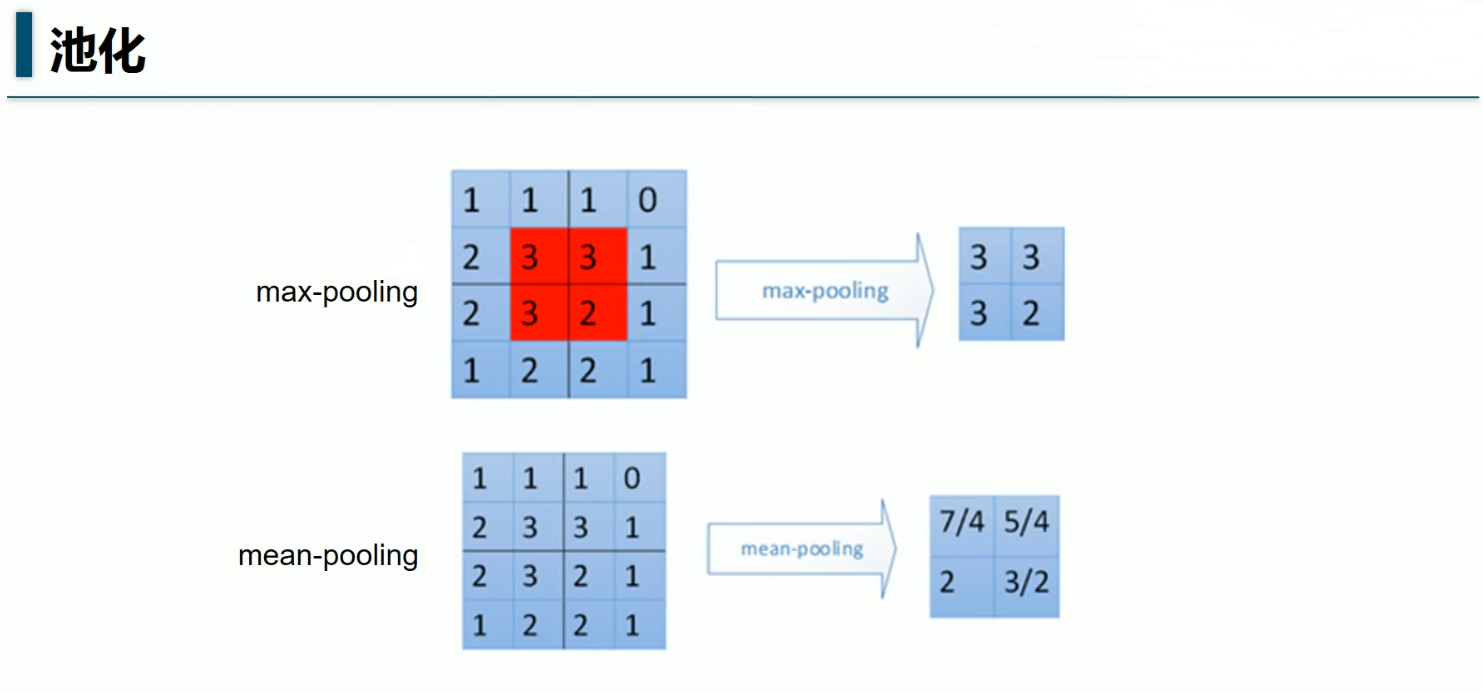
#池化层
def max_pool_2x2(x):
'''ksize[1,x,y,1],x,y表示窗口大小'''
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
#定义2个placeholder
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784]) #28x28
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])
#将x转换为向量
'''[batch,in_height,in_weight,in_channels]'''
x_image = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1])
#初始化第一个卷积层的W,b
'''窗口x,窗口y,channels,卷积核filter个数(特征图数量)'''
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5,5,1,32])
'''每一个卷积核对应一个偏置值'''
b_conv1 = biases_variable([32])
#第一层的卷积与池化
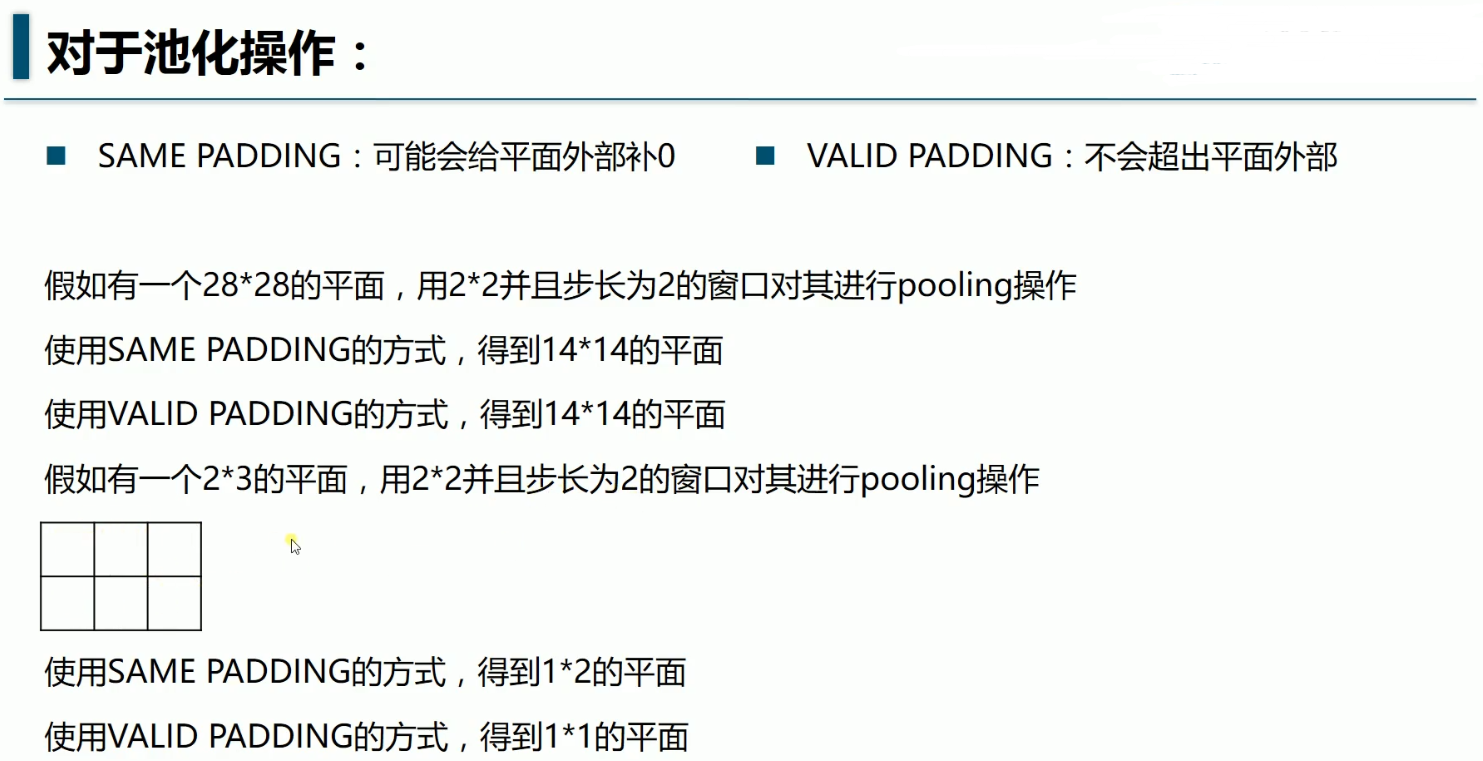
'''28%2=0,所以SAME不补,padding=0,池化后的x应该是,
((28+2×0-2)/2 )+1=14
第1个2是2倍的padding,第2个2是窗口x=2,第三个2是stride
池化输入与窗口都是正方形,所以池化后的y=14 ,
池化后图片14×14
'''
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image,W_conv1)+b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) #14×14,32张
#初始化第二个卷积层的W,b
'''窗口x,窗口y,channels(上一层特征图数量),卷积核filter个数(特征图数量)'''
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5,5,32,64])
'''每一个卷积核对应一个偏置值'''
b_conv2 = biases_variable([64])
#第二层的卷积与池化
'''((14+2×0-2)/2 )+1=7,7×7'''
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1,W_conv2)+b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)#7×7,64张
#初始化第一个全连接层
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024])
b_fc1 = biases_variable([1024])
#求第一个全连接层的输出
#1,将最后一层卷积池化层的输出变为扁平化
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2,[-1,7*7*64])
#2,计算全连接层的输出
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat,W_fc1)+b_fc1) #-1×1024
#keep_prob用来表示全连接层的输出率
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1,keep_prob)
#初始化第二个全连接层
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024,10])
b_fc2 = biases_variable([10])
#计算输出
'''
-1是batch,这里的batch是100,
所以这里输出的是100×10,
也就是每行是1张图片,一共有100行
每一列是1个特征,一共有10列
'''
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1,W_fc2)+b_fc2) #-1×10
#交叉熵损失函数
coss_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(labels=y,logits= prediction))
#使用Adam优化器
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(coss_entropy)
#结果存放在一个布尔列表中
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(prediction,1),tf.argmax(y,1))
#求准确率
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for epoch in range(21):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict = {x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys,keep_prob:0.7})
acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict = {x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels,keep_prob:1.0})
print("第"+str(epoch)+"次迭代,测试集准确率是"+str(acc))
自己的小笔记本4×i7,GTX960+4G,跑不起来
在阿里云的天池实验室跑,巨慢,21次迭代需要半个小时
结果:
Extracting MNIST_data/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Extracting MNIST_data/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
Extracting MNIST_data/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Extracting MNIST_data/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
第0次迭代,测试集准确率是0.7688
第1次迭代,测试集准确率是0.7831
第2次迭代,测试集准确率是0.8829
第3次迭代,测试集准确率是0.8883
第4次迭代,测试集准确率是0.889
第5次迭代,测试集准确率是0.8919
第6次迭代,测试集准确率是0.8908
第7次迭代,测试集准确率是0.893
第8次迭代,测试集准确率是0.894
第9次迭代,测试集准确率是0.8949
第10次迭代,测试集准确率是0.8927
第11次迭代,测试集准确率是0.8935
第12次迭代,测试集准确率是0.8948
第13次迭代,测试集准确率是0.9873
第14次迭代,测试集准确率是0.9881
第15次迭代,测试集准确率是0.9864
第16次迭代,测试集准确率是0.9885
第17次迭代,测试集准确率是0.9906
第18次迭代,测试集准确率是0.9876
第19次迭代,测试集准确率是0.9884
第20次迭代,测试集准确率是0.9902
最后的准确率达到了99.02%