昨日回顾:
hashlib 摘要 md5 sha系列
文件的一致性校验
密文的认证
logging 记录日志
两种用法 basicConfig不常用 getLogger()常用
可以通过一个参数去控制全局的日志输出情况
可以帮助开发者同时向文件和屏幕输出信息
configparser
有分组section和有配置项option的配置文件,默认.ini结尾的文件
collections
在基础数据类型之外又额外增加了一些新的数据类型
collections模块
在内置数据类型(dict、list、set、tuple)的基础上,collections模块还提供了几个额外的数据类型
1.namedtuple: 生成可以使用名字来访问元素内容的tuple
from collections import namedtuple
Point = namedtuple('Point',['x','y'])
p = Point(1,2)
print(p) #Point(x=1, y=2)
print(p.x) #1
print(p.y) #2
2.deque: 双端队列,可以快速的从另外一侧追加和推出对象
from collections import deque
# 双端队列
dq = deque()
dq.append(1)
dq.append(2)
dq.append(3)
print(dq) #deque([1, 2, 3])
print(dq.pop()) #3
print(dq.popleft()) #1
dq.appendleft(4)
dq.appendleft(5)
print(dq) #deque([5, 4, 2])
3.Counter: 计数器,主要用来计数
from collections import Counter 在验证密码难易程度时,防止密码过于简单如:111111
c = Counter('abcdeabcdabcaba')
print(c) #Counter({'a': 5, 'b': 4, 'c': 3, 'd': 2, 'e': 1})
4.OrderedDict: 有序字典
from collections import OrderedDict
d = OrderedDict()
d['a'] = 1
d['z'] = 2
d['b'] = 3
print(d) #OrderedDict([('a', 1), ('z', 2), ('b', 3)])
按写入顺序排序
d['z'] = 0
print(d) #OrderedDict([('a', 1), ('z', 0), ('b', 3)])
5.defaultdict: 带有默认值的字典
有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],
将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,
将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中。
dic = {}
l = [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90]
for i in l:
if i > 66:
if dic.get('k1'):
dic['k1'].append(i)
else:
dic['k1'] = [i]
if i < 66:
if dic.get('k2'):
dic['k2'].append(i)
else:
dic['k2'] =[i]
print(dic) #{'k2': [11, 22, 33, 44, 55], 'k1': [77, 88, 99, 90]}
from collections import defaultdict
d = defaultdict(set)
print(d) #defaultdict(<class 'set'>, {}) 定义了一个空字典
print(d['a']) #set() 没有a键的值,所以打印set()
d['b'] = 10
print(d) #defaultdict(<class 'set'>, {'a': set(), 'b': 10})
d = defaultdict(list) # callable 可调用的
print(d) #defaultdict(<class 'list'>, {}) 空字典
print(d[1]) #[] 有键无值空列表
print(d) #defaultdict(<class 'list'>, {1: []})
time模块
import time
时间
计算执行代码的时间 time.time() # 1524536396.9483523
让程序停在这里一段时间 sleep
记录时间的格式:
给人看的
给机器看的
计算用的
import time
时间戳时间
print(time.time()) # 时间戳时间 # 计算时间差 精准的运算
格式化时间
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))# 字符串格式化时间 # 记录下来给人看
print(time.strftime('%y-%m-%d'))# 字符串格式化时间
print(time.strftime('%x %X'))# 字符串格式化时间
print(time.strftime('%c'))# 字符串格式化时间
结构化时间
print(time.localtime())# 本地结构化时间
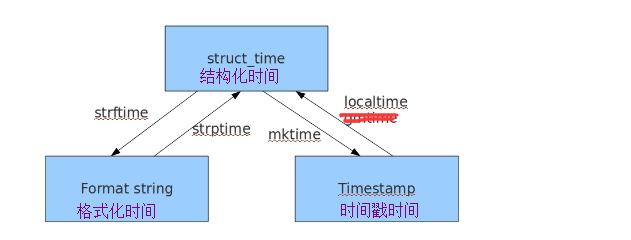
t = time.strptime('1991-9-10 4:40:30','%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') 格式转结构
print(t) #time.struct_time(tm_year=1991, tm_mon=9, tm_mday=10, tm_hour=0, tm_min=0, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=1, tm_yday=253, tm_isdst=-1)
print(time.mktime(t)) #684448830.0 结构转时间戳
p=time.localtime(666666666) 时间戳转结构 gmtime英国时间戳
print(p) #time.struct_time(tm_year=1991, tm_mon=2, tm_mday=16, tm_hour=9, tm_min=11, tm_sec=6, tm_wday=5, tm_yday=47, tm_isdst=0)
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',p)) 结构转格式 #1991-02-16 09:11:06
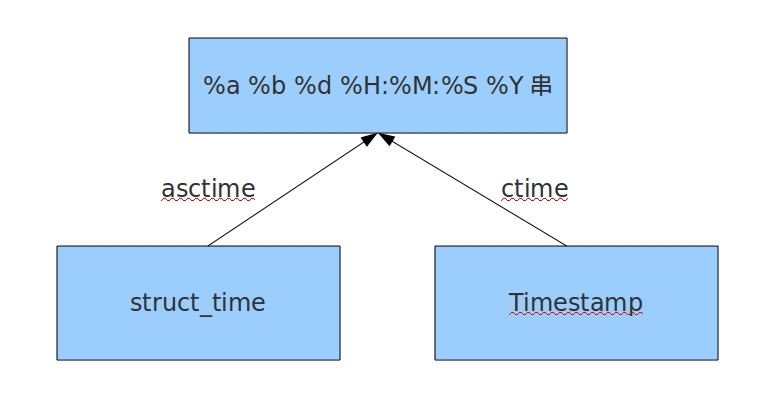
print(time.ctime(6666666666))#Wed Apr 4 19:51:06 2181 时间戳转ctime
print(time.strftime('%c'))#Tue Apr 24 16:42:21 2018
p=time.struct_time(tm_year=1991, tm_mon=2, tm_mday=16, tm_hour=9, tm_min=11, tm_sec=6, tm_wday=5, tm_yday=47, tm_isdst=0)
print(time.asctime(p))#Sat Feb 16 09:11:06 1991 结构转ctime
作业
y-m-d h:M:S
从当前时间开始 比起y-m-d h:M:S过去了多少年 多少月 多少天 多少h,多少m,多少s
import time
def cal_time(fmt_time,fmt): 参数为格式化的时间和格式
now = time.time() 现在的时间戳
time_before =time.mktime(time.strptime(fmt_time,fmt)) 参数的时间戳
how_long = now - time_before 现在的时间戳减参数的时间戳 等于时间差的时间戳
struct_time = time.gmtime(how_long) (gmtime英国的)时间差的时间戳的结构化,元组形式
return '过去了%d年%d月%d日,%d小时%d分%d秒'% 用时间戳起始减去时间差的时间戳
(struct_time.tm_year - 1970,
struct_time.tm_mon - 1,struct_time.tm_mday - 1,
struct_time.tm_hour,struct_time.tm_min,struct_time.tm_sec)
ret = cal_time('1991-9-10 4:40:30','%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
print(ret)
rondom模块
import random
随机 打乱顺序有关的
print(random.random()) # 大于0且小于1之间的小数
print(random.uniform(1,4)) 大于1小于4的小数
print(random.randint(1,1000)) # 大于等于1且小于等于1000之间的整数
print(random.randrange(1,2)) # 不包含2
print(random.randrange(1,20,2)) # 大于等于1且小于20之间的奇数
print(random.choice([1,'23',[4,5]])) 随机选择一个返回
print(random.sample([1,'23',[4,5]],2))随机选择多个返回,返回的个数为函数的第二个参数
item=[1,3,5,7,9]打乱列表顺序
import random
random.shuffle(item)
print(item)
要求 生成随机验证码
基础需求: 6位数字验证码 数字可以重复
进阶需求: 字母+数字 4位验证码 数字字母都可以重复
import random
def id_code(num):
ret = ''
for i in range(num):
number = str(random.randint(0,9))
alph = chr(random.randint(65,90))
alph1 = chr(random.randint(97,122))
chioc = random.choice([alph,alph1])
chioe = random.choice([number,chioc])
ret += chioe
return ret
print(id_code(6))
sys模块
sys模块与python解释器打交道,os模块是与操作系统打交道。sys是system的缩写
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径
sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0),错误退出sys.exit(1)
sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息
sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值
sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称
import sys
print('*'*6)
sys.exit() #退出程序,正常退出时exit(0),错误退出sys.exit(1)
print('-'*6) #这行不会打印
内存
程序在运行起来的时候
启动解释器 加载一些基础的内容 内置函数 内置模块 -->内存里
sys.argv的应用
import sys
print(sys.argv) # 列表 列表的第一项是当前文件所在的路径
if sys.argv[1] == 'alex' and sys.argv[2] == '3714':
print('登陆成功')
else:
sys.exit()
user = input('>>>')
pwd = input('>>>')
if user == 'alex' and pwd == '3714':
print('登陆成功')
else:
sys.exit()
print('我能完成的功能')
执行一个程序
debug
直接执行
import sys
import logging
inp = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv)>1 else 'WARNING' 判断如果sys.argv列表的值大于1,说明还有其他参数第一个参数是用户名第二个是密码,否则'WARNING'
logging.basicConfig(level=getattr(logging,inp)) # DEBUG 用logging模块打印
num = int(input('>>>'))
logging.debug(num)
a = num * 100
logging.debug(a)
b = a - 10
logging.debug(b)
c = b + 5
print(c)