CAS (Compare-And-Swap) 是一种硬件对并发的支持,针对多处理器
操作而设计的处理器中的一种特殊指令,用于管理对共享数据的并
发访问。
CAS 是一种无锁的非阻塞算法的实现。
CAS 包含了 3 个操作数:
需要读写的内存值 V
进行比较的值 A
拟写入的新值 B
当且仅当 V 的值等于 A 时,CAS 通过原子方式用新值 B 来更新 V 的值,否则不会执行任何操作。
原子变量:
类的小工具包,支持在单个变量上解除锁的线程安全编程。事实上,此包中的类可
将 volatile 值、字段和数组元素的概念扩展到那些也提供原子条件更新操作的类。
类 AtomicBoolean、AtomicInteger、AtomicLong 和 AtomicReference 的实例各自提供对
相应类型单个变量的访问和更新。每个类也为该类型提供适当的实用工具方法。
AtomicIntegerArray、AtomicLongArray 和 AtomicReferenceArray 类进一步扩展了原子操
作,对这些类型的数组提供了支持。这些类在为其数组元素提供 volatile 访问语义方
面也引人注目,这对于普通数组来说是不受支持的。
核心方法:boolean compareAndSet(expectedValue, updateValue)
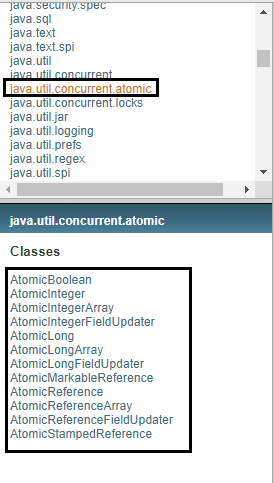
java.util.concurrent.atomic 包下提供了一些原子操作的常用类:
AtomicBoolean 、AtomicInteger 、AtomicLong 、 AtomicReference
AtomicIntegerArray 、AtomicLongArray
AtomicMarkableReference
AtomicReferenceArray
AtomicStampedReference
i++ 的原子性问题:
int i =10;
i=i++;
最后i=10;
在计算机底层的执行:
int temp = i;//临时变量
i = i +1;
i=temp;
结论:i++的操作实际上分为三个步骤“读-改-写”
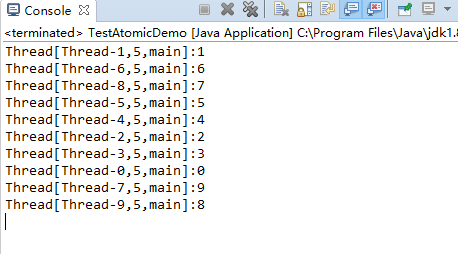
public class TestAtomicDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { AtomicDemo ad = new AtomicDemo(); //创建10个线程进行操作 for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){ new Thread(ad).start(); } } } class AtomicDemo implements Runnable{ private int serialNumber = 0; public int getSerialNumber() { return serialNumber++; } @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(400); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+":"+getSerialNumber()); } }
此时的数据会有重复值的问题

画图实例:
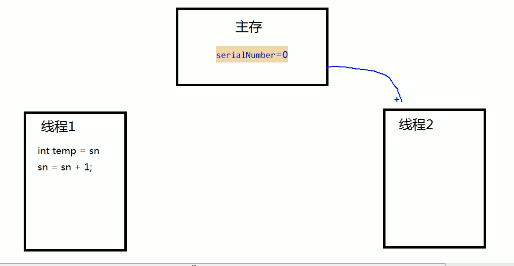
此时线程1在临时变量中进行操作数据
如果正在写的过程中线程2进行读取数据(在线程1写之前)
然后线程2也在进行写1
使用volition可以保持数据可见性,但是不可以保证数据的原子性
此时使用volition数据重复依然存在
原子变量
java.util.concurrent.atomic包下提供了常用的原子变量
1、volatile保证了内存可见性
2、CAS算法保证数据的原子性
具体CAS见上文!
图示:

此时的线程1已经进行读取而且在整写数据,线程2开始读取数据
线程1中v=A是可以进行操作的回将B的值写进主存:

线程2中V和A值不同,将不会进行操作!
当多个线程进行操作时,当且只有一个线程会对数据进行行更新
线程2失败之后,还会立即进行对其进行操作
对上述的代码进行修改:
public class TestAtomicDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { AtomicDemo ad = new AtomicDemo(); //创建10个线程进行操作 for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){ new Thread(ad).start(); } } } class AtomicDemo implements Runnable{ private AtomicInteger serialNumber = new AtomicInteger(); public int getSerialNumber() { //获取并且递增 return serialNumber.getAndIncrement(); } @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(400); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+":"+getSerialNumber()); } }
模拟CAS算法
public class TestCompareAndSwap { public static void main(String[] args) { final CompareAndSwap cas = new CompareAndSwap(); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { int expectiveValue = cas.get(); boolean bool = cas.compareAndSet(expectiveValue, (int)(Math.random()*101)); System.out.println(bool); } }).start(); } } } class CompareAndSwap{ private int value; //获取当前的内存知 public synchronized int get(){ return value; } //比较 //expectiveValue预估值 public synchronized int compareAndSwap(int expectiveValue,int newValue){ int oldValue = value; if(oldValue == expectiveValue){ this.value = newValue; } return oldValue; } //设置 public synchronized boolean compareAndSet(int expectiveValue,int newValue){ return expectiveValue == compareAndSwap(expectiveValue, newValue); } }
