一 如何copy列表
1、浅copy:是把原列表的第一层地址不加区分完全拷贝
拷贝原列表,产生新列表
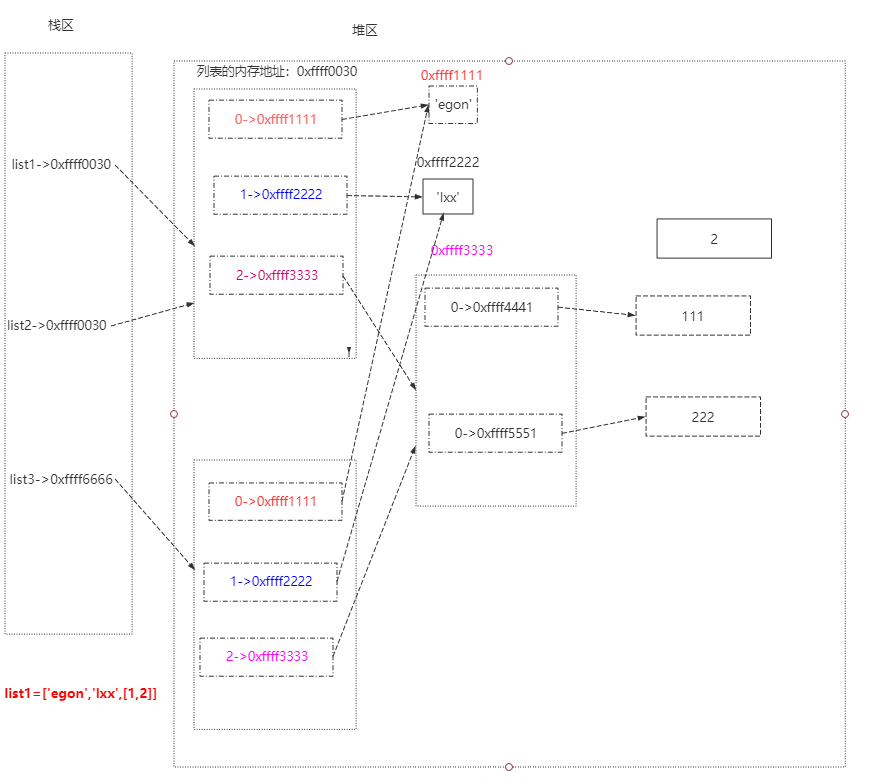
1.2 浅copy的方法
list1 = ['egon','lxx',[1,2]]
list2 = list1.copy()
2、深copy
想让两个列表完全独立开,并且针对改操作而不是读操作
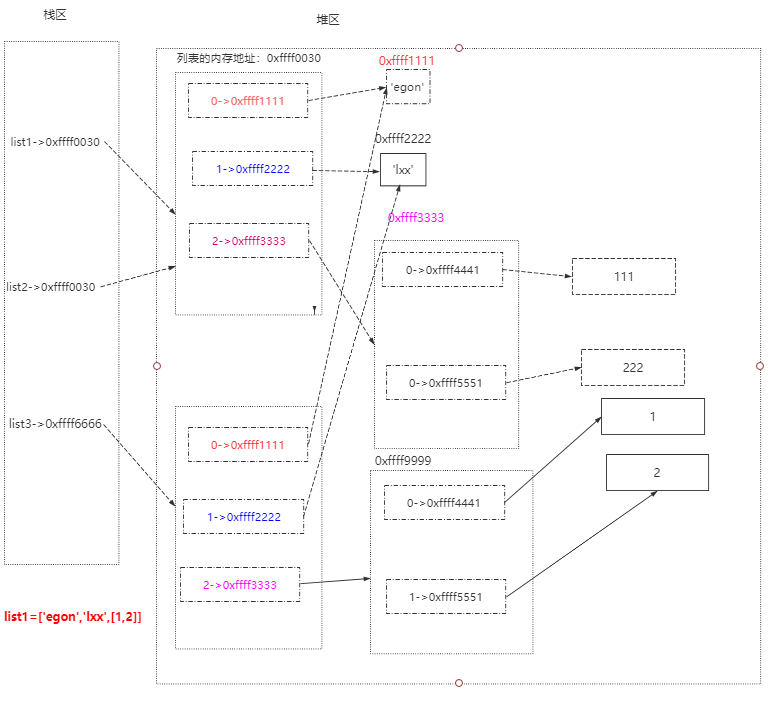
2.2 深copy的方法
list1 = ['egon','lxx',[1,2]]
import copy
list2 = copy.deepcopy(list1)
区别:
浅copy是共用同一地址,深copy则是重新申请一个地址,改变其中一个的可变类型时,两者不会同时改变
二 流程控制之while 循环
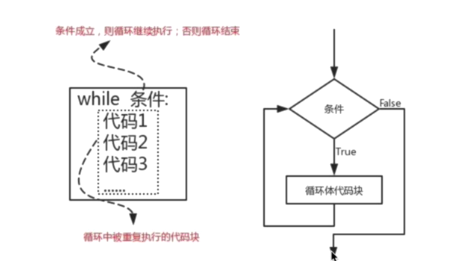
1、循环的语法与基本使用
while 条件:
代码1
代码2
代码3
print()
如:
count = 0
while count < 5:
print(count)
count += 1
print('顶级代码')
2、死循环与效率问题
count = 0
while count < 5:
print(count)
count = 0
while count < 5:
print(count)
while True:
name = input('yourr name')
print(name)
以上都不会出现效率问题
while True:
1+1
没有输出,后台一直运行
纯计算,没有IO的死循环会导致致命的效率问题
3、循环应用
username = 'abc'
pwd = '123'
inp_name = input('请输入您的账号:')
inp_pwd = input('请输入您的密码:')
if username== inp_name and pwd == inp_pwd :
print('welcome')
else:
print('return back')
需求:输入错误的话,能够接着再输2次,没有while则需要再输入三遍相同的程序,很繁琐,而且却输对了还要再输两边。
需要重复代码,而且输对了不需再重复
username = 'abc'
pwd = '123'
while 1:
inp_name = input('请输入您的账号:')
inp_pwd = input('请输入您的密码:')
if username== inp_name and pwd == inp_pwd :
print('welcome')
else:
print('return back')
4、退出循环两种方式
4.1、条件改为False:等到下次循环判断条件时才会生效
username = 'abc'
pwd = '123'
tag = True
while tag:
tag = False
inp_name = input('请输入您的账号:')
inp_pwd = input('请输入您的密码:')
if username== inp_name and pwd == inp_pwd :
print('welcome')
#tag = False(之后代码还会运行,下次循环判断条件时才生效)
else:
print('return back')
4.2 break,只要运行到break就会立刻终止本层循环
username = 'abc'
pwd = '123'
while True:
inp_name = input('请输入您的账号:')
inp_pwd = input('请输入您的密码:')
if username== inp_name and pwd == inp_pwd :
print('welcome')
break #终止本层循环
else:
print('return back')
print('====end====')
即如果if结果是True,则结尾不会打印====end====,如果是False,就会有
5、while循环嵌套
5.1 tag类型
tag = True
while tag:
while tag:
while tag:
tag = False
username = 'abc'
pwd = '123'
tag = True
while tag :
inp_name = input('请输入您的账号:')
inp_pwd = input('请输入您的密码:')
if username== inp_name and pwd == inp_pwd :
print('welcome')
while tag:
cmd = input('输入命令:')
if cmd == 'q':
tag = False
else
print('order {x} is loading'.format(x = cmd))
else:
print('return back')
print('====end====')
5.2 break:每一层必须配一个break
while True:
while True:
while True:
break
break
break
username = 'abc'
pwd = '123'
while True:
inp_name = input('请输入您的账号:')
inp_pwd = input('请输入您的密码:')
if username== inp_name and pwd == inp_pwd :
print('welcome')
while True:
cmd = input('输入命令:')
if cmd == 'q':
print('order {x} is loading'.format(x = cmd))
break
break #终止本层循环
else:
print('return back')
print('====end====')
6、while + continue:结束本次循环,直接进入下一次
在continue之后添加同级代码毫无意义,因为永远无法运行
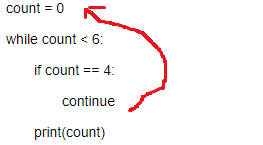
count = 0
while count < 6:
if count == 4:
continue
print(count)
count +=1
7、while + else(针对break)
else包含的代码会在while循环结束后,并且在while喜欢实在没有被break打断的情况下正常结束的,才不会运行
while count < 6:
if count == 4:
break (后面程序都不运行)
count += 1
continue
print(count)
count+=1
else:
print('...')
应用案例:
username = 'abc'
pwd = '123'
count = 0
tag = True
while tag:
if count == 3:
break
inp_name = input('请输入您的账号:')
inp_pwd = input('请输入您的密码:')
if username== inp_name and pwd == inp_pwd :
print('welcome')
while tag:
cmd = input('输入命令:')
if cmd == 'q':
tag = False
else
print('order {x} is loading'.format(x = cmd))
else:
print('return back')
count += 1