B. DZY Loves Chemistry
DZY loves chemistry, and he enjoys mixing chemicals.
DZY has n chemicals, and m pairs of them will react. He wants to pour these chemicals into a test tube, and he needs to pour them in one by one, in any order.
Let's consider the danger of a test tube. Danger of an empty test tube is 1. And every time when DZY pours a chemical, if there are already one or more chemicals in the test tube that can react with it, the danger of the test tube will be multiplied by 2. Otherwise the danger remains as it is.
Find the maximum possible danger after pouring all the chemicals one by one in optimal order.
Input
The first line contains two space-separated integers n and m 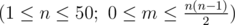 .
.
Each of the next m lines contains two space-separated integers xi and yi (1 ≤ xi < yi ≤ n). These integers mean that the chemical xi will react with the chemical yi. Each pair of chemicals will appear at most once in the input.
Consider all the chemicals numbered from 1 to n in some order.
Output
Print a single integer — the maximum possible danger.
Examples
input
1 0
output
1
input
2 1
1 2
output
2
input
3 2
1 2
2 3
output
4
Note
In the first sample, there's only one way to pour, and the danger won't increase.
In the second sample, no matter we pour the 1st chemical first, or pour the 2nd chemical first, the answer is always 2.
In the third sample, there are four ways to achieve the maximum possible danger: 2-1-3, 2-3-1, 1-2-3 and 3-2-1 (that is the numbers of the chemicals in order of pouring).
能够相互反应的元素构成一个集合,用并查集找到有几个集合,从每个集合中各取一个放入杯中,然后不管从哪个集合取一个元素加入杯中都能够有办法翻倍,所以答案就是2的(元素个数减去集合个数)次方。
1 //2017-08-06 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 const int N = 60; 10 int fa[N], arr[N]; 11 long long pow[N]; 12 13 void init(){ 14 pow[0] = 1; 15 for(int i = 1; i < N; i++){ 16 fa[i] = i; 17 pow[i] = pow[i-1]*2; 18 } 19 } 20 21 int getfa(int x){ 22 if(fa[x] == x)return x; 23 return fa[x] = getfa(fa[x]); 24 } 25 26 void Merge(int a, int b){ 27 int af = getfa(a); 28 int bf = getfa(b); 29 if(af != bf){ 30 fa[bf] = af; 31 } 32 } 33 34 int main() 35 { 36 int n, m, a, b; 37 while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m)!=EOF){ 38 init(); 39 while(m--){ 40 scanf("%d%d", &a, &b); 41 Merge(a, b); 42 } 43 int cnt = 0; 44 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 45 if(fa[i] == i)cnt++; 46 if(m == 0)printf("1 "); 47 else printf("%lld ", pow[n-cnt]); 48 } 49 50 return 0; 51 }
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 static final int N = 60; 5 static int[] fa = new int[N]; 6 static int[] arr = new int[N]; 7 static long[] pow = new long[N]; 8 9 static void init(){ 10 pow[0] = 1; 11 for(int i = 1; i < N; i++){ 12 fa[i] = i; 13 pow[i] = pow[i-1]*2; 14 } 15 } 16 17 static int getfa(int x){ 18 if(fa[x] == x)return x; 19 return fa[x] = getfa(fa[x]); 20 } 21 22 static void merge(int a, int b){ 23 int af = getfa(a); 24 int bf = getfa(b); 25 if(af != bf) 26 fa[bf] = af; 27 } 28 29 public static void main(String args[]){ 30 int n, m, a, b; 31 Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in); 32 while(cin.hasNext()){ 33 n = cin.nextInt(); 34 m = cin.nextInt(); 35 init(); 36 for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){ 37 a = cin.nextInt(); 38 b = cin.nextInt(); 39 merge(a, b); 40 } 41 int cnt = 0; 42 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 43 if(fa[i] == i) 44 cnt++; 45 if(m == 0)System.out.printf("1 "); 46 else System.out.println(pow[n-cnt]); 47 } 48 } 49 }