A. Tree
把每条路径先拆开拆成u->lca和lca->v(去掉lca),然后在树上dfs,回溯的时候把儿子挂到当前节点/带权并查集维护路径乘积)
B. Coin
就是求((p-q)/p+q/p*x)^k的偶次项系数之和,代入x=1,-1加加减减就行了 。
概率计算,但最终结果不用除法,用逆元。只算分子即可,分母就是p的k次幂。
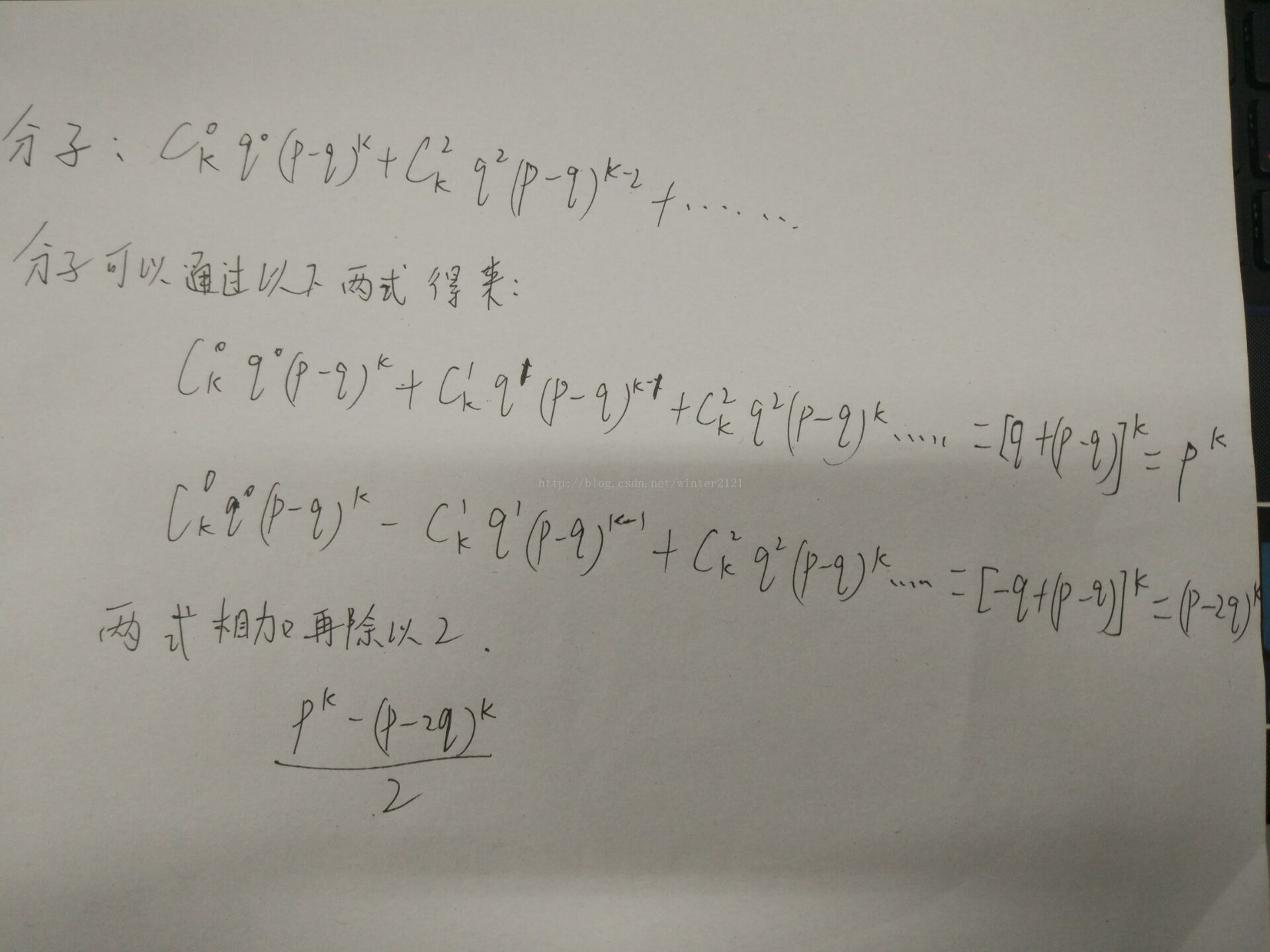
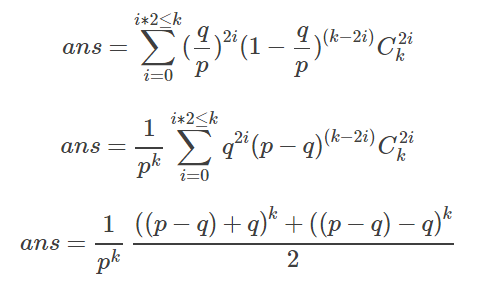
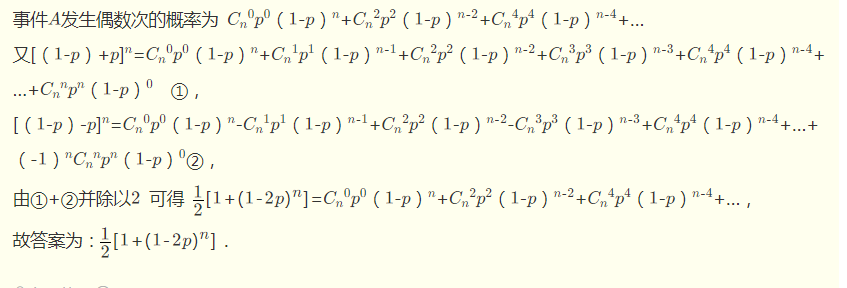
https://wenku.baidu.com/view/8316d8390912a2161479297c.html?qq-pf-to=pcqq.group (二项分布中偶数项之和与奇数项之和
C. Sum
这样的数的位数和一定是可以整除233的。
//1.任何数乘9的位数和都为9,直接输出233个9。因为任何正整数乘以9的数位和都是9的倍数。
2.需要找到一个k使得k*x之后的值,每一位上的值相加是233的倍数
那么我们可以想到,如果能够造一个k使得k*x上的每一位之和是x*233就行啦
再仔细看题,x最多取到1000000,所以我们打印233个0000001就行了,这样使得最后得到的每一位之和就是233个x。
//当x<10时可以直接输出233个x,当1000>x>=10时,不妨设k*x=233个x,那么k=10(233个10),当1000<=x<10000,k=100(233个100),等等。手动模拟一下就懂了。
E. Maximum Flow
【分析】:打印出来相邻两个数的差是有规律的, 差值的规律如下:
2^0+1 第一次出现的位置为2^1, 第二次出现的位置为2^1+2^0, 接下来出现的位置依次为:2^1+2^0+k*2^1;
2^2+1 第一次出现的位置为2^2, 第二次出现的位置为2^2+2^1, 接下来出现的位置依次为:2^2+2^1+k*2^2;
2^4+1 第一次出现的位置为2^3, 第二次出现的位置为2^3+2^2, 接下来出现的位置依次为:2^3+2^2+k*2^3;
2^6+1 第一次出现的位置为2^4, 第二次出现的位置为2^4+2^3, 接下来出现的位置依次为:2^4+2^3+k*2^4;
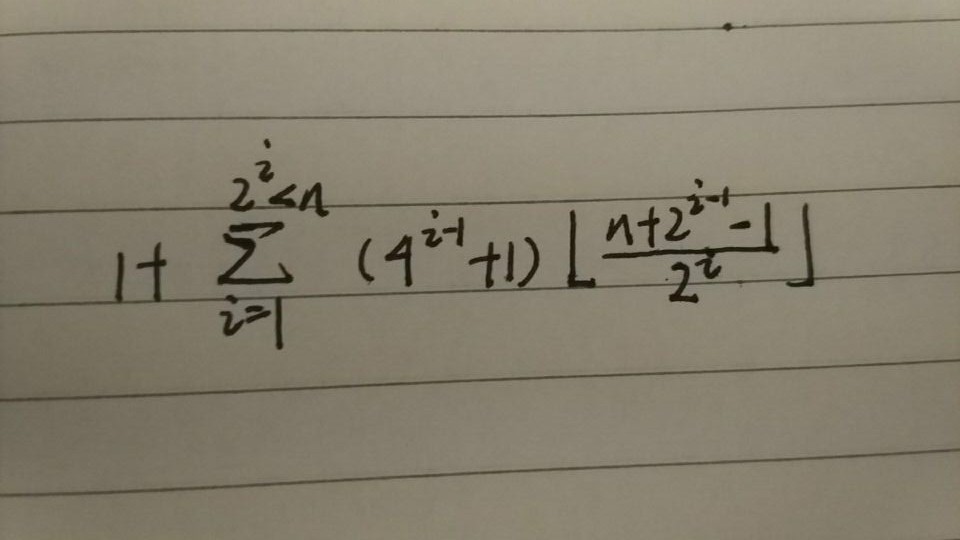
上下双阶乘可约掉一部分, 除法用逆元,还有判断一下m和n的一些特殊值

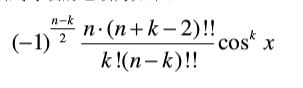 <——公式
<——公式- 当m大于n时,答案显然为0。
- 当n为奇数且m为偶数或n为偶数且m为奇数时答案显然为0。
- 当n为奇数,且m为1时,答案的绝对值为n。
- 当n为偶数,且m为0时,答案的绝对值为1。
- 其余情况答案的绝对值均为【 n * (n-m+2) * (n-m+4) * ... * (n+m-4) * (n+m-2) 】/(m!)。(注意逆元的运用)
- 上面出现绝对值的情况,3和4 当(n/2)%2 == 0 时符号为正,否则为负;5 当((n-m)/2)%2 == 0时,符号为正,否则符号为负。
F. Trig Function
求出k然后比较分子分母大小然后从小的开始+=2算出双阶乘就好了
G. Xor
B:
 B题-二项分布公式题/注意逆元
B题-二项分布公式题/注意逆元
 参考http://blog.csdn.net/Mitsuha_/article/details/78005772?locationNum=5&fps=1
参考http://blog.csdn.net/Mitsuha_/article/details/78005772?locationNum=5&fps=1
 矩阵优化dp版
矩阵优化dp版
 参考http://blog.csdn.net/cillyb/article/details/78005332
参考http://blog.csdn.net/cillyb/article/details/78005332
 出0题/构造
出0题/构造
 公式题1
公式题1
 二发
二发

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; void exgcd(ll a,ll b,ll& d,ll& x,ll& y) { if(!b) { d = a; x = 1; y = 0; } else{ exgcd(b, a%b, d, y, x); y -= x*(a/b); } } ll inv(ll a, ll p) { ll d, x, y; exgcd(a, p, d, x, y); return d == 1 ? (x+p)%p : -1; } int mod=1e9+7; ll find1(int x,int n) //注意n等于0的时候 { ll a=x; ll ans=1; while (n) { if (n&1) ans=ans*a%mod; a=a*a%mod; n>>=1;//效果跟n/=2;一样 } return ans; } int main() { int T; scanf("%d",&T); while(T--) { ll p,q,k; ll x,y; scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&p,&q,&k); if(p>q) { ll t=q; q=p; p=t; } x=q-2*p; y=q; x=find1(x,k); y=find1(y,k); x=(x+y)%mod; y=(2*y)%mod; // printf("%lld %lld ",x,y); printf("%lld ",(x*inv(y,mod))%mod); } }

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int MOD=1e9+7; long long POW(long long x,long long n) { long long res=1; while(n) { if(n&1)res=(res*x)%MOD; x=(x*x)%MOD; n/=2; } return res; } int main() { int T;cin>>T; while(T--) { long long p,q,k; scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&p,&q,&k); long long x=POW(p-2*q,k); long long y=POW(p,k); cout<<( ((1+x*POW(y,MOD-2))%MOD) * POW(2,MOD-2) )%MOD<<endl; } return 0; }

#include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int maxn=3; struct Matrix//???? { ll a[maxn][maxn]; void init() { memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); for(int i=1;i<maxn;i++) a[i][i]=1; } } ; const ll mod=1000000007; Matrix mul(Matrix a,Matrix b) //(a*b)%mod ???? { Matrix ans; memset(ans.a,0,sizeof(ans.a)); for(int i=1;i<maxn;i++) for(int j=1;j<maxn;j++) { ans.a[i][j]=0; for(int k=1;k<maxn;k++) { ans.a[i][j]+=a.a[i][k]*b.a[k][j] ; ans.a[i][j]%=mod; } } return ans; } Matrix pow(Matrix a,ll m) { Matrix res ; memset(res.a,0,sizeof(res.a)); for(int i=1;i<maxn;i++) { res.a[i][i]=1; } while(m) { if(m&1) { res=mul(a,res); } a=mul(a,a); m/=2; } return res; } ll quick(ll n,ll m) { ll ans = 1; while(m){ if(m & 1) ans = ans * n % mod; m >>= 1; n = n * n % mod; } return ans; } int main() { double p; int t=0; int n; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--) { ll p,q,k; scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&p,&q,&k); ll nums= q*quick(p,mod-2)%mod; ll numx=(p-q)*quick(p,mod-2)%mod; Matrix ans; ans.a[1][1]=(numx)%mod; ans.a[2][1]=(nums)%mod; // printf("%lld ",quick(27,mod-2)%mod*14%mod); /* ll pp = (numx * numx % mod + nums * nums % mod) % mod; ll qq = (numx * numx) % mod; printf("%lld ",(pp * numx % mod + qq * nums % mod) % mod);*/ if(k==1) { printf("%lld ",ans.a[1][1]%mod); continue; } Matrix base,res; base.a[1][1]=numx,base.a[1][2] =nums; base.a[2][1]=nums,base.a[2][2]= numx; res=pow( base, k - 1 ); ans=mul( base,res); printf("%lld ",ans.a[1][1]%mod); } } //http://blog.csdn.net/qq_33951440/article/details/78005483

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int mod = 1e9+7; typedef long long ll; ll p, q, n; ll qmod(ll x, ll q) { ll res = 1; while(q) { if(q%2) res = res*x%mod; x = x*x%mod; q /= 2; } return res; } int main(void) { int _; cin >> _; while(_--) { scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &p, &q, &n); ll ni2 = qmod(2LL, mod-2); ll fm = qmod(p, n); ll fz = qmod(p-2*q, n); ll nifm = qmod(fm, mod-2); ll tmp = (1+fz*nifm%mod)%mod*ni2%mod; printf("%lld ", tmp); } return 0; }
C:

#include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; int main() { int t,x; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--){ cin>>x; printf("1"); for(int i=2;i<=233;i++) { printf("0000001"); } printf(" "); } return 0; }
E: http://www.docin.com/p-385138324.html?qq-pf-to=pcqq.group 【用以表示cosnx的关于cosx的多项式的通项公式】

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const ll mod=1000000007; ll sum[100]; ll la[100]; ll two[100]; int main() { sum[0]=1; la[0]=1; two[0]=1; for(int i=1; i<=64; i++) { two[i]=two[i-1]*2ll; sum[i]=(sum[i-1]*2%mod+la[i-1]*3%mod)%mod; la[i]=la[i-1]*4%mod; } ll n; while(~scanf("%lld",&n)) { n--; ll pos; for(ll i=62; i>=0; i--) { if(n>=two[i]) { pos=i; break; } } ll ans=n%mod; // cout<<pos<<endl; pos=(1ll<<pos); n-=pos; ans+=((1ll*pos/2ll)%mod)*((pos-1ll)%mod); ans%=mod; for(ll i=0; i<63; i++) { if(n&(1ll<<i)) ans+=sum[i]; ans%=mod; } printf("%lld ",ans%mod); } }

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<string> using namespace std; const int MAXN = 30010; string lib[MAXN]; int tot; int cmpa(string &str, string &a){ for(int i = 0; i < a.length(); ++i){ if(str[i] != a[i]){ return 0; } } return 1; } int cmpd(string &str, string &d){ for(int i = 1; i <= d.length(); ++i){ if(str[str.length() - i] != d[d.length() - i]){ return 0; } } return 1; } int cmpbc(string &str, string &b, string &c){ int mid = str.length() / 2; for(int i = 0; i < c.length(); ++i){ if(str[mid + i] != c[i]){ return 0; } } for(int i = 1; i <= b.length(); ++i){ if(str[mid - i] != b[b.length() - i]){ return 0; } } return 1; } int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); int T, q; for(cin >> T; T && cin >> q; --T){ tot = 0; int ctrl; for (int k = 0; k < q; ++k) { cin >> ctrl; if (ctrl == 1) { cin >> lib[tot++]; } else { string a, b, c, d; cin >> a >> b >> c >> d; int maxLen = a.length() + b.length(); if (c.length() + d.length() > maxLen) maxLen = c.length() + d.length(); maxLen *= 2; int cnt = 0; for (int i = 0; i < tot; ++i) { if (lib[i].length() >= maxLen && lib[i].length() % 2 == 0) { if (cmpa(lib[i], a) && cmpd(lib[i], d) && cmpbc(lib[i], b, c)) { ++cnt; } } } cout << cnt << endl; } } } return 0; }
F:

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<string> #include<cstring> #include<cstdlib> #include<sstream> #include<fstream> #include<vector> #include<list> #include<deque> #include<stack> #include<queue> #include<map> #include<set> #include<cmath> #include<utility> #include<numeric> #include<iterator> #include<algorithm> #include<functional> #include<ctime> #include<cassert> using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; typedef std::pair<int,int> P; #define FOR(i,init,len) for(int i=(init);i<(len);++i) #define For(i,init,len) for(int i=(init);i<=(len);++i) #define fi first #define se second #define pb push_back #define is insert namespace IO { inline char getchar() { static const int BUFSIZE=5201314; static char buf[BUFSIZE],*begin,*end; if(begin==end) { begin=buf; end=buf+fread(buf,1,BUFSIZE,stdin); if(begin==end) return -1; } return *begin++; } } inline void read(int &in) { int c,symbol=1; while(isspace(c=IO::getchar())); if(c=='-') { in=0;symbol=-1; } else in=c-'0'; while(isdigit(c=IO::getchar())) { in*=10;in+=c-'0'; } in*=symbol; } inline int read() { static int x;read(x);return x; } ll gcd(ll a,ll b) { return b?gcd(b,a%b):a; } ll lcm(ll a,ll b) { return a/gcd(a,b)*b; } const ll mod=998244353LL; const int maxm=1e4+10; ll qpow(ll a,ll b) { ll ans=1; while(b) { if(b&1) ans=ans*a%mod; a=a*a%mod; b>>=1; } return ans; } ll f[maxm],invf[maxm]; ll n,m; int main() { #ifdef MengLan int Beginning=clock(); //freopen("in","r",stdin); //freopen("out","w",stdout); #endif // MengLan f[0]=1; FOR(i,1,maxm) f[i]=f[i-1]*i%mod; invf[maxm-1]=qpow(f[maxm-1],mod-2); for(int i=maxm-2;i>=0;--i) invf[i]=invf[i+1]*(i+1)%mod; while(cin>>n>>m) { if((n&1)^(m&1)) { puts("0");continue; } if(m>n) { puts("0");continue; } if(m==0) { puts("998244352");continue; } ll ans=1; for(ll i=n-m+2;i<=n+m-2;i+=2) { ans*=i;ans%=mod; } ans=ans*n%mod; ll k=1; For(i,1,m) { k=k*i%mod; } ll x=qpow(k,mod-2); ans=ans*x%mod; if(((n-m)/2)&1) ans=(mod-ans)%mod; cout<<ans<<endl; } #ifdef MengLan printf("Time: %d ",clock()-Beginning); #endif // MengLan return 0; }

#include<cstdio> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; const LL MOD=998244353; LL quick_pow(LL y,LL k) { LL res = 1; while (k) { if (k & 1) res=(res* y)%MOD; y=(y*y)%MOD; k >>= 1; } return res; } LL fun1(LL n) { LL t=1; for(LL i=n;i>=1;i--) t=(t*i)%MOD; return t; } LL fun2(LL n,LL m) { LL count=1; while(n>m) { count=(count*n)%MOD; n=n-2; } return count; } int main() { LL n,m; while(~scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m)) { if(n%2!=m%2||m>n) { printf("0 "); continue; } if(m==0) { printf("998244352 "); continue; } LL x,y; x=(n*fun2(n+m-2,n-m))%MOD; y=fun1(m); LL a=quick_pow(y,MOD-2); LL ans=(x*a)%MOD; if((n-m)/2%2) ans=(MOD-ans)%MOD; printf("%lld ",ans); } }
