结构体,类,指针与引用 | 07
类的定义
首先C++类在定义的时候,结尾需要加上分号;,这是一个比较蛋疼的地方.函数的定义是不需要在结尾加上分号的. 同时注意了, 定义结构体结尾也是需要;的.
类中有两个关键字: private和public
class Person{
private:
int age;
double money;
int books[100];
public:
string name;
void say(){
cout << "I'm " << name << endl;
}
int get_age(){
return age;
}
void add_money(double x){
money += x;
}
};
类的使用
Person c;
c.name = "rowry";
c.set_age(18);
c.say(); // 执行方法
cout << c.get_age() << endl;
结构体和类的差别
结构体默认就是public的,但是类默认是private,如果类缺省了前面的限定修饰符的话.
还有就是结构体是不能定义方法的,但是类可以.
结构体和类都是可以使用构造函数的.
结构体
结构体的关键字是struct.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Person{
int age,height;
double money;
Person(){};// 无参构造函数
Person(int _age,int _height,double _money){
age = _age,height=_height,money=_money;
}
};
int main(){
Person c(); //直接无参构造,括号可以省略
Person d(18,180,100.0); // 传参
return 0;
}
指针
指针其实就是一种变量,专门用来存储地址的变量.
int a = 10;
int *p = &a; // 定义指针,存储a的地址
然后就是指针的使用,注意,一旦修改了指针,那么对应变量的值也会修改
int a = 10;
int* p = &a;
cout << p << endl; // 输出地址 0x7fff3573ab74
cout << *p << endl; // 输出a的值
*p = 12; // 如果修改 *p, 那么 a的值也会修改
cout << a << endl; // a = 12
数组也是一种指针.
指针可以做运算.
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)cout << *(a + i) << endl;
return 0;
}
引用
引用其实就是类似于取了个别名,在方法形参定义的时候很常用,如果需要主函数和调用函数对一个变量同时进行修改的话.
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void f(int& x){
x+= 100;
}
int main(){
int a = 10;
int& p = a; // p和a是使用的相同的地址
cout << p << endl;
p += 5; // p修改为15,那么a也是15
cout << a << endl;
f(p); // 经过操作后,给p +100
cout << a << endl;
return 0;
}
链表
关于.和->
struct Node{
int val;
Node* next;
Node(){}
Node(int _val){
val = _val,next=NULL;
}
};
// 如果是值的话直接使用.
Node node = Node(1);
node.val;
node.next;
// 如果是指针的话就使用 ->
Node* p = new Node(1);
p->val;
p->next;
有关于链表的定义
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int val;
Node *next;
Node(){}
Node(int _val){
val = _val;
next = NULL;
}
};
int main(){
// Node node = Node(1);
// Node* p = &node;
// new,生成一个结构体,并把地址给到p
// new Node(1) 返回的是地址, Node(1)返回的是值
Node* p = new Node(1);
auto q = new Node(); // auto可以推断出来是 Node*
q -> val = 2;
p -> next = q;
q -> next = NULL;
return 0;
}
如何遍历单链表
for(Node* i=head;i;i=i->next){
cout << i->val << endl;
}
习题七
斐波那契数列

class Solution {
public:
int Fibonacci(int n) {
int a=0,b=1;
while(n--){
int c = a + b;
b=a,a=c;
}
return a;
}
};
替换空格

class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpaces(string &str) {
string res;
for(auto c:str){
if(c==' ')res+="%20";
else res+=c;
}
return res;
}
};
思路就是定义一个新的字符串,然后一个字符一个字符进行复制,如果是空格,那么就添加%20,否则就添加原字符.
求1+2+...+n
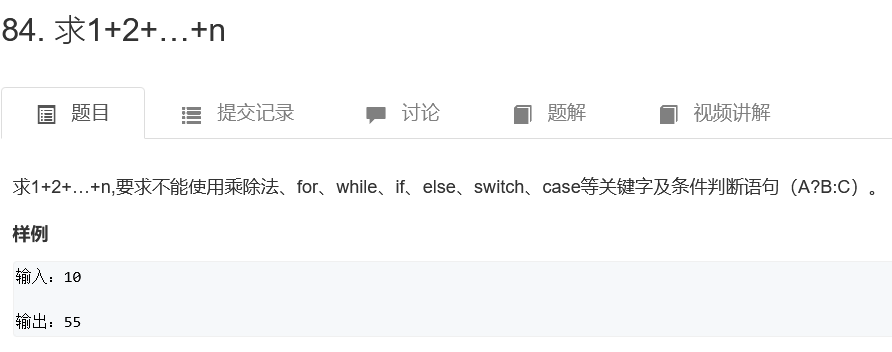
class Solution {
public:
int getSum(int n) {
int res = n;
n>0 && (res += getSum(n-1));
return res;
}
};
这个是利用了&&短路的特性.
在O(1)时间删除链表结点
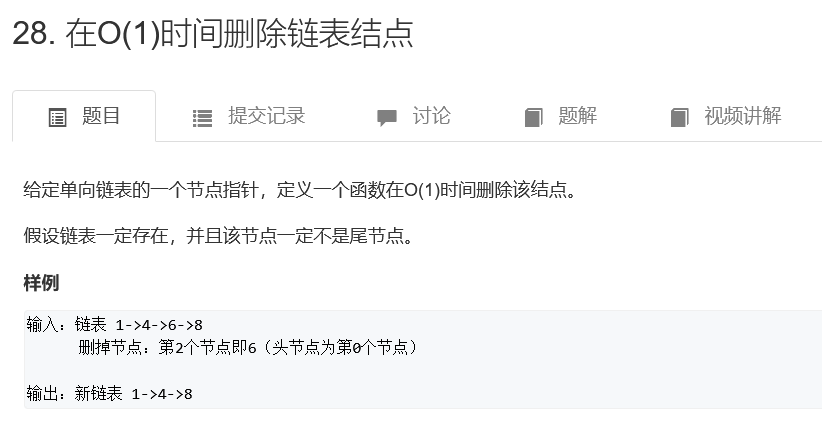
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
// 伪装,删除真正的点
node->val = node->next->val;
node->next = node->next->next;
}
};
经典的链表删除问题,必须掌握.
但是这个题目并没有给前一个结点,那么就把当前结点变成"前一个结点",然后删除真正的结点.
合并两个排序的链表
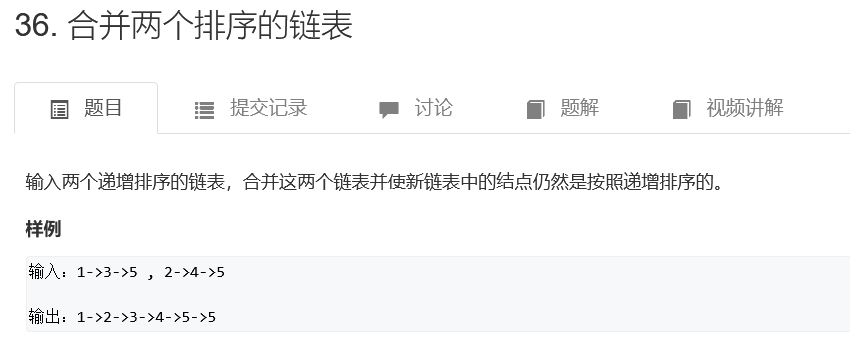
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1); // 定义一个虚拟头节点
ListNode* cur = dummy;
while(l1 && l2){
if(l1->val < l2->val){
cur = cur->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}else{
cur = cur->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
if(l1)cur->next = l1;
if(l2)cur->next = l2;
return dummy -> next;
}
};
左旋转字符串
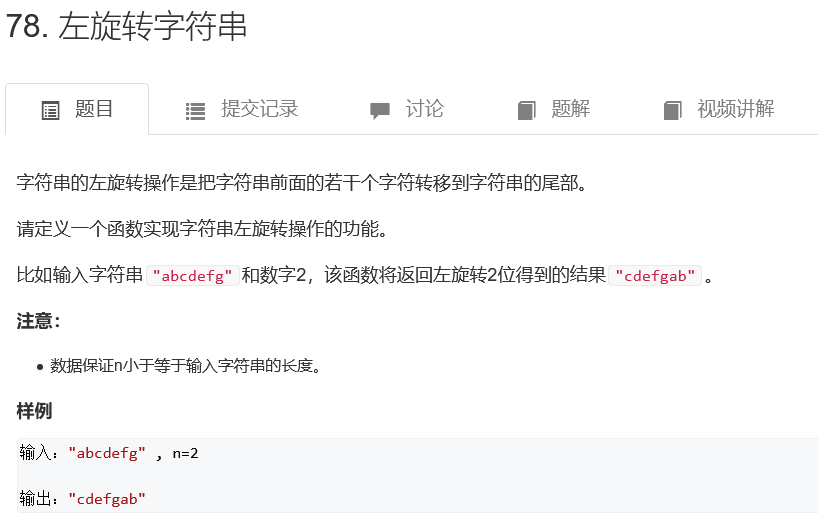
class Solution {
public:
string leftRotateString(string str, int n) {
string res=str.substr(n)+str.substr(0,n);
return res;
}
};
把字符串转换成整数
class Solution {
public:
int strToInt(string str) {
int k = 0;
while (k < str.size() && str[k] == ' ') k ++ ; // 跳过所有的空格
long long res = 0;
int minus = 1;
if (k < str.size()){
if (str[k] == '-') minus = -1, k ++ ;
else if (str[k] == '+') k ++ ;
}
while (k < str.size() && str[k] >= '0' && str[k] <= '9'){ // 这里就阻止了开头的情况了
res = res * 10 + str[k] - '0';
if (res > 1e11) break; // 如果大于一个数的话就直接退出
k ++ ;
}
res *= minus;
if (res > INT_MAX) res = INT_MAX;
if (res < INT_MIN) res = INT_MIN;
return res;
}
};
C语言有atoi(str.c_str())函数,可以将字符串转为数字.stoi(str)
反转链表


/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* pre = NULL;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur){
auto next = cur -> next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};
**记住了,需要三个指针pre,cur,next**
两个链表的第一个公共结点

首先只有两种情况,一种是有一个公共结点,另外一种情况就是两个结点是平行的.

每次让两个结点按照(a+b+c)的走法走(两个结点同时向后走一步),两个走的长度是一样的(也就是两个结点相等的时候),这样就可以判断是否有公共结点了.

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *findFirstCommonNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
auto pa=headA,pb=headB;
while(pa!=pb){ // 两个结点相等就是判断条件
if(pa)pa=pa->next;
else pa=headB;
if(pb)pb=pb->next;
else pb=headA;
}
return pa;
}
};
删除链表中重复的节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1); // 头结点可能被删除
dummy->next = head;
auto p = dummy; // p是从虚拟头结点开始的
while(p->next){
auto q = p->next; // q可以理解为 "next"探路指针
while(q->next && q->next->val == p->next->val)q=q->next;
if(p->next==q)p=q;
else p->next = q->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
题目的意思就是如果一个点出现了重复超过1次,那么就要删除全部的这个点.
这个和之前的去重还是不太一样的...
首先是链表删除的题目,然后为了避免头结点被删除的情况,这种会定义一个虚拟头结点dummy

指针p和指针q是一前一后的,这样才能保证删除.