本文是基于Frank Xu的一个webcast上的串并总结,图片等都截至视频,谨致谢.
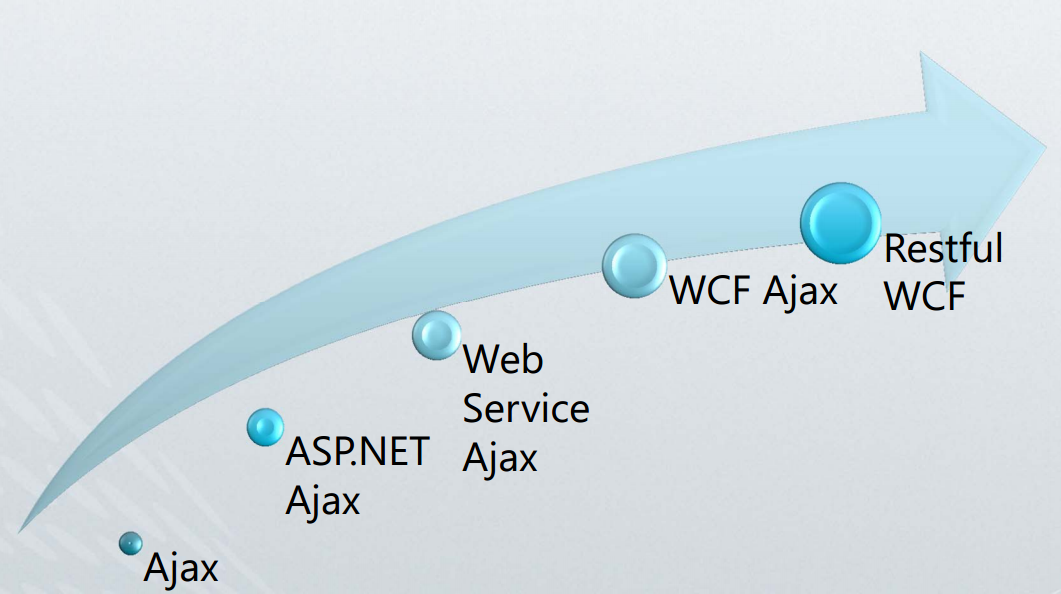
路线图
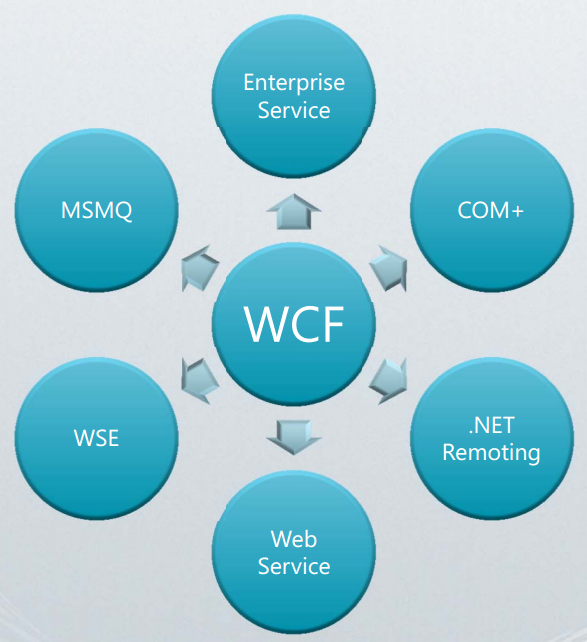
什么是WCF
Windows Communication Foundation是MS为构建面向服务的应用提供的分布式通信编程框架,是.net framework的重要组成部分,集成了多项微软的分布式技术
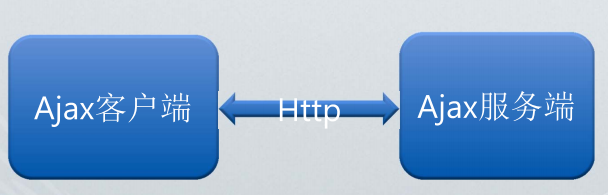
什么是Ajax
Asynchronous JavaScript and XML,即异步JavaScript和XML,基于JavaScript和HTTP请求,其本质原理就是利用XMLHttpRequest对象来直接与服务器进行通信
将以下内容复制进一个文本编辑器,然后保存在你的一个web容器中,并在同级目录下新建一个data.txt的文件,然后运行,就进行了一次Ajax调用的操作了。see, it easy, right?

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>纯AJAX例子:读取数据</title> </head> <body> <script type="text/javascript"> function ajaxCall() { var xmlHttp; try{// Firefox, Opera 8.0+, Safari xmlHttp=new XMLHttpRequest();//实例化XMLHttpRequest对象 }catch (e){ // Internet Explorer 5+ try{ xmlHttp=new ActiveXObject("Msxml2.XMLHTTP"); }catch (e){ try{ xmlHttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); }catch (e){ alert("浏览器不支持AJAX!"); return false; } } } //绑定数据处理函数。 xmlHttp.onreadystatechange=function(){ if(xmlHttp.readyState==4){ if (xmlHttp.status == 200){ document.getElementById('txtResult').innerHTML = document.getElementById('txtUsername').value + xmlHttp.responseText; } else { alert('请求出错.'); // there was a problem with the request, // for example the response may be a 404 (Not Found) // or 500 (Internal Server Error) response codes } } } xmlHttp.open("GET","data.txt",true);//异步请求数据 xmlHttp.send(null); } </script> <form style="text-align:left"> 姓名: <input type="text" id="txtUsername" style="400px;" /> <br /> 测试:<input type="button" id="btn" value="测试" onclick="ajaxCall();" style="400px;" /> <br /> 结果: <textarea id="txtResult" style="400px;"></textarea> </form> </body> </html>
什么是ASP.NET AJAX
是微软专为asp.net应用程序所开发的ajax框架,研发代号为Atlas,由Microsoft Ajax Library和asp.net服务器控件两块组成,其本质原理就是让Sys.Net.WebRequestExecutor执行Web请求,封装了XMLHttpRequest对象。

为了实现Asp.net Ajax, ScriptManager是必须的服务器控件之一,然后服务也必须加上ScriptService标签。这是一大不友好处。但是用vs2008的模板是很容易也很快就可以做完成的一件事情:新建一个web site,然后选择已安装的模板里的Asp.net Web Service就可以创建一个基于web service的asp.net site了。但是2010以后,这一模板却默认被移除了,所以需要先创建一个web site,然后新加item,找到Web serice添加进来即可。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head runat="server"> <title>Ajax 调用Web服务,Call Web Services with ASP.NET AJAX</title> <script type="text/javascript"> function aspnetAjaxSearch() { var name = $get("UserName").value; AjaxWebService.SayHelloWorld(name,AjaxCallBack); } function AjaxCallBack(result) { $get("AjaxResult").value = result.toString(); } </script> </head> <body> <form runat="server"> <asp:ScriptManager ID="ScriptManager" runat="server"> <Services> <asp:ServiceReference Path="~/AjaxWebService.asmx" /> </Services> </asp:ScriptManager> <p> 输入姓名 </p> <fieldset> <label> 姓名<input type="text" id="UserName" /></label> <button onclick="aspnetAjaxSearch();"> Search </button> </fieldset> <fieldset> <label> 结果<input type="text" id="AjaxResult" /></label> </fieldset> </form> </body> </html>

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.Web.Services; using System.Web.Services.Protocols; using System.Xml.Linq; using System.Web.Script.Services; /// <summary> /// Summary description for AjaxWebService,This demo is finished by Frank Xu Lei. /// It is a demo for Asp.NET Ajax Call WebService /// </summary> [WebService(Namespace = "http://abc.com/")] [WebServiceBinding(ConformsTo = WsiProfiles.BasicProfile1_1)] //Web Service可以被 ASP.NET AJAX客户端调用 [ScriptService] public class AjaxWebService : System.Web.Services.WebService { public AjaxWebService () { } [WebMethod, ScriptMethod] //WebMethod,设置此方法可以被Web客户端调用 //指定调用方法的http动词,以及返回值数据格式 public string SayHelloWorld(string name) { return string.Format("Ajax Hello {0}",name); } }
这是基于asmx的,里面的内容就一行:
<%@ WebService Language="C#" CodeBehind="~/App_Code/AjaxWebService.cs" Class="AjaxWebService" %>
基于svc的就是WCF服务了。对于wcf,一定需要在web.config里面配置<system.serviceModel>节点,宣告BBS(behaviors,bindings,services),一经宣告,其实上面提到的purce ajax也好,asp.net ajax也好,都是可以调用wcf服务的。但是为什么WCF反而还多出这么些步骤了,这是因为WCF web编程模型必须要解决以下几个问题:一个是HTTP Verb,一个是URI处理和数据格式,所以一般一个WCF 操作就形如以下这样:

using System; using System.Linq; using System.Runtime.Serialization; using System.ServiceModel; using System.ServiceModel.Activation; using System.ServiceModel.Web; [ServiceContract(Namespace="abc")] [AspNetCompatibilityRequirements(RequirementsMode = AspNetCompatibilityRequirementsMode.Allowed)] public class AjaxWCFService { // Add [WebGet] attribute to use HTTP GET [OperationContract] public String SayHello(String name) { return String.Format("Ajax, Hello {0}", name); } // Add more operations here and mark them with [OperationContract] }
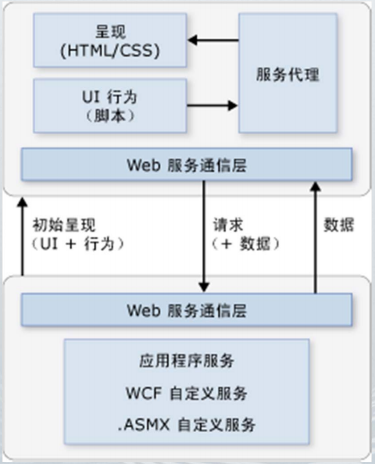
什么是Web Service
他不是技术,他是一套技术规范、标准的集合,就是我们常说的Web服务。同样他不是asp.net web service,后者是由微软开发的一个支持web服务规范的一个框架,其内嵌至asp.net中。我们看一下下面的图应该可以理解web service了。
什么是REST
Representational State Transfer,是一种架构,而不是一个规范。是一种典型的client-server架构,REST=3老的Web规范+3新的规范,3老是指客户-服务器,无状态性,缓存。3新指统一接口,分层系统,按需代码。
什么是RESTful Web服务
也称RESTful Web API,是使用HTTP Verb和REST设计原则的Web服务,那么什么是REST的设计原则呢,有人总结为四大原则:

原则一: 使用HTTP的方法进行资源访问 1) 使用HTTP POST方法去创建 资源 2) 使用HTTP GET方法去读取 资源 3) 使用HTTP PUT 方法去更新 资源 4) 使用HTTP DELETE方法去删除 资源 原则二: 使用无状态/无会话的服务设计 很长时间以来,人们采用有状态的服务设计从而在客户端与服务端的多次交互中维护一定的上下文。表格分页应用就是最常见的一个例子,通常程序员在HTTP Session中保持当前页的变量currentPage,当用户用地址http://www.foo.com/articles?action=nextPage来获取下一页的时候,服务可以根据currentPage获取下一页的数据,即返回第currentPage+1页的数据。 然而,有状态的设计使得程序很难随着工作负载的增加而进行伸缩。比如某个服务实例拥有10000个会话的状态,则通常很难通过增加服务实例来分担其工作负载:工作负载被锁定了! 反之,如果程序被设计成一个无状态的,则可以自由增加服务实例,并且在这些实例之间平衡负载,从而使得服务具有较好的伸缩性,这在大规模分布式系统中尤其重要!! 原则三: 用目录结构风格的URL设计来表示资源 用清晰的URL路径表示资源可以使客户端更容易理解和操作资源。URL可以被看作是一种自我解释的接口,不需要太多解释就可以让人明白该URL指向的是什么资源以及如何获得相关的资源。 下面是几个例子,供大家参考: http://www.foo.com/research/articles/{article_title} http://www.foo.com/research/articles/{year}/{month}/{day}/{article_title} 原则四: 使用XML或JSON来传输数据 服务和请求的消息数据中包含了对于资源的属性的描述,服务应该采取结构良好并且易于阅读的方式来描述资源。资源可能是数据库中的某个记录集合或者是一个具体的记录,可以是文档,甚至可以是数据中心的服务器。XML、JSON都是结构良好的语言,并且适于阅读。我个人比较偏好使用JSON,更加简洁。下面是两个XML和JSON消息的例子,供大家参考。 JSON Example: { "menu": { "id": "file", "value": "File", "popup": { "menuitem": [ {"value": "New", "onclick": "CreateNewDoc()"}, {"value": "Open", "onclick": "OpenDoc()"}, {"value": "Close", "onclick": "CloseDoc()"} ] } } } 相应的XML: <menu id="file" value="File"> <popup> <menuitem value="New" onclick="CreateNewDoc()" /> <menuitem value="Open" onclick="OpenDoc()" /> <menuitem value="Close" onclick="CloseDoc()" /> </popup> </menu>
创建支持Ajax的WCF应该怎么做

<system.serviceModel> <serviceHostingEnvironment aspNetCompatibilityEnabled="true" /> </system.serviceModel>
详细原因可以查看msdn的说法.
什么是安全,WCF的安全解决方案
三方面来看,一是保证服务端安全,二是保证客户端安全和保证数据安全。服务端安全就是指客户端有效,免于攻击。 客户端安全就是指证服务端有效,不会欺骗。数据安全指数据的安全,完整,有效。


<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <configuration> <system.web> <compilation debug="true" /> </system.web> <!-- When deploying the service library project, the content of the config file must be added to the host's app.config file. System.Configuration does not support config files for libraries. --> <system.serviceModel> <services> <service behaviorConfiguration="WCFService.WCFServiceBehavior" name="WCFService.WCFService"> <endpoint address="WCFService" binding="wsHttpBinding" bindingConfiguration="MessageAndUserName" contract="WCFService.IWCFService"> </endpoint> <endpoint address="mex" binding="mexHttpBinding" contract="IMetadataExchange" /> <host> <baseAddresses> <add baseAddress="http://localhost:8001/"/> </baseAddresses> </host> </service> </services> <behaviors> <serviceBehaviors> <behavior name="WCFService.WCFServiceBehavior"> <serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true" /> <serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults="false" /> <serviceCredentials> <serviceCertificate x509FindType="FindBySubjectName" findValue="WCFServerPK" storeLocation="LocalMachine"/> <clientCertificate > <authentication certificateValidationMode="None" /> </clientCertificate> <userNameAuthentication userNamePasswordValidationMode="Custom" customUserNamePasswordValidatorType="WCFService.MyUserNamePasswordValidator,WCFService" /> </serviceCredentials> </behavior> </serviceBehaviors> </behaviors> <bindings> <wsHttpBinding> <binding name="MessageAndUserName" > <security mode="Message"> <transport clientCredentialType="None"/> <message clientCredentialType="UserName"/> </security> </binding> </wsHttpBinding> </bindings> </system.serviceModel> </configuration>

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <configuration> <system.serviceModel> <bindings> <wsHttpBinding> <binding name="WSHttpBinding_IWCFService" closeTimeout="00:01:00" openTimeout="00:01:00" receiveTimeout="00:10:00" sendTimeout="00:01:00" bypassProxyOnLocal="false" transactionFlow="false" hostNameComparisonMode="StrongWildcard" maxBufferPoolSize="524288" maxReceivedMessageSize="65536" messageEncoding="Text" textEncoding="utf-8" useDefaultWebProxy="true" allowCookies="false"> <readerQuotas maxDepth="32" maxStringContentLength="8192" maxArrayLength="16384" maxBytesPerRead="4096" maxNameTableCharCount="16384" /> <reliableSession ordered="true" inactivityTimeout="00:10:00" enabled="false" /> <security mode="Message"> <transport clientCredentialType="Windows" proxyCredentialType="None" realm=""> <extendedProtectionPolicy policyEnforcement="Never" /> </transport> <message clientCredentialType="UserName" negotiateServiceCredential="true" algorithmSuite="Default" establishSecurityContext="true" /> </security> </binding> </wsHttpBinding> </bindings> <client> <endpoint address="http://localhost:8001/WCFService" binding="wsHttpBinding" bindingConfiguration="WSHttpBinding_IWCFService" contract="ClientProxy.IWCFService" name="WSHttpBinding_IWCFService"> <identity> <certificate encodedValue="AwAAAAEAAAAUAAAAaHVNCjRUhKcLhdiQj6OKqoQuua8gAAAAAQAAAPgBAAAwggH0MIIBYaADAgECAhBxCLtwjs80j01ASx27FgBgMAkGBSsOAwIdBQAwFjEUMBIGA1UEAxMLV0NGU2VydmVyUEswHhcNMTAxMDE2MDQyNTMyWhcNMzkxMjMxMjM1OTU5WjAWMRQwEgYDVQQDEwtXQ0ZTZXJ2ZXJQSzCBnzANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOBjQAwgYkCgYEAyKwsLLhGG1PlU4jm6Kpa045GH7ZOWX1UaPNLezMkUpDNnoBeeGXrN1Rs/14t+eDP272camnbU+2NQl8ejkIdYxdZ38Dz7FnOMbBxkJqLRz1DPBKIrb0Qkyfip72I+XGcRZG+dyNA779pnNMlAtkAAFAT8eJd2aosoO4OizOs+cECAwEAAaNLMEkwRwYDVR0BBEAwPoAQqY66whxaxoF8zts5rjLnEqEYMBYxFDASBgNVBAMTC1dDRlNlcnZlclBLghBxCLtwjs80j01ASx27FgBgMAkGBSsOAwIdBQADgYEAd/TDzhMnDxOYf2aeWZtGPTZxSN56+uNPCMZRG1eH6MTMGlt6yuiKR1xfHpttsZfjk80vxrKOVuyezaljyJ8zN9wb5hjF2j7OO0DUlG+hpNT3exDGN+/VAbxn2MSwZEyDziTCiz77P+StXoML+b1qMAWZHNM1gjCxbd7T+hbZGPM=" /> </identity> </endpoint> </client> <behaviors> <endpointBehaviors> <behavior name="clientBehavior"> <clientCredentials> <serviceCertificate> <authentication certificateValidationMode="None" /> </serviceCertificate> </clientCredentials> </behavior> </endpointBehaviors> </behaviors> </system.serviceModel> </configuration>
这里有个WCF配置文件的注释版本

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <configuration> <system.ServiceModel> <!-- services 元素包含应用中驻留的所有service的配置要求 --> <services> <!-- 每个服务的配置 属性说明: name - 指定这个service配置是针对的那个服务,为一个实现了某些Contract的服务类的完全限定名 (名称空间.类型名),ServiceHost载入一个服务后,会到配置文件中的<services>下找有没有 name属性跟服务匹配的<service>的配置 behaviorConfiguration - 指定在<serviceBehaviors>下的一个<behavior>的name,这个特定<behavior> 给这个service制定了一些行为,比如服务是否允许身份模拟--> <service name="名称空间.类型名" behaviorConfiguration="behavior名"> <host> <baseAddresses> <!-- 在此可以定义每种传输协议的baseAddress,用于跟使用同样传输协议Endpoint定义的相对地 址组成完整的地址,但是每种传输协议只能定义一个baseAddress。HTTP的baseAddress同时是service 对外发布服务说明页面的URL--> <add baseAddress="http://address" /> </baseAddresses> <timeouts></timeouts> </host> <!-- 每个服务可以有多个Endpoint,下面<endpoint>元素对每个Endpoint分别进行配置 属性说明: address - 指定这个Endpoint对外的URI,这个URI可以是个绝对地址,也可以是个相对于baseAddress的 相对地址。如果此属性为空,则这个Endpoint的地址就是baseAddress binding - 指定这个Endpoint使用的binding,这个banding可以是系统预定义的9个binding之一, 比如是basicHttpBinding,也可以是自定义的customBinding。binding决定了通讯的类型、 安全、如何编码、是否基于session、是否基于事务等等 contract - 指定这个Endpoint对应的Contract的全限定名(名称空间.类型名),这个Contract应该被 service元素的name指定的那个service实现 bindingConfiguration - 指定一个binding的配置名称,跟<bindings>下面同类<binding>的name匹配 behaviorConfiguration - 指定这个endpoint的behavior,指向<behaviors>下的同样配置名称的<endpointBehaviors> name - Endpoint的名称,可选属性,每个Contract都可以有多个Endpoint,但是每个Contract对应的 多个Endpoint名必须是唯一的--> <endpoint address="URI" binding="basicHttpBinding" contract="Contract全限定名" bindingConfiguration="binding名" behaviorConfiguration="String" name=""> <!-- 用户定义的xml元素集合,一般用作SOAP的header内容--> <headers> <!-- 任何xml内容 --> </headers> </endpoint> </service> </services> <bindings> <!-- 指定一个或多个系统预定义的binding,比如<basicHttpBinding>,当然也可以指定自定义的customBinding, 然后在某个指定的binding下建立一个或多个配置,以便被Endpoint来使用这些配置 --> <basicHttpBinding> <!-- 某一类的binding的下面可能有多个配置,binding元素的name属性标识某个binding--> <binding name="binding名"> </binding> </basicHttpBinding> </bindings> <!-- 定义service和Endpiont行为--> <behaviors> <!-- 定义service的行为--> <serviceBehaviors> <!-- 一个或多个系统提供的或定制的behavior元素 属性说明: name - 一个behavior唯一标识,<service>元素下<endpoint>的behaviorConfiguration属性指向这个name--> <behavior name="此Behavior名称"> <!-- 指定service元数据发布和相关信息 属性说明: httpGetEnabled - bool类型的值,表示是否允许通过HTTP的get方法获取sevice的WSDL元数据 httpGetUrl - 如果httpGetEnabled为true,这个属性指示使用哪个URL地址发布服务的WSDL, 如果这个属性没有设置,则使用服务的HTTP类型的baseAddress后面加上?WSDL--> <serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true" httpGetUrl="http://URI:port/address" /> <!--指定验证服务端的凭据--> <serviceCredentials> <!--指定服务端的证书 属性说明: storeName - 证书的存储区,可能值为:AddressBook,AuthRoot,CertificateAuthority Disallowed,My,Root,TrustedPeople,TrustedPublisher storeLocation - 证书存储位置,可能值为:CurrentUser,LocalMachine x509FindType - 查找证书的方式,可能的值:FindBySubjectName,FindByThumbPrint,FindByIssuerName...... findValue - 对应查找方式的要查找证书的值 --> <serviceCertificate storeName="存储区" storeLocation="存储位置" x509FindType="FindBySubjectName" findValue="server1" /> </serviceCredentials> </behavior> </serviceBehaviors> <!-- 定义Endpiont的行为--> <endpointBehaviors> <!-- 一个或多个系统提供的或定制的behavior元素 属性说明: name - 一个behavior唯一标识,<client>元素下<endpoint>的behaviorConfiguration属性指向这个name--> <behavior name="此Behavior名称"> <!--指定客户端的凭据--> <clientCredentials> <!--指定客户端的证书 属性说明: storeName - 证书的存储区,可能值为:AddressBook,AuthRoot,CertificateAuthority Disallowed,My,Root,TrustedPeople,TrustedPublisher storeLocation - 证书存储位置,可能值为:CurrentUser,LocalMachine x509FindType - 查找证书的方式,可能的值:FindBySubjectName,FindByThumbPrint,FindByIssuerName...... findValue - 对应查找方式的要查找证书的值 --> <clientCertificate storeName="存储区" storeLocation="存储位置" x509FindType="FindBySubjectName" findValue="Client1" /> <serviceCertificate> <authentication certificateValidationMode="None" /> </serviceCertificate> </clientCredentials> </behavior> </endpointBehaviors> </behaviors> <!-- 包含客户端跟服务端连接使用到的Endpoint的配置 --> <client> <!-- 每个客户端Endpoint设置 属性说明: address - 对应到服务端这个Endpoint的address binding - 指定这个Endpoint使用的binding,这个banding可以是系统预定义的9个binding之一, 比如是basicHttpBinding contract - 指定这个Endpoint对应的Contract的全限定名(名称空间.类型名) name - Endpoint的配置名,客户端代理类的构造方法中的endpointConfigurationName对应到这个name bindingConfiguration - 指定客户端binding的具体设置,指向<bindings>元素下同类型binding的name behaviorConfiguration - 指定这个endpoint的behavior,指向<behaviors>下的同样配置名称的<endpointBehaviors>--> <endpoint address="URI" binding="basicHttpBinding" bindingConfiguration="binding名" behaviorConfiguration="String" contract="Contract全限定名" name="endpoint配置名" > <!-- 用于客户端验证服务端身份,可选以下一种方式验证服务端--> <identity> <userPrincipalName></userPrincipalName> <servicePrincipalName></servicePrincipalName> <!--如果客户端验证是windows,这里指定DNS名;如果是Certificate,这里指定证书subject name--> <dns></dns> <rsa></rsa> <!--指定服务端证书的公钥 属性说明: encodedValue - 服务端证书的公钥的base64编码,用于加密用户名和密码--> <certificate encodedValue=""></certificate> <!-- 用户指定在客户端证书存储区内的服务端证书 属性说明: storeName - 证书的存储区,可能值为:AddressBook,AuthRoot,CertificateAuthority Disallowed,My,Root,TrustedPeople,TrustedPublisher storeLocation - 证书存储位置,可能值为:CurrentUser,LocalMachine x509FindType - 查找证书的方式,可能的值:FindBySubjectName,FindByThumbPrint,FindByIssuerName...... findValue - 对应查找方式的要查找证书的值 --> <certificateReference storeName="存储区" storeLocation="存储位置" x509FindType="FindBySubjectName" findValue="Client1" /> </identity> </endpoint> </client> </system.ServiceModel> </configuration>
