abstract:
- V const & a 加速
F. Mirror
题意
问题:
有n个人在y=0的平面上(及xoz平面)。z=0平面上有一面镜子(边平行于坐标轴)。z=a平面上有q个点(保证a大于所有人的z坐标)。 所有人面朝镜子,且在镜子和q个点之间(即每个人的z坐标保证0<z<a)。
问对于某个点,让所有人能够通过镜子看到那个点的镜子的最小面积。
题解
三维几何+镜像+凸包
首先考虑镜面,我们可以通过(初中科学的)镜面反射原理,关于z=0做出z=a的对称平面z=-a。问题就变成了n个人看z=-a上的某个点。(下图绿点是人,红点是询问点)

然后观察,镜子的高和宽是独立的。 于是我们分别求它们的最大值即可。
求高比较简单,我们朝-x方向看yoz平面。通过把每个人跟点Q的像Q‘相连,我们发现离Q’z轴距离最近的人对应着镜子的下边界,最远的人对应着上边界,通过维护所有人z坐标的max_z&min_z以及相似三角形可以直接求出两个边界,复杂度为O(1)。
我们用同样的方法,朝-y方向看xoz平面。 通过把每个人跟点Q的像Q‘相连,我们发现,左右边界并不对应着最左边与最右边的人。而且随着询问点的变化,对应着左右边界的人也在变化。
如果我们暴力的找对应左右边界的人,复杂度为n*q ,不可行。
我们发现,对应着左右边界的人虽然随着询问点变化,但他们都在凸包上(如下图)。
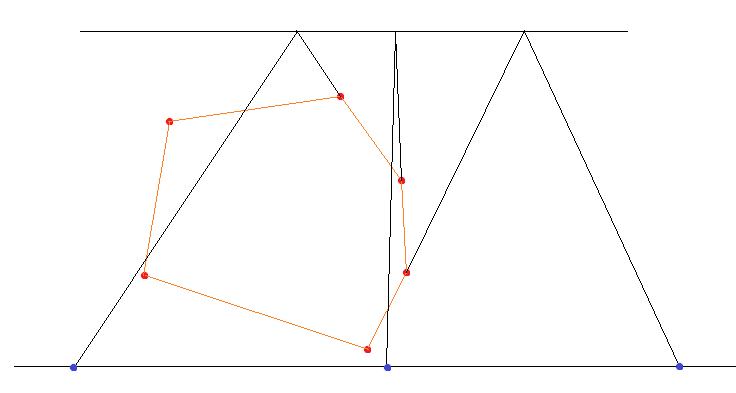
更进一步,如果我们将询问点按照x坐标排序,随着询问的x坐标增加,左右边界的人在凸包上的变化是顺时针旋转的。(考虑你从左到右观察一个正前方的凸包)
于是我们就能够通过一个nlogn的凸包预处理然后O(1)地回答每个询问,复杂度为O(q+nlogn)
剩下的是实现”从左到右看凸包时凸包左右边界的顺时针更新“。
首先是写out,in函数(右手法则,向外转就是逆时针),用来逆时针、顺时针遍历凸包上的点。因为极角排序凸包存的点是逆时针的(极角排序的那个角是与y轴的逆时针夹角。),所以out就是++。
先找到凸包的下上顶点,作为初始的左右边界的对应点。
然后根据x坐标从小到大枚举询问点Q。
对于每个Q,不断顺时针更新左边界对应的人,直到他与Q的连线在他凸包上顺时针的下一个人与Q的连线的外面(直观上显然正确)。 右边界同理。
某些编辑器比如codeforces不能混用iostream与stdio
代码
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
#define debug(x) cerr<<#x<<" = "<<(x)<<endl
#define rep(i,j,k) for(int i = (int)j;i <= (int)k;i ++)
#define FAST_IO ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr)
//#define double long long
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 5;
const db eps = 1e-7;
int n, q, a;
long double ans[maxn];
bool eq(double a, double b) { return abs(a - b) <= eps; }
struct V {
double x, y;
V(double a = 0.0, double b = 0.0) :x(a), y(b) {}
void sc() { scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y); }
double operator |(V const &o)const {
return x * o.y - o.x * y;
}
bool operator <(V const &o)const {
if (eq(x, o.x))return y < o.y;
return x < o.x;
}
V operator -(V const &o)const { return V(x - o.x, y - o.y); }
void pr() { printf("%lf %lf
", x, y); }
}st[maxn];
pair<V, int> Q[maxn];
bool cmpr(V const &a, V const &b) {
V v1 = a - st[0], v2 = b - st[0];
return (v1 | v2) < -eps;
}
vector<V> ch;
void getCH() {
sort(st + 1, st + n, cmpr);
ch.push_back(st[0]);
rep(i, 1, n-1) {
while (ch.size() > 1 && (st[i] - ch.back() | ch.back() - ch[ch.size() - 2]) < eps)ch.pop_back();
ch.push_back(st[i]);
}
}
int out(int x) { return x ? x - 1 : ch.size() - 1; }
int in(int x) { return x + 1 == (int)ch.size() ? 0 : x + 1; }
double getx(double xs, double z, double xq) {
return xs + z / (z + a) * (xq - xs);
}
int main() {
//FAST_IO;
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
cin >> n >> a;
rep(i, 0, n - 1)st[i].sc();
db zmn = st[0].y, zmx = st[0].y;
rep(i, 0, n - 1) {
zmn = min(zmn, st[i].y);
zmx = max(zmx, st[i].y);
}
rep(i, 0, n - 1)st[i].y = a - st[i].y;
sort(st, st + n);
ch.clear();
getCH();
cin >> q;
ll qx = 0, qy = 0;
rep(i, 1, q) {
Q[i].first.sc();
Q[i].second = i;
}
sort(Q + 1, Q + 1 + q);
int lp = 0, rp = 0;
rep(i, 0, ch.size() - 1)ch[i].y = a - ch[i].y;
while (ch[in(rp)].y < ch[rp].y)rp = in(rp);
while (ch[out(lp)].y > ch[lp].y)lp = out(lp);
rep(i, 1, q) {
while (true) {
int ni = in(lp);
if (getx(ch[ni].x, ch[ni].y, Q[i].first.x) < getx(ch[lp].x, ch[lp].y, Q[i].first.x))lp = ni;
else break;
}
while (true) {
int ni = in(rp);
if (getx(ch[ni].x, ch[ni].y, Q[i].first.x) > getx(ch[rp].x, ch[rp].y, Q[i].first.x))rp = ni;
else break;
}
double x = abs(getx(ch[rp].x, ch[rp].y, Q[i].first.x) - getx(ch[lp].x, ch[lp].y, Q[i].first.x));
double h = getx(0, zmx, Q[i].first.y) - getx(0, zmn, Q[i].first.y);
ans[Q[i].second] = (long double)x * h;
//printf("%.20lf
", x*h);
}
rep(i, 1, q)printf("%.20lf
", (double)ans[i]);
}
cin >> n;
}
/*
1
3 3
-2 1
7 2
3 1
3
2 5
-2 4
8 10
*/
心路历程
当有两个以上的bug时你就炸了
wa0:FAST_IO codeforces以用就wa
wa1:输出rep(i,1,q) not rep(i,1,n)//最后才发现
wa2:凸包板子里面下标从0开始。
Problem F Fair Chocolate-Cutting
题意
来源:ICPC Asia Regional Contest, Yokohama, 2018–12–09
让你求所有平分凸多边形的线段中最长和最短的那两条。
输出它们的长度。
题解
证明题+硬核平面几何
我们有结论:(目前不会证明)
某合法(平分多边形的)线段的端点在顶点上时一定是局部最长或最短的。
除此之外,当某合法线段垂直于任意“外角”平分线时,也是局部最短的
于是问题就转化成
1.对于每个顶点,找到过它的合法线段。

2.对于每个角(跳过一些线段的“相邻”两条线段的延长线交出的角),找到垂直它的平分线的合法线段。注意特判掉角不存在的情况,即两边平行。
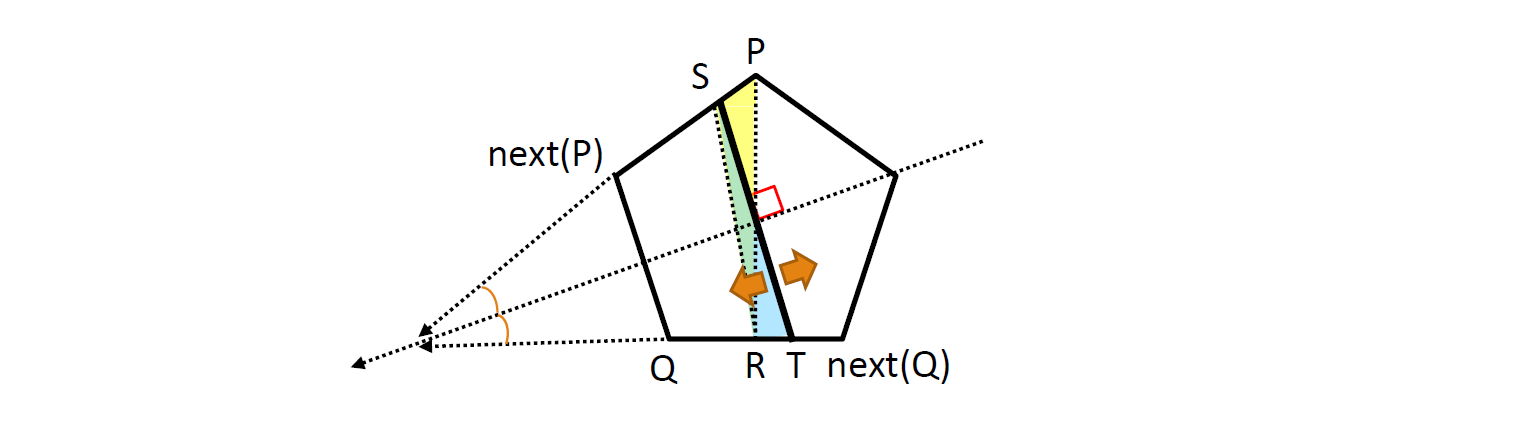
对于1,只要从该顶点开始不断逆时针扫顶点,直到刚刚超过1/2的总面积。然后把上一个三角形分割一下。
对于2,直接用平面几何知识以及三角函数求解
代码
#include<complex>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iomanip>
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
typedef long double ld;
using namespace std;
typedef complex<double> point;
#define rep(i,j,k) for(int i = (int)j;i <= (int)k;i ++)
#define F(i,N)for(int i = 0;i < (int)(N);i ++)
#define Decimal fixed<<setprecision(20)
#define PB push_back
#define EB emplace_back
#define X real();
#define Y imag();
#define curr(PP,i) PP[i]
#define next(PP,i) PP[(i+1)%PP.size()]
#define diff(PP,i) (next(PP,i)-curr(PP,i))
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double INF = 1e18;
int n;
vector<point> V;
double sumS,nowS,mx,mn;
double cross(const point& a, const point& b) {
return imag(conj(a)*b);
}
double dot(const point& a, const point& b) {
return real(conj(a)*b);
}
double area(const vector<point>& p) {
double A = 0;
F(i, p.size()) A += cross(curr(p, i), next(p, i));
return A / 2.;
}
double triArea(int a, int b, int c) {
a %= n, b %= n, c %= n;
if (a == b || b == c || c == a)return 0;
vector<point> tmp = { V[a],V[b],V[c] };
return area(tmp);
}
double distancePP(point const &a, point const &b) {
return abs(a - b);
}
//seg
struct segment :public vector<point> {
segment(const point &a, const point &b) {
push_back(a); push_back(b);
}
};
point crosspoint(segment const &l,segment const &m) {
double A = cross(l[1] - l[0], m[1] - m[0]);
double B = cross(l[1] - l[0], l[1] - m[0]);
if (abs(A) < eps&&abs(B) < eps)return m[0];//same line
if (abs(A) < eps)return point(INF, INF);//parallel
return m[0] + B / A*(m[1] - m[0]);
}
double angle(const point& a, const point& b) {
auto tmp = abs(arg(a) - arg(b));
return min(tmp, 2 * PI - tmp);
}
double angle(const segment &s1, const segment &s2) {
return angle(s1[1] - s1[0], s2[1] - s2[0]);
}
point projection(const segment &l, const point &p) {
double t = dot(p - l[0], l[0] - l[1]) / norm(l[0] - l[1]);
return l[0] + t * (l[0] - l[1]);
}
double distanceLP(const segment &l, const point &p) {
return abs(p - projection(l, p));
}
bool intersectSP(const segment &s,const point &p) {//point on seg
return abs(s[0] - p) + abs(s[1] - p) - abs(s[1] - s[0]) < eps;
}
double seica(int a,int b) {
a %= n; b %= n;
vector<point> tmp;
int i = a;
while (1) {
tmp.EB(V[i]);
if (i == b)break;
i = (i + 1) % n;
}
if (tmp.size() < 3)return 0;
else return area(tmp);
}
void checkV(int p,int q) {
p %= n; q %= n;
double remain = (sumS / 2) - nowS;
double rate = remain / triArea(p, q, q + 1);
point tmp = V[q] + rate * (V[(q + 1) % n] - V[q]);
mn = min(mn, distancePP(V[p], tmp));
mx = max(mx, distancePP(V[p], tmp));
}
void checkSeg(int p, int q) {
p %= n, q %= n;
nowS -= triArea(p, p + 1, q);
segment a(V[(p + 1) % n], V[p]);
segment b(V[(q) % n], V[(q + 1) % n]);
point crossp = crosspoint(a, b);
if (crossp == point(INF, INF)) {
double sqS = area({ V[p],V[(p + 1) % n],V[q],V[(q + 1) % n] });
if (nowS + sqS < sumS / 2 + eps)return;
bool flag = 0;
if (intersectSP(b, projection(b, a[0])) || intersectSP(b, projection(b, a[1])))flag = 1;
if (intersectSP(a, projection(a, b[0])) || intersectSP(a, projection(a, b[1])))flag = 1;
if (!flag)return;
mn = min(mn, distanceLP(b, a[0]));
return;
}
double tmpS=0;
if (distancePP(crossp, a[0]) > distancePP(crossp, a[1]) + eps) {
tmpS = seica(q + 1, p);
swap(a[0], a[1]);
swap(b[0], b[1]);
}
else {
tmpS= seica(p + 1, q);
}
double theta = angle(a, b);
double T = distancePP(crossp, a[0])*distancePP(crossp, b[0])*sin(theta) / 2;
double leg = (2 * (T - tmpS) + sumS) / sin(theta);
bool flag = 0;
if (leg > distancePP(a[1], crossp)*distancePP(a[1], crossp) + eps)flag = 1;
if (leg + eps < distancePP(a[0], crossp)*distancePP(a[0], crossp))flag = 1;
if (leg > distancePP(b[1], crossp)*distancePP(b[1], crossp) + eps)flag = 1;
if (leg + eps < distancePP(b[0], crossp)*distancePP(b[0], crossp))flag = 1;
if (flag)return;
mn = min(mn, 2*sqrt(leg)*sin(theta / 2));
}
int main() {
mx = 0;
mn = 1e18;
cin >> n;
F(i, n) {
db a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
V.EB(a, b);
}
int q = 1;
sumS = area(V);
F(i, n) {
while (nowS + triArea(i, q, q + 1) < sumS / 2 + eps) {
nowS += triArea(i, q, q + 1);
q++;
}
checkV(i,q);
checkSeg(i,q);
}
cout << Decimal << mn << endl;
cout << Decimal << mx << endl;
cin >> n;
return 0;
}
/*
4
0 0
10 0
10 10
0 10
3
0 0
6 0
3 10
*/
心路历程
关键是不会证明。
复数大法好啊!!!(其实还是慢5倍??下面那题)
B. Ali and Wi-Fi
题意
来源ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest, Tishreen Collegiate Programming Contest
100个圆,每个圆代表wifi覆盖区域,每个wifi有一个网速。你最多可以连入m个WiFi,网速为这些wifi的总和。
问你最大的网速是多少。
题解
想法题+圆模板
我们知道n个圆最多可以把平面分成n^2-n+2个区域(递推进阶题233)。所以可以考虑遍历每个区域,计算它被哪些圆。。。
我们发现维护一块区域很难,而要取最大的m个更难考虑。
于是考虑维护圆与圆的交点。我们发现每个区域都是圆交出来的,i.e.交点都在区域的边界上。
于是我们可以枚举交点来代替枚举区域,显然交点个数也是n^2级别的。(考虑圆内含的情况,所以要把每个圆心也枚举一遍)
这样枚举的另一个好处是可以很简单地处理m:
枚举每个交点,计算有几个圆包含它。然后直接在这些圆中取最大的m个。
复杂度为n^2nnlogn。
如果我们用优先队列来维护最大的m个,那么复杂度里可以去掉一个n。
代码
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<iomanip>
#include<complex>
using namespace std;
#define debug(x) cerr<<#x<<" = "<<(x)<<endl
#define rep(i,j,k) for(int i = (int)j;i <= (int)k;i ++)
#define F(i,N)for(int i = 0;i < (int)(N);i ++)
#define FAST_IO ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr)
#define EB emplace_back
#define Decimal fixed<<setprecision(20)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define INF 1000000000
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
typedef long double ld;
#define double long double
//typedef complex<double> point;
#define X real()
#define Y imag()
const int maxn = 2e5 + 5;
const db eps = 1e-10;
const db PI = acos(-1.);
int dcmp(ld x)
{
if (fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
return x < 0 ? -1 : 1;
}
struct V {
ld x, y;
V() {}
void sc() { scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y); }
V(double a, double b) : x(a), y(b) { }
V operator+(const V &o)const { return V(x + o.x, y + o.y); }
V operator-(const V &o)const { return V(x - o.x, y - o.y); }
double L() { return sqrt(x * x + y * y); }
V N() {
double l = L();
return V(x / l, y / l);
}
V rot(double th) { return V(x * cos(th) - y * sin(th), x * sin(th) + y * cos(th)); }
V operator*(double z) { return V(x * z, y * z); }
double operator*(const V &o) const { return x * o.x + y * o.y; }
double operator|(const V &o) const { return x * o.y - o.x * y; }
double operator==(const V &o) const { return dcmp(x - o.x) == 0 && dcmp(y - o.y) == 0; }
void pr() { printf("%lf %lf
", x, y); }
};
vector<V> p;
typedef V point;
V conj(V p) { return V(p.x, -p.y); }
double arg(V p) { return atan2(p.y, p.x); }
double norm(V p) { return p.L()*p.L(); }
double abs(V p) { return p.L(); }
double cross(const point& a, const point& b) {
return imag(conj(a)*b);
}
double dot(const point& a, const point& b) {
return real(conj(a)*b);
}
struct circle
{
point c;
ld r, v;
circle() {}
circle(point c, ld r, ld v) :c(c), r(r), v(v) {}
inline point pt(double a)
{
return point(c.x + cos(a)*r, c.y + sin(a)*r);
}
};
int getCircleCircleIntersection(circle C1, circle C2, point &t1, point &t2)
{
ld d = abs(C1.c - C2.c);
if (dcmp(d) == 0)
{
if (dcmp(C1.r - C2.r) == 0) return -1;// same cir
return 0;// include
}
if (dcmp(C1.r + C2.r - d) < 0) return 0;// disjoint
if (dcmp(fabs(C1.r - C2.r) - d) > 0) return 0;// include
ld a = arg(C2.c - C1.c);
ld da = acos((C1.r*C1.r + d * d - C2.r*C2.r) / (2 * C1.r*d));
point p1 = C1.pt(a - da), p2 = C1.pt(a + da);
t1 = p1;
if (p1 == p2) return 1;
t2 = p2;
return 2;
}
vector<circle> A;
circle aa[105];
vector<point> P;
point pp[10105];
priority_queue<int > Q;
int ans, sum;
int n, m, tot;
int main() {
FAST_IO;
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
tot = ans = 0;
cin >> n >> m;
F(i, n) {
cin >> aa[i].c.x >> aa[i].c.y >> aa[i].r >> aa[i].v;
}
F(i, n) {
rep(j, i + 1, n - 1) {
point t1, t2;
int num = getCircleCircleIntersection(aa[i], aa[j], t1, t2);
if (num == 1) {
pp[tot++] = t1;
}
else if (num == 2) {
pp[tot++] = t1;
pp[tot++] = t2;
}
}
}
F(i, n)pp[tot++] = aa[i].c;
F(j, tot) {
F(i, n) {
if (dcmp(abs(pp[j] - aa[i].c) - aa[i].r) <= 0) {
Q.push(-aa[i].v);
if (Q.size() > m)Q.pop();
}
}
sum = 0;
while (!Q.empty()) {
sum -= Q.top();
Q.pop();
}
ans = max(ans, sum);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
cin >> t;
return 0;
}
心路历程
没初始化。
瞎debug发现long double int求和会爆精度。
priority_Q太久没用,忘记pop是从头上弹出的了orz。
vector 和对于1e6的数据其实只比数组慢10ms。