最近一直在看数据结构与算法,下面是对有线性结构的栈与队列的总结:
| 栈相关的内容 |
定义:栈是限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除操作的线性表。(后进先出的线性表)
操作:在可以插入与删除的一端称为栈顶,另外一端称为栈底, 栈的插入称为进栈,栈的删除称为出栈。
图解:A,B,C依次入栈,然后依次出栈得到C,B,A 如图所示:
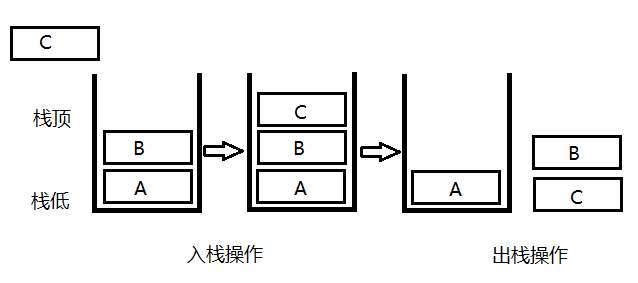
栈的存储结构:栈通常有顺序栈和链栈两种存储结构
1. 顺序存储结构:通过数组实现,只准栈顶进出元素,不过由于数组的大小是事先确定的,而且需要连续的空间,当容量不过时需要手动扩展。
java实现代码:
public class Stack {
private int maxSize; // size of stack array
private double[] stackArray;
private int top; // top of stack
public Stack(int s) // constructor
{
maxSize = s; // set array size
stackArray = new double[maxSize]; // create array
top = -1; // no items yet
}
public void push(double j) // put item on top of stack
{
stackArray[++top] = j; // increment top, insert item
}
public double pop() // take item from top of stack
{
return stackArray[top--]; // access item, decrement top
}
public double peek() // peek at top of stack
{
return stackArray[top];
}
public boolean isEmpty() // true if stack is empty
{
return (top == -1);
}
public boolean isFull() // true if stack is full
{
return (top == maxSize-1);
}
}
class StackApp{
public static void main(String[] args){
Stack theStack = new Stack(10); // make new stack
theStack.push(20); // push items onto stack
theStack.push(40);
theStack.push(60);
theStack.push(80);
while( !theStack.isEmpty() ){ // delete item from stack
double value = theStack.pop();
System.out.print(value); // display it
System.out.print(" ");
} // end while
System.out.println("");
}
}
//the result:80.0 60.0 40.0 20.0
2.链式存储结构:通过链表实现,最大的优点是存储空间不固定可以伸缩。
class Link{
public double dData; // data item
public Link next; // next link in list
public Link(double dd){// constructor
dData = dd;
}
public void displayLink(){ // display ourself
System.out.print(dData + " ");
}
} // end class Link
class LinkList{
private Link first; // ref to first item on list
public LinkList(){ // constructor
first = null;
} // no items on list yet
public boolean isEmpty(){ // true if list is empty
return (first==null);
}
public void insertFirst(double dd){ // insert at start of list
Link newLink = new Link(dd); // make new link
newLink.next = first; // newLink --> old first
first = newLink; // first --> newLink
}
public double deleteFirst(){ // delete first item
Link temp = first; // save reference to link
first = first.next; // delete it: first-->old next
return temp.dData; // return deleted link
}
public void displayList(){
Link current = first; // start at beginning of list
while(current != null) // until end of list,
{
current.displayLink(); // print data
current = current.next; // move to next link
}
System.out.println("");
}
} // end class LinkList
class LinkStack
{
private LinkList theList;
public LinkStack(){ // constructor
theList = new LinkList();
}
public void push(double j){ // put item on top of stack
theList.insertFirst(j);
}
public double pop(){ // take item from top of stack
return theList.deleteFirst();
}
public boolean isEmpty(){ // true if stack is empty
return ( theList.isEmpty() );
}
public void displayStack(){
System.out.print("Stack (top-->bottom): ");
theList.displayList();
}
} // end class LinkStack
class LinkStackApp
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
LinkStack theStack = new LinkStack(); // make stack
theStack.push(20); // push items
theStack.push(40);
theStack.displayStack(); // display stack
theStack.push(60); // push items
theStack.push(80);
theStack.displayStack(); // display stack
theStack.pop(); // pop items
theStack.pop();
theStack.displayStack(); // display stack
} // end main()
}
//the result:
//Stack (top-->bottom): 40.0 20.0
//Stack (top-->bottom): 80.0 60.0 40.0 20.0
//Stack (top-->bottom): 40.0 20.0
| 队列相关的内容 |
定义:只允许在一端进行插入操作,而在另一端进行删除操作的线性表。(先进先出的线性表)
操作:可以插入的一端称为队尾,可以删除的一端称为队头,栈的插入称为入队,栈的删除称为出队。
图解:
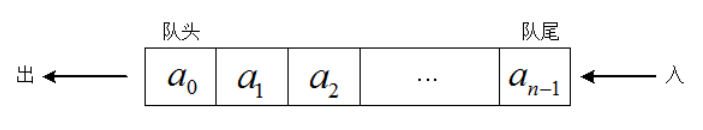
队列的存储结构:队列通常也有顺序和链式两种存储结构
1. 顺序存储结构:
我们在队尾进行插入,在队头进行删除,因此必须保证队头元素在数组下标为0的位置处,故要将队列中的每个元素向前移动一个位置
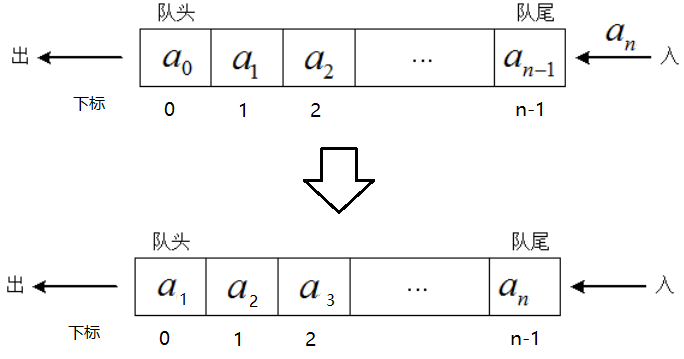
此时,会有涉及到一个问题,即性能问题,在队尾插入一个元素,不需要移动任何元素,时间复杂度是O[1],但是在队头删除一个元素,要队列中所有的元素都要向前移动一个位置,确保下标为0的位置不为空,时间复杂度是O[n],如果我们不限定出队操作时所有的元素都要向前移动,即通过移动front,rear来控制队头与队尾所在的位置。
如图,我删除队头元素a0,然后自增front,将a1作为新的队头,则可以免去移动队列中元素所带来的性能损耗。
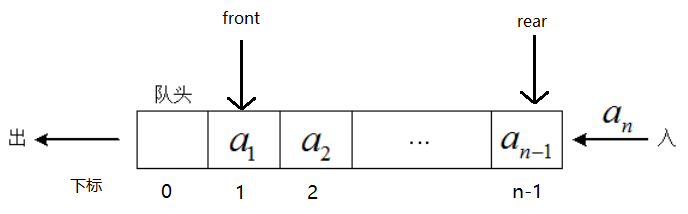
然后此时,新的问题产生了,即假溢出,就是front一直增加时间,直到rear没有位置进行插入,队尾入队已经满了。图如下:
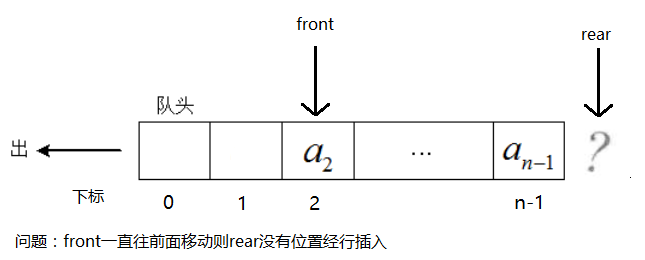
于是引入了循环队列,后面满了,就从头再开始,也就是头尾相接的循环,这种头尾相接的顺序存储结构称为循环队列。
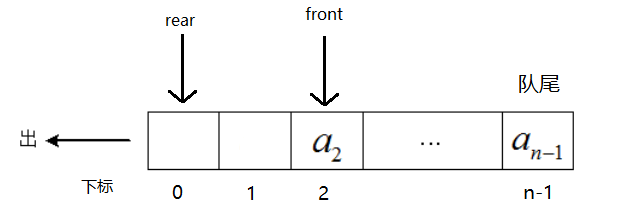
注意:因为用的是数组,所以还会面临一个数组溢出的问题。
java实现代码:
class Queues
{
private int maxSize;
private int[] queArray;
private int front;
private int rear;
public Queues(int s){ // constructor
maxSize = s+1; // array is 1 cell larger
queArray = new int[maxSize]; // than requested
front = 0;
rear = -1;
}
public void insert(int j){ // put item at rear of queue
if(rear == maxSize-1)
rear = -1;
queArray[++rear] = j;
}
public int remove(){ // take item from front of queue
int temp = queArray[front++];
if(front == maxSize)
front = 0;
return temp;
}
public int peek(){ // peek at front of queue
return queArray[front];
}
public boolean isEmpty(){ // true if queue is empty
return ( rear+1==front || (front+maxSize-1==rear) );
}
public boolean isFull(){ // true if queue is full
return ( rear+2==front || (front+maxSize-2==rear) );
}
public int size(){ // (assumes queue not empty)
if(rear >= front) // contiguous sequence
return rear-front+1;
else // broken sequence
return (maxSize-front) + (rear+1);
}
} // end class Queue
class QueueApp
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Queues theQueue = new Queues(5); // queue holds 5 items
theQueue.insert(10); // insert 4 items
theQueue.insert(20);
theQueue.insert(30);
theQueue.insert(40);
theQueue.remove(); // remove 3 items
theQueue.remove(); // (10, 20, 30)
theQueue.remove();
theQueue.insert(50); // insert 4 more items
theQueue.insert(60); // (wraps around)
theQueue.insert(70);
theQueue.insert(80);
while( !theQueue.isEmpty() ) // remove and display
{ // all items
int n = theQueue.remove(); // (40, 50, 60, 70, 80)
System.out.print(n);
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println("");
} // end main()
} // end class QueueApp
//the result:40 50 60 70 80
2.链式存储结构:通过线性表中的单链表经行实现,尾进头出。
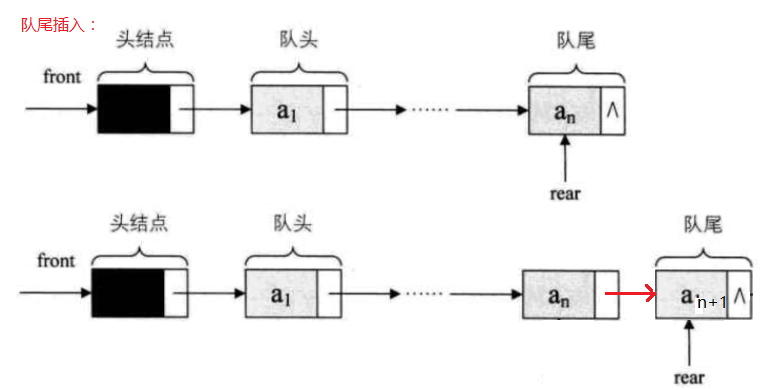
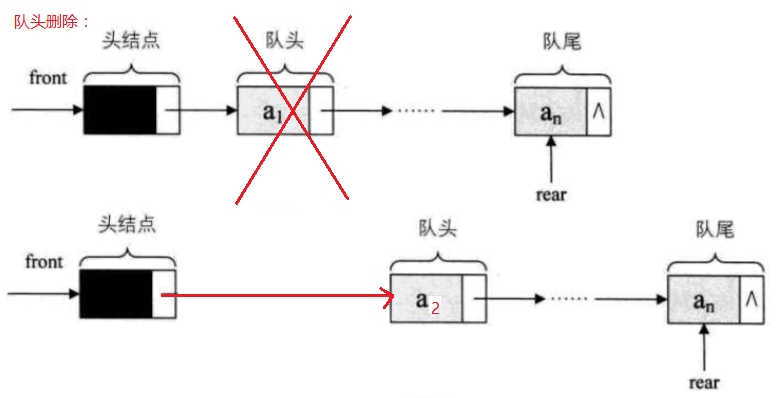
代码:
class Link
{
public double dData; // data item
public Link next; // next link in list
public Link(double d){ // constructor
dData = d;
}
public void displayLink(){ // display this link
System.out.print(dData + " ");
}
} // end class Link
class FirstLastList{
private Link first; // ref to first item
private Link last; // ref to last item
public FirstLastList(){ // constructor
first = null; // no items on list yet
last = null;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){ // true if no links
return first==null;
}
public void insertLast(double dd){ // insert at end of list
Link newLink = new Link(dd); // make new link
if( isEmpty() ) // if empty list,
first = newLink; // first --> newLink
else
last.next = newLink; // old last --> newLink
last = newLink; // newLink <-- last
}
public double deleteFirst(){ // delete first link
double temp = first.dData;
if(first.next == null) // if only one item
last = null; // null <-- last
first = first.next; // first --> old next
return temp;
}
public void displayList(){
Link current = first; // start at beginning
while(current != null){ // until end of list,
current.displayLink(); // print data
current = current.next; // move to next link
}
System.out.println("");
}
} // end class FirstLastList
class LinkQueue
{
private FirstLastList theList;
public LinkQueue(){ // constructor
theList = new FirstLastList(); // make a 2-ended list
}
public boolean isEmpty(){ // true if queue is empty
return theList.isEmpty();
}
public void insert(double j){ // insert, rear of queue
theList.insertLast(j);
}
public double remove(){ // remove, front of queue
return theList.deleteFirst();
}
public void displayQueue(){
System.out.print("Queue (front-->rear): ");
theList.displayList();
}
} // end class LinkQueue
class LinkQueueApp
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
LinkQueue theQueue = new LinkQueue();
theQueue.insert(20); // insert items
theQueue.insert(40);
theQueue.displayQueue(); // display queue
theQueue.insert(60); // insert items
theQueue.insert(80);
theQueue.displayQueue(); // display queue
theQueue.remove(); // remove items
theQueue.remove();
theQueue.displayQueue(); // display queue
} // end main()
} // end class LinkQueueApp
//the result:
//Queue (front-->rear): 20.0 40.0
//Queue (front-->rear): 20.0 40.0 60.0 80.0
//Queue (front-->rear): 60.0 80.0