spring容器的本质
1.问题
- 1、什么是spring容器?
- 2、spring容器如何启动?
- 3、spring容器的本质是什么?
- 4、spring容器在spring家族中扮演什么地位?
- 5、spring容器设计思想?
2.关键词
容器,会话,上下文,工厂,注册表,解析,定义,初始化,懒加载
BeanFactory,BeanDefinition,ApplicationContext
3.全文概要
spring容器本质上就是一个存放了一个个描述不同对象属性和方法的定义单元,需要使用的时候就通过反射机制根据把对象创建好,再将描述的属性初始化。其中涉及了一系列精妙的设计模式和实现思路,这给我们写标准的优质代码提供了绝佳的模板。本文力求讨论spring容器最核心的机制,用最少的代码讲清楚spring容器的本质。
4.架构
4.1spring整体架构
上图是spring框架的整体架构,从架构图我们可以看出来spring的根基就是core container,就是我们说的IOC容器。在此基础上才有AOP,DATA和WEB的繁荣,本章我们讨论的是spring家族的基石,spring容器,也就是我们上文提到的IOC容器。所有其他的spring组件都是在容器上构建出来的,所以我们暂时去掉所有其他的组件功能介绍,只讨论IOC容器。
spring容器最核心的三个jar包是bean,context,core。bean是spring基石,一切结尾bean,context维护了应用的上下文,如果bean是演员,那么context就是舞台,而core则是道具。
4.1上下文ApplicationConext
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
String getId();
String getApplicationName();
String getDisplayName();
long getStartupDate();
ApplicationContext getParent();
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
- ApplicationConext:从类图的继承关系我们看到基础类ApplicationConext继承了资源,消息,事件,环境,工厂五种能力,ApplicationConext只包含了简单的只读属性。
- ConfigurableApplicationContext:继承了生命周期管控能力,同时继承ApplicationConext,拓展了context的环境,事件等写的属性。
- AbstractApplicationContext:大部分的能力在该类定义实现,该类继承类加载能力接口DefaultResourceLoader和读写context的ConfigurableApplicationContext,ioc容器启动的流程详细解析该类。
- GenericApplicationContext:通用上下文,
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:注解可配置上下文,
- GenericGroovyApplicationContext:groovy配置文件上下文,
- GenericXmlApplicationContext:通用xml配置文件上下文,
- StaticApplicationContext:消息可读取上下文,
- AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext:可刷新可配置化上下文,
- AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext:可刷新可配置化上下文,
- AbstractXmlApplicationContext:xml配置文件类型的上下文,
- ClassPathXmlAp-plicationContext:终端类路径xml上下文,
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:文件系统xml上下文,
4.2BeanFactory
spring的世界一切皆为bean。
- AliasRegistry:别名注册表
- BeanFactory:工厂
- BeanDefinitionRegistry:
DefaultListableBeanFactory这个收敛了所以上层的能力,具体包含核心的BeanDefinitionRegistry和BeanFactory,也就是bean的定义和生产bean的工厂。
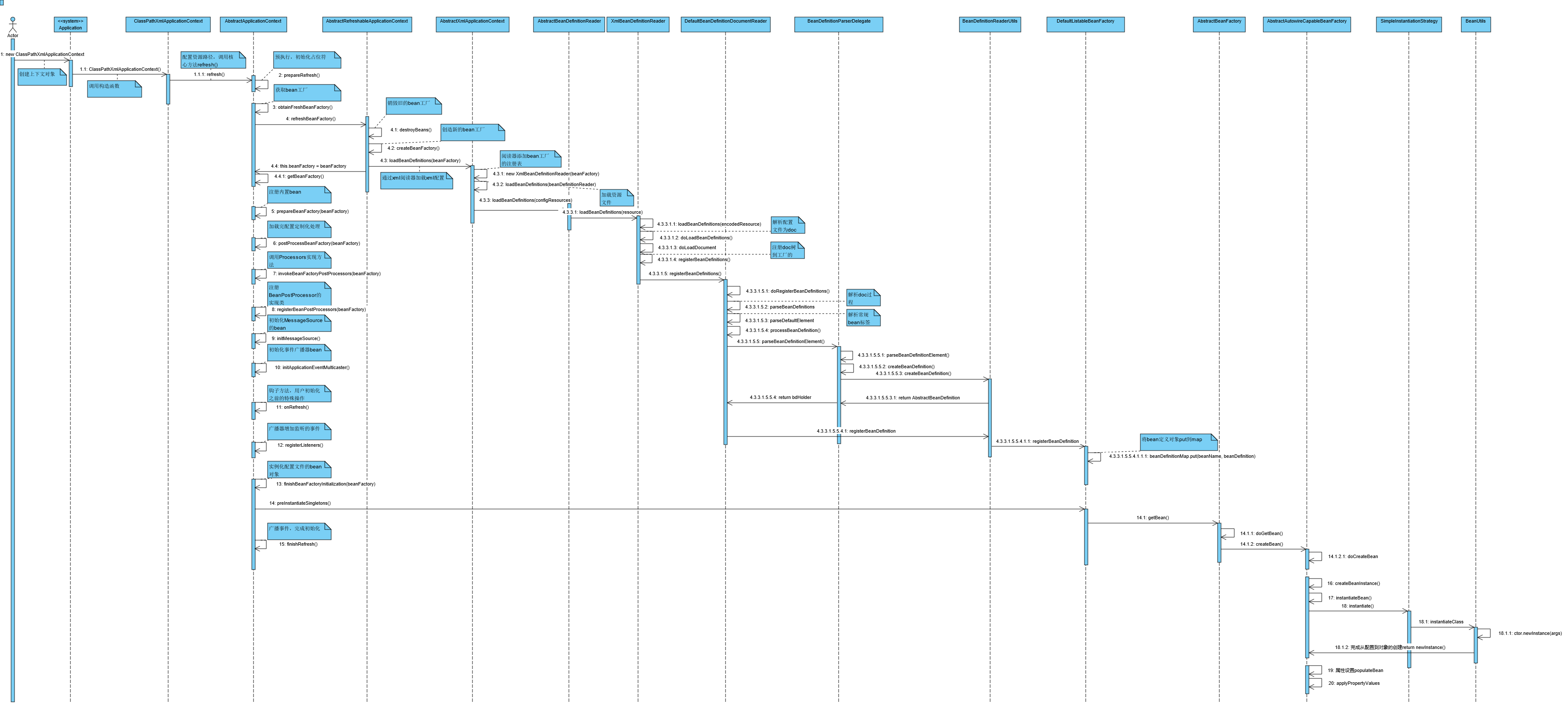
5.过程
容器启动核心过程如下图,包含容器读取配置文件后创建对象,然后对象属性初始化的过程:
5.1启动容器
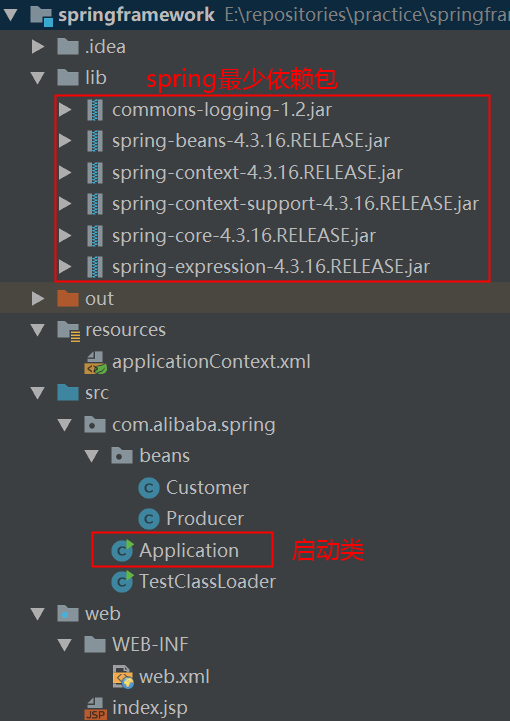
我们要探究spring最核心的容器原理,就要先排除到其他高级属性的干扰,只依赖最少的jar包来构建工程,然后一步步跟踪容器启动的过程。
- 构建工程:新建java工程,引入最少所需依赖的spring包
-
新建测试启动类Application
package com.alibaba.spring; import com.alibaba.spring.beans.Producer; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /** * @author Lin ZhenHua */ public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Producer producer = context.getBean(Producer.class); System.out.println("running the test case with name = " + producer.getCount()); } } -
新建spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean name="producer" class="com.alibaba.spring.beans.Producer"> <property name="count" value="10" /> </bean> </beans> -
执行结果
七月 10, 2018 11:31:16 上午 org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext prepareRefresh 信息: Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@5197848c: startup date [Tue Jul 10 11:31:16 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchy 七月 10, 2018 11:31:17 上午 org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader loadBeanDefinitions 信息: Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [applicationContext.xml] running the test case with name = 10
经过以上几个步骤之后,我们成功的将配置文件里面描述的对象,通过spring的IOC容器创建了出来,而且不需要再使用new的形式来创建对象,下面我们将进行深入的解剖IOC容器的工作流程。
5.2入口
-
创建spring容器上下文对象,调用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext构造函数,传入配置文件路径参数
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); /** * loading the definitions * from the given XML file and automatically refreshing the context */ public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException { this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null); } public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { super(parent); setConfigLocations(configLocations); if (refresh) { refresh(); //核心方法 } } -
调用refresh()方法启动IOC容器
/** * Load or refresh the persistent representation of the configuration */ public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { //容器重启同步监控锁,防止刷新进行到一半被重复执行 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. //填充配置文件占位符,记录容器启动时间和启动状态 prepareRefresh(); //完成配置文件定义到注册表登记bean的流程,此时对象还未被创建 // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. //配置类加载器,定制特殊bean,添加BeanPostProcessor可供回调 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. //工厂加载完配置,初始化之前回调PostProcessBeanFactory,作为工厂扩展功能 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. //调用上文注册的扩展接口PostProcessBeanFactory的实现,为扩展接口为列表类型 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. // bean扩展:postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization //分别在Bean初始化之前和初始化之后得到执行 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. //初始化MessageSource对象,国际化 initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. //初始化事件广播器 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. //临时钩子方法,提供一些初始化完成前的特殊操作,传送门 onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. //注册监听器 registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. //实例化工厂注册表里面的bean(懒加载的除外,用到才实例化) finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. //初始化生命周期,广播事件 finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
5.3准备工作
-
容器初始化之前的初始化工作
protected void prepareRefresh() { this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis(); this.closed.set(false); this.active.set(true); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Refreshing " + this); } // Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment //初始化占位符 initPropertySources(); // Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable // see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties //校验配置文件 getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); // Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents, // to be published once the multicaster is available... this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationEvent>(); }
5.4创建BeanFactory
-
创建BeanFactory,这个是整个IOC容器启动流程的两大核心模块之一
//AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { //关闭旧工厂,创建新工厂 refreshBeanFactory(); //返回创建的新工厂 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); } return beanFactory; } -
重置BeanFactory,存在则销毁,不存在则创建
//AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java 120
@Override protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { //存在BeanFactory()则销毁,即清除工厂里面Map存放的对象 if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { //返回新建的DefaultListableBeanFactory DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); //工厂标识id beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); //设置容器是否允许对象覆盖,循环依赖 customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } } -
创建BeanFactory,构造出子类对象DefaultListableBeanFactory,从前文架构部分我们可以看出这个类的重要地位,里面涵盖了工厂BeanFactory,对象定义BeanDefinition,和注册表AliasRegistry的能力,是一个完整的对象工厂,下文就是使用该工厂将配置文件的信息转换为类定义信息,再进行对象创建,属性赋值。
//AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java 199
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() { return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory()); }
5.5读取配置文件
-
读取xml配置文件
//AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java 80
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. //实例化一个工厂类的XML文件阅读器 XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's // resource loading environment. beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. //开启xml文件校验,可在实现的子类关闭 initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); //beanDefinitionReader阅读器加载资源文件 loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); } -
加载资源文件
//AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java 120
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); if (configResources != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); } //configLocations最终解析成资源对象configResources,效果跟上面分支一样 String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); if (configLocations != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); } } -
循环加载所有资源文件
//AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java 177
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null"); int counter = 0; for (Resource resource : resources) { counter += loadBeanDefinitions(resource); } return counter; } -
阅读器从资源对象获取路径,读取配置文件
//XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java 303
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource)); }//XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java 314
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource()); } //使用ThreadLocal存放配置文件路径 Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); if (currentResources == null) { currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4); this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources); } if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); } try { InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream(); try { InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); } //打开文件流,读取文件内容 return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); } finally { inputStream.close(); } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); } finally { currentResources.remove(encodedResource); if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove(); } } } -
读取配置文件内容
//XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java 388
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { try { //xml文件生成Document文件数 Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (SAXParseException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (SAXException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } }
5.6注册对象
-
注册对象,将XML配置文件描述的Bean转换到BeanFactory的注册表上,返回增量的bean数量
//XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java 505
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); //注册表已存在Definition数量(对象的描述) int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); //将doc树的bean定义注册到工厂类的注册表属性 documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; } -
document阅读器,将已经转成内存document的对象加载到注册表上
//DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java 90
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) { this.readerContext = readerContext; logger.debug("Loading bean definitions"); Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root); } -
遍历document逐个解析xml标签
//DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java 116
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) { // Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In // order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly, // keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create // the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes, // then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference. // this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one. BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; //创建解析DOM树对象的工具BeanDefinitionParserDelegate this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { //如果不包含<profile>标签则略过该操作,非必要方法,略过 String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray( profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec + "] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource()); } return; } } } preProcessXml(root);//预留方法,解析前的扩展操作 parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);//核心方法,解析DOM树 postProcessXml(root);//预留方法,解析后的扩展操作 this.delegate = parent; }
5.7解析配置文件
-
解析内存的DOM文件树
//DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java 161
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) node; //包含http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans的为默认命名空间 if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); } else { //非默认命名空间的有<mvc/>、<context/>、<aop/>等 delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); } } } } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(root); } } -
解析默认命名空间的 标签
//DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java 182
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) { importBeanDefinitionResource(ele); } else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) { processAliasRegistration(ele); } else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) { processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);//解析命名空间为bean的标签 } else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) { // recurse doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele); } } -
解析标签细节,新建BeanDefinition包装类,持有BeanDefinition引用,beanName和别名
//DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java 298
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { //将DOM树对象转化为BeanDefinition包装类bdHolder BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele); if (bdHolder != null) { bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder); try { // Register the final decorated instance. BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry()); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" + bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex); } // Send registration event. getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder)); } }//BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.java 427
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele) { return parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, null); }//BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.java 436
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) { String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE); String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE); List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<String>(); if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) { String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr)); } String beanName = id; if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) { beanName = aliases.remove(0); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName + "' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases"); } } if (containingBean == null) { checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele); } //DOM树标签映射到BeanDefinition对象 AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean); if (beanDefinition != null) { if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) { try { if (containingBean != null) { beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName( beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true); } else { beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition); // Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible, // if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix. // This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility. String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName(); if (beanClassName != null && beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() && !this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) { aliases.add(beanClassName); } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " + "using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]"); } } catch (