一、什么是ServletContext
1.什么是ServletContext
ServletContext代表是一个web应用的上下文对象(web应用对象),里面封装的都是web应用信息。
一个ServletContext对应一个应用。也就是说在一个web应用中我们可以有多个servlet但是我们在任何一个servlet中拿到的都是同一个ServletContext对象。
2.ServletContext的生命周期
- 在服务器一启动的时候就会创建
- 在服务器关闭的时候销毁
3.如何获取ServletContext对象
-
通过init方法当中一个参数ServletConfig来获取
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { ServletContext sc = config.getServletContext(); System.out.println(sc); } -
直接在HttpServlet当中获取this.getServletContext,这种方法本质还是通过config来去获取的
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext(); System.out.println("OneServlet service"); }需要注意的是,若是我们重写了init方法并且没有去加载父类的方法则获取不到ServletConfig对象。那这是为什么呢?我们可以从源码来剖析:
我们先进入getServletContext()方法:
@Override public ServletContext getServletContext() { return getServletConfig().getServletContext(); }接着我们进入getServletConfig()方法:
/** * Returns this servlet's {@link ServletConfig} object. * * @return ServletConfig the <code>ServletConfig</code> object that * initialized this servlet */ @Override public ServletConfig getServletConfig() { return config; }可以看到,该方法直接 返回了一个config对象,接下来我们便寻找config对象是如何赋值的:
@Override public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { this.config = config; this.init(); }接下来我们便在init(ServletConfig config)方法中发现了config是通过init传入的参数来初始化的。到这我们便明白了,若是我们重写了init方法那么我们便没有办法初始化config对象这时候就会报错啦!
4.只有一个ServletContex对象
上面我们提到过一个web应用只有一个ServletContext对象,接下来我们便用代码证明它确实只有一个!
第一步:先创建两个servlet
@WebServlet("/OneServlet") public class OneServlet extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { ServletContext sc = config.getServletContext(); System.out.println(sc); } protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("OneServlet service"); } }@WebServlet("/TwoServlet") public class TwoServlet extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { ServletContext sc = config.getServletContext(); System.out.println(sc); } protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("TwoServlet service"); } }第二步:启动服务器,浏览器访问
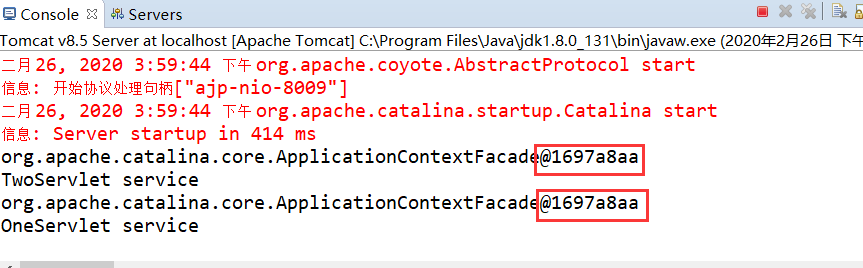
我们可以看到打印出来的两个对象的id是一样的!!!所以我们成功的证明了一个web应用中只有一个ServletContext对象。
二、通过context获取当前应用的绝对路径
我们知道我们程序经常要获取web应用中的资源,但是我们的代码都被编译成class文件放进了classes文件夹中,这与我们编写程序时的目录不符合。所以我们需要用到Servletcontext对象来进行获取资源路径。
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
ServletContext sc = config.getServletContext();
String realPath = sc.getRealPath("test.txt");
System.out.println(realPath);
}
我们在init中调用了这个getRealPath(String path)这个方法获取到了绝对路径如下:
D: omcatapache-tomcat-8.5.47webappsServletContext est.txt
当然我们获取的时应用的绝对路径,而后面的test.txt是我们的输入参数,该方法会将参数自动拼接到尾部得到一个完整的路径。
若是加载classes中的文件我们还可以使用类加载器的方式进行获取目录:
String path = OneServlet.class.getClassLoader().getResource("com/thinmoon/d.txt").getPath();
若是使用这种方法,我们需要注意getResource("com/thinmoon/d.txt")中的文件必须存在,因为这个方法并不是向上面一样进行字符串的拼接。这个方法是先寻找到资源文件然后在获取资源的路径,所以文件必须存在!
三、ServletContext是一个域对象
什么是域?域就是能够存储数据,那么域对象就是能够存储数据的对象。上文我们提到了一个web应用只有一个ServletContext对象,所以很自然我们就能够知道ServletContext域对象的作用范围是整个web应用,所有的web资源都可以进行存取数据,那么web数据就是可以共享的。
- 获取完ServletContext之后向里面写数据
context.setAttribute(String name,Object value); - 获取完ServletContext之后,通过name取出存放的数据
context.getAttribute(String name); - 获取完ServletContext之后,删除指定名称的值
Context.removeAttribute(String name);
通过上面的几种方法我们便可以在不同的servlet中传递数据!