在WPF程序中,数据绑定是非常常用的手段。伴随着数据绑定,我们通常还需要编写一些Converter。而编写Converter是一件非常枯燥的事情,并且大量的converter不容易组织和维护。
今天在网上发现了一篇文章SwitchConverter – A "switch statement" for XAML,它可以通过XAML的方式编写一些类似switch-case方式的converter,十分简洁明了。例如,对如如下的数据绑定转换:
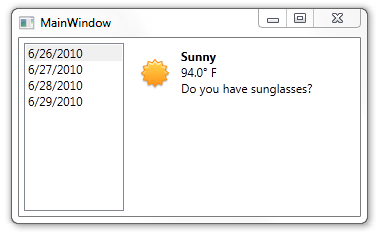
可以直接在XAML中通过如下方式写converter:
<Grid> <Grid.Resources> <e:SwitchConverter x:Key="WeatherIcons"> <e:SwitchCase When="Sunny" Then="Sunny.png" /> <e:SwitchCase When="Cloudy" Then="Cloudy.png" /> <e:SwitchCase When="Rain" Then="Rain.png" /> <e:SwitchCase When="Snow" Then="Snow.png" /> </e:SwitchConverter> </Grid.Resources> <Image Source="{Binding Condition, Converter={StaticResource WeatherIcons}}" /> </Grid>
原文已经附上了代码的工程,但由于担心哪天方校长抖威风而导致该文章失效,这里将其转录了下来,一共三个文件:
SwitchCase.cs

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Diagnostics.Contracts; using System.Linq; using System.Windows; using System.Windows.Markup; namespace SwitchConverterDemo { /// <summary> /// An individual case in the switch statement. /// </summary> [ContentProperty( "Then" )] public sealed class SwitchCase : DependencyObject { #region Constructors /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="T:SwitchCase"/> class. /// </summary> public SwitchCase( ) { } #endregion #region Properties /// <summary> /// Dependency property for the <see cref="P:When"/> property. /// </summary> public static readonly DependencyProperty WhenProperty = DependencyProperty.Register( "When", typeof( object ), typeof( SwitchCase ), new PropertyMetadata( default( object ) ) ); /// <summary> /// The value to match against the input value. /// </summary> public object When { get { return (object)GetValue( WhenProperty ); } set { SetValue( WhenProperty, value ); } } /// <summary> /// Dependency property for the <see cref="P:Then"/> property. /// </summary> public static readonly DependencyProperty ThenProperty = DependencyProperty.Register( "Then", typeof( object ), typeof( SwitchCase ), new PropertyMetadata( default( object ) ) ); /// <summary> /// The output value to use if the current case matches. /// </summary> public object Then { get { return (object)GetValue( ThenProperty ); } set { SetValue( ThenProperty, value ); } } #endregion } // class } // namespace
SwitchCaseCollection.cs

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Collections.ObjectModel; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Diagnostics.Contracts; using System.Linq; namespace SwitchConverterDemo { /// <summary> /// A collection of switch cases. /// </summary> public sealed class SwitchCaseCollection : Collection<SwitchCase> { #region Constructors /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="T:SwitchCaseCollection"/> class. /// </summary> internal SwitchCaseCollection( ) { } #endregion #region Methods /// <summary> /// Adds a new case to the collection. /// </summary> /// <param name="when">The value to compare against the input.</param> /// <param name="then">The output value to use if the case matches.</param> public void Add( object when, object then ) { Add( new SwitchCase { When = when, Then = then } ); } #endregion } // class } // namespace
SwitchConverter.cs

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Collections.ObjectModel; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Diagnostics.Contracts; using System.Globalization; using System.Linq; using System.Windows; using System.Windows.Data; using System.Windows.Markup; namespace SwitchConverterDemo { /// <summary> /// Produces an output value based upon a collection of case statements. /// </summary> [ContentProperty( "Cases" )] public class SwitchConverter : IValueConverter { #region Constructors /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="T:SwitchConverter"/> class. /// </summary> public SwitchConverter( ) : this( new SwitchCaseCollection( ) ) { } /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="T:SwitchConverter"/> class. /// </summary> /// <param name="cases">The case collection.</param> internal SwitchConverter( SwitchCaseCollection cases ) { Contract.Requires( cases != null ); Cases = cases; StringComparison = StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase; } #endregion #region Properties /// <summary> /// Holds a collection of switch cases that determine which output /// value will be produced for a given input value. /// </summary> public SwitchCaseCollection Cases { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// Specifies the type of comparison performed when comparing the input /// value against a case. /// </summary> public StringComparison StringComparison { get; set; } /// <summary> /// An optional value that will be output if none of the cases match. /// </summary> public object Else { get; set; } #endregion #region Methods /// <summary> /// Converts a value. /// </summary> /// <param name="value">The value produced by the binding source.</param> /// <param name="targetType">The type of the binding target property.</param> /// <param name="parameter">The converter parameter to use.</param> /// <param name="culture">The culture to use in the converter.</param> /// <returns>A converted value. If the method returns null, the valid null value is used.</returns> public object Convert( object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture ) { if ( value == null ) { // Special case for null // Null input can only equal null, no convert necessary return Cases.FirstOrDefault( x => x.When == null ) ?? Else; } foreach ( var c in Cases.Where( x => x.When != null ) ) { // Special case for string to string comparison if ( value is string && c.When is string ) { if ( String.Equals( (string)value, (string)c.When, StringComparison ) ) { return c.Then; } } object when = c.When; // Normalize the types using IConvertible if possible if ( TryConvert( culture, value, ref when ) ) { if ( value.Equals( when ) ) { return c.Then; } } } return Else; } /// <summary> /// Converts a value. /// </summary> /// <param name="value">The value that is produced by the binding target.</param> /// <param name="targetType">The type to convert to.</param> /// <param name="parameter">The converter parameter to use.</param> /// <param name="culture">The culture to use in the converter.</param> /// <returns>A converted value. If the method returns null, the valid null value is used.</returns> public object ConvertBack( object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture ) { throw new NotSupportedException( ); } /// <summary> /// Attempts to use the IConvertible interface to convert <paramref name="value2"/> into a type /// compatible with <paramref name="value1"/>. /// </summary> /// <param name="culture">The culture.</param> /// <param name="value1">The input value.</param> /// <param name="value2">The case value.</param> /// <returns>True if conversion was performed, otherwise false.</returns> private static bool TryConvert( CultureInfo culture, object value1, ref object value2 ) { Type type1 = value1.GetType( ); Type type2 = value2.GetType( ); if ( type1 == type2 ) { return true; } if ( type1.IsEnum ) { value2 = Enum.Parse( type1, value2.ToString( ), true ); return true; } var convertible1 = value1 as IConvertible; var convertible2 = value2 as IConvertible; if ( convertible1 != null && convertible2 != null ) { value2 = System.Convert.ChangeType( value2, type1, culture ); return true; } return false; } #endregion } // class } // namespace
这种绑定的方式非常简洁有效,但也有限制,只能处理简单的switch-case形式的关联,并且不能有转换逻辑。不过已经可以替换很大一部分Converter了(非常典型的应用就是这种枚举到图片的转换)。
另外,网上也有一些开源库,实现了一些常见的通用Converter。例如:http://wpfconverters.codeplex.com/。在自己编写Converter之前,不妨先使用这些通用的Converter。
