题目描述
如题,给出一个无向图,求出最小生成树,如果该图不连通,则输出orz
输入格式:
第一行包含两个整数N、M,表示该图共有N个结点和M条无向边。(N<=5000,M<=200000)
接下来M行每行包含三个整数Xi、Yi、Zi,表示有一条长度为Zi的无向边连接结点Xi、Yi
输出格式:
输出包含一个数,即最小生成树的各边的长度之和;如果该图不连通则输出orz
输入样例#1:
4 5
1 2 2
1 3 2
1 4 3
2 3 4
3 4 3
输出样例#1:
7
说明:
时空限制:1000ms,128M
数据规模:
对于20%的数据:N<=5,M<=20
对于40%的数据:N<=50,M<=2500
对于70%的数据:N<=500,M<=10000
对于100%的数据:N<=5000,M<=200000
样例解释:
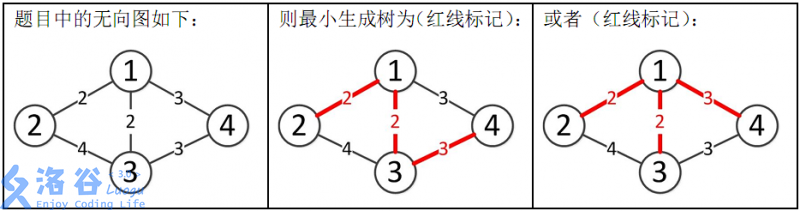
所以最小生成树的总边权为2+2+3=7
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
struct edge {
ll u, v, w;
} e[10000001];
bool cmp(const edge &x, const edge &y) { return x.w < y.w; }
ll fa[10000001], n, m, ans;
ll get(int x) {
if (fa[x] == x)
return x;
return fa[x] = get(fa[x]);
}
void kruskal() {
ll f1, f2, k = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
f1 = get(e[i].u);
f2 = get(e[i].v);
if (f1 != f2) {
fa[f1] = f2;
ans += e[i].w;
k++;
if (k == n - 1)
break;
}
}
if (k < n - 1)
cout << "orz" << endl;
else
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) fa[i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> e[i].u >> e[i].v >> e[i].w;
}
sort(e + 1, e + m + 1, cmp);
kruskal();
return 0;
}