java注解篇
什么是注解?
注释是给开发者看的,可以提升代码的可阅读性和可维护性,但是对于java编译器和虚拟机来说是没有意义的,编译后的字节码文件中没有任何注释信息。 而注解和注释有些类似,不过注解是给编译器和虚拟机看的。编译器和虚拟机可以在运行过程中获取注解信息,然后根据注解信息做各种想做的事。
注解如何使用?
- 定义注解
- 使用注解
- 通过注解获取信息做各种想做的事
定义注解
下面定义了一个自定义注解:
public @interface Anno0 {
String value() default "";
}
注解的定义需要注意:
- 注解的定义和普通的类,接口一样,不过注解的关键字是
@interface。 - 注解的方法修饰符必须且只能为public, 不能有其他的修饰符如static,final,private等。默认为public。
- 注解的方法类型只能为基本数据类型、枚举、Class、String、注解及以上类型的一维数组类型。
- 方法名后的()不是定义参数的地方,也不能在里面定义任何参数。如value()、name()。方法名表示注解的属性。
- defult表示默认值, 默认值得类型必须和前面定义的类型一样。如value属性的类型是String, 默认值是空的字符串 ""。
- 如果没有默认值,使用注解时,必须要为属性赋值。如果只有一个属性时,将属性名设为value,使用时可以省略属性名。如下:
public @interface Anno1 {
String value();
String name() default "";
}
public @interface Anno2 {
String name();
}
// 注解的使用
@Anno1(value = "value属性没有默认值必须要传值")
public class AnnoTest {
}
@Anno1(value = "value属性没有默认值必须要传值",name = "覆盖掉默认的name属性值")
public class AnnoTest {
}
@Anno0("不写赋值的属性名称时,默认给value赋值,必须保证有value这个属性")
public class AnnoTest {
}
@Anno2(name = "必须有属性名为value()时,才可以忽略不写属性名,括号内直接赋值")
public class AnnoTest {
}
使用注解
使用target注解标注注解的使用范围:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Anno0 {
String value() default "";
}
ElementType取值:
public enum ElementType {
/** 类、接口(包括注解类型)、枚举类上 */
TYPE,
/** 字段(包括常量)上 */
FIELD,
/** 方法上 */
METHOD,
/** 方法参数上 */
PARAMETER,
/** 构造方法上 */
CONSTRUCTOR,
/** 本地变量上 */
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/** 注解上 */
ANNOTATION_TYPE,
/** 包上 */
PACKAGE,
/**
* 类型参数上
*
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_PARAMETER,
/**
* 使用到类型的任意语句中
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_USE
}
使用Retention注解表示该注解的生效范围
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Anno0 {
String value() default "";
}
RetentionPolicy的取值:
public enum RetentionPolicy {
/**
* 只在源码中生效,编译及运行时就丢失了,也就是class文件中就不存在了。
*/
SOURCE,
/**
* 注解会被保留在编译后的class文件中,但是不会被保留在VM虚拟机在运行阶段
*/
CLASS,
/**
* 注解在源码,class字节码以及运行阶段都存在
* @see java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement
*/
RUNTIME
}
正常情况下,自定义注解上都要标注target和retention注解。
无参数
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Anno2 {
}
// 使用注解
@Anno2
public class AnnoTest {
}
一个参数的
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Anno0 {
String value() default "";
}
@Anno0("属性名为value可以省略")
public class AnnoTest {
}
多个参数
public @interface Anno1 {
String value();
String name() default "";
}
@Anno1(value = "属性名为value可以省略",name = "多个参数注解要指定属性名")
public class AnnoTest {
}
数组类型参数
public @interface Anno3 {
String[] name() default {};
}
@Anno3(name = {"数组类型", "以逗号分隔", "大括号{}包裹"})
public class AnnoTest {
}
// 当只有一个值时可以省略大括号
@Anno3(name= "数组类型")
public class AnnoTest {
}
// 当属性名为value时,可以省略
@Anno3({"数组类型", "属性值为value省略"})
public class AnnoTest {
}
// 只有一个值
@Anno3("数组类型")
public class AnnoTest {
}
不同ElementType的用法
// Type 类型可以用在类,接口,注解,枚举类型上
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Anno4 {
String name();
}
@Anno4(name = "用在注解上")
public @interface AnnoTest{}
@Anno4(name = "用在类上")
class TypeTest{}
@Anno4(name = "用在接口上")
interface InterfaceTest{}
@Anno4(name = "用在枚举上")
enum EnumTest{}
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR,
ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Anno5 {
String name();
}
public class AnnotationTest {
@Anno5(name = "作用在字段上")
private String name;
@Anno5(name = "作用在构造方法上")
AnnotationTest(){}
@Anno5(name = "作用在方法上")
void fun1(@Anno5(name = "作用在参数上") String param) {
@Anno5(name = "作用在本地变量")
int i = 1;
}
}
jdk8新增了TYPE_PARAMETER和TYPE_USE类型
@Target({ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER, ElementType.TYPE_USE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Anno6 {
String value() default "";
}
abstract class Test<@Anno6("作用在泛型参数上=TYPE_PARAMETER") K,V>{
abstract K fun1(V v);
}
class Test1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test<@Anno6("作用在类型参数上=TYPE_USE")String, Integer> test = new Test<String, Integer>() {
@Override
@Anno6("作用在类型参数上=TYPE_USE") String fun1( @Anno6("作用在类型参数上=TYPE_USE")Integer integer) {
return String.valueOf(integer);
}
};
}
}
注解信息的获取
为了运行时能准确获取注解的信息,Java在java.lang.reflect反射包下新增了AnnotatedElement接口,他主要用于表示目前正在虚拟机中运行的程序中已 使用注解的元素,通过该接口提供的方法可以利用反射技术读取注解信息。 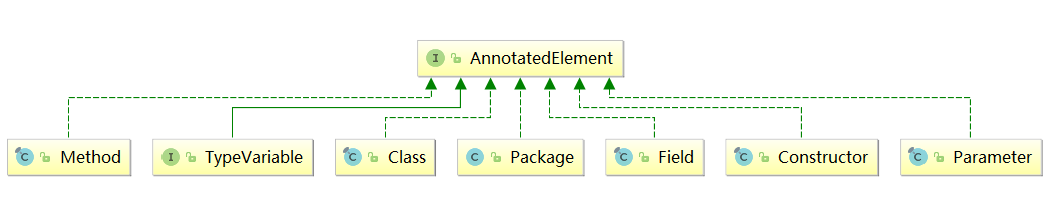
- Package: 用来表示包信息
- Class: 用来表示类信息
- Constructor: 用来表示构造方法信息
- Field: 用来表示类中的属性信息
- Method: 用来表示方法信息
- Parameter: 用来表示方法参数信息
- TypeVariable: 用来表示类型变量信息,如类上定义的泛型类型变量,方法上定义的泛型变量
AnnonatedElement常用方法
| 返回值 | 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| A extends Annotation | getAnnotation(Class AnnotationClass) | 该元素如果存在指定类型的注解,则返回该注解,否则返回null |
| Annotation[] | getAnnotations() | 返回此元素上的所有注解,包括从父类上继承的 |
| boolean | isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) | 如果指定类型的注解存在此元素上,则返回true,否则false |
| Annotation[] | getDeclaredAnnotations() | 返回直接存在此元素上的所有注解,不包括父类继承的注解。 |
使用案例:
public class AnnotationUseTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Anno4 anno4 = A.class.getAnnotation(Anno4.class);
System.out.println("获取类A上的Anno4注解信息:" + anno4.name());
Annotation[] annotations = A.class.getAnnotations();
System.out.println("获取类A上的所有注解:");
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println("类A上的注解:" + annotation);
}
Anno4 annotation = AnnoTest.class.getAnnotation(Anno4.class);
System.out.println("获取AnnoTest注解上的Anno4注解的信息:" + annotation);
Field desc = ReflectionUtils.findField(A.class, "desc");
Optional.ofNullable(desc).ifPresent(a -> {
System.out.println("字段上的注解:" + a.getAnnotation(Anno5.class));
System.out.println(a.getAnnotatedType().getAnnotation(Anno6.class));
});
Constructor<?> constructor = A.class.getDeclaredConstructors()[0];
Anno5 annotation1 = constructor.getAnnotation(Anno5.class);
System.out.println("构造方法上的注解:" + annotation1);
Method setDesc = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(A.class, "setDesc", String.class);
Optional<Method> method = Optional.ofNullable(setDesc);
method.ifPresent(f -> System.out.println("方法上的注解:" + f.getAnnotation(Anno5.class)));
Annotation annotation2 = method.map(f -> f.getParameters()[0]).map(f -> f.getAnnotations()[0]).get();
System.out.println("作用在方法参数上:" + annotation2);
Anno6 annotation3 = B.class.getTypeParameters()[0].getAnnotation(Anno6.class);
System.out.println("类型参数上的注解--TYPE_PARAMETER:" + annotation3);
Method test = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(A.class, "test");
Optional.ofNullable(test).ifPresent(f ->
System.out.println(f.getAnnotatedReturnType().getAnnotation(Anno6.class))
);
}
}
@Anno4(name = "用在类上的注解")
class A {
@Anno5(name = "用在类属性上")
private @Anno6("用在成员变量类型上--TYPE_USE") String desc;
@Anno5(name = "用在构造方法上")
A() {
}
@Anno5(name = "用在方法上")
void setDesc(@Anno5(name = "用在方法参数上") String desc) {
@Anno5(name = "用在本地变量上") Integer aa = 0;
this.desc = desc;
}
@Anno6("用在返回类型上") String test() {
@Anno6("用在局部变量类型上--TYPE_USE") String name = "aaa";
return "";
}
}
interface B<@Anno6("作用在类型参数上") String>{
}
@Inherit 类之间注解的继承
首先看这个注解的源码:
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Inherited {
}
根据ElementType的值可以知道这个注解是专门作用在注解上的。
作用:让子类可以继承父类中被@Inherited修饰的注解。注意是继承父类的,如果接口上的注解也用@Inherited修饰了,那么接口的实现类无法继承这个注解 首先我们看不加这个注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Anno7 {
String[] notes() default {};
String desc() default "";
}
自定义一个注解。首先来看不加这个注解的效果
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Anno7 {
String[] notes() default {};
String desc() default "";
}
@Anno7(desc = "不加Inherited")
abstract class AbstractAnno7{
}
public class Anno7Test extends AbstractAnno7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Annotation[] annotations = Anno7Test.class.getAnnotations();
// annotations数组为空数组,因此无结果打印
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
}
可以看到我们获取不到父类的注解信息。下面在试试加上这个注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
public @interface Anno7 {
String[] notes() default {};
String desc() default "";
}
再次执行上面的main方法:
@Anno7(desc = "加Inherited")
abstract class AbstractAnno7{
}
public class Anno7Test extends AbstractAnno7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Annotation[] annotations = Anno7Test.class.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);//@com.xiazhi.annocation.Anno7(desc=加Inherited, notes=[])
}
}
}
再试下在接口上使用该注解:
@Anno7(desc = "使用在接口上")
interface IAnno7{}
public class Anno7Test implements IAnno7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Annotation[] annotations = Anno7Test.class.getAnnotations();
// 无结果
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
}
Repeatable 重复使用注解
定义注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Anno8 {
}
看下面一段代码:
@Anno8
@Anno8 // 这里会报错
public class Anno8Test {
}
默认情况下,注解是不允许重复使用的,如果我们想像上面一样重复使用注解,需要添加Repeatable注解 看一下Repeatable注解:
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Repeatable {
/**
* Indicates the <em>containing annotation type</em> for the
* repeatable annotation type.
* @return the containing annotation type
*/
Class<? extends Annotation> value();
}
注意value是没有默认值的,因此使用时要对value属性赋值。值是一个容器注解。容器注解的定义要求如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Anno8s {
Anno8[] value();
}
容器注解必须有一个value参数,参数类型为子注解类型的数组。 使用Repeatable注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Repeatable(Anno8s.class)
public @interface Anno8 {
}
@Anno8
@Anno8
public class Anno8Test {
}
此时使用重复注解就不会报错了。
spring对于注解的增强
要先导入spring-core的依赖。 首先我们来看一个问题:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface A1{
String value() default "a1";
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@A1
@interface B1{
String value() default "b1";
}
@B1("hello")
public class DemoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotation(DemoTest.class, B1.class));
System.out.println(AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotation(DemoTest.class,A1.class));
}
}
AnnotatedElementUtils是spring封装的工具类。此时有个问题,如果我们像要在给B1赋值的时候同时给B1上的A1设置值,是没有办法的,这是由于注解定义 无法继承导致的。Spring通过Aliasfor注解解决了这个问题。 通过Aliasfor解决上面的问题:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface A1{
String value() default "a1";
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@A1
@interface B1{
String value() default "b1";
@AliasFor(value = "value",annotation = A1.class)
String a1Value();
}
@B1(value = "hello", a1Value = "给A1的value赋值")
public class DemoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotation(DemoTest.class, B1.class));
System.out.println(AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotation(DemoTest.class, A1.class));
}
}
运行结果:
@com.xiazhi.annocation.B1(value=hello, a1Value=给A1的value赋值)
@com.xiazhi.annocation.A1(value=给A1的value赋值)
我们看一下使用Aliasfor的地方的代码:
@AliasFor(value = "value",annotation = A1.class)
String a1Value();
annatation表示要给哪儿个注解赋值,value表示注解的方法,本例中我们要将a1Value()的值赋值给A1注解的value方法。
Aliasfor 注解
看一下Aliasfor注解:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Documented
public @interface AliasFor {
@AliasFor("attribute")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String attribute() default "";
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
}
在value和attribute方法上使用了Aliasfor注解,说明给value赋值时同时就会给attribute赋值,给attribute赋值时同时会给value赋值
在同一个注解中使用Aliasfor
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface An{
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
@AliasFor("name") //如果不指定annotation属性,则默认是当前注解,如果不指定value和attribute,则自动将修饰的参数作为value和attribute的值
String value() default "";
}
@An(value = "hello")//同一个注解内设置Aliasfor注解时,如果给两个属性都赋值会报错
public class DemoTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
An mergedAnnotation = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotation(DemoTest2.class, An.class);
System.out.println(mergedAnnotation);
}
}