我地理解:主要是为了现实某一功能和方法,所采用的不同实现方式。将不同的实现方式抽象出共同的借口,在它的继承类中实现具体的方式。
这样如果有新的实现方式只要继承其借口实现它即可,不会对其他已经存在的策略造成影响。
也即是:策略
(策略模式定义了一系列的算法,并将每一个算法封装起来,而且使它们还可以相互替换。策略模式让算法独立于使用它的客户而独立变化。)
应用场景:
需要在不同情况下使用不同的策略(算法),或者策略还可能在未来用其它方式来实现
设计原则:
Favor composition over inheritance.(优先使用对象组合,而非类继承)
一、策略模式定义
参考Gang of Four's (GOF) Design Patterns书里的定义:Define a family of algorithms, encapsulate each one, and make them interchangeable. [The] Strategy [pattern] lets the algorithm vary independently from clients that use it
策略模式(Strategy)属于对象行为型设计模式,主要是定义算法族,分别封装起来,让他们之间可以项目替换,此模式让算法的变化独立于使用算法的客户
二、核心概念和用法
策略模式主要用到了三个核心的OOP概念:封装、继承和多态。还包含了一些基本的设计原则:1)封装变化。2)多用组合,少用继承。3)针对接口编程,不针对实现编程。
此模式的适用场景是:当一个类的某些行为将会经常发生变化或者在运行时需要改变时,可以使用策略模式。
这个模式的核心是把类的变化行为提取为一个接口,然后将类的变化部分用这个接口对象代替,也即声明为这个接口的一个属性,然后增加一个设置这个接口的方法,以便以后修改这个类的具体行为,这样这个类可以不用管这个变化行为的具体实现,将实现委托给这个接口的具体实现。而关于这个接口的一系列实现,可以看成是一族算法。这样就实现了将类中变化的部分封装,算法的使用跟算法的实现分离,算法被提取出来之后还可以更好的进行复用。
三、模式参与者
下面快速浏览一下这个模式主要参与者:
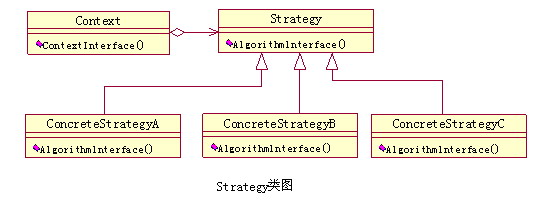
- Context超类
定义了所有需要继承这个类的子类的属性跟方法,并且定义了改变这个父类变化行为的方法
- 算法接口
定义了具体行为的方法声明,由这个接口的实现类来具体实现接口定义的行为方法。
- 具体算法类
一组具体的算法接口实现类,代表不同的行为。
- 客户类(Client Class)
负责创建Context类的实例,并负责创建算法的实现的实例,然后赋给Context类实例的正确算法实现对象。
四、核心模式图表
策略模式diagram
五、一个简单的策略模式的实现
为了更好的理解策略模式,下面提供一个简单的例子(代码参考wiki网站)
- //StrategyExample test application
- class StrategyExample {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Context context;
- // Three contexts following different strategies
- context = new Context(new FirstStrategy());
- context.execute();
- context = new Context(new SecondStrategy());
- context.execute();
- context = new Context(new ThirdStrategy());
- context.execute();
- }
- }
- // The classes that implement a concrete strategy should implement this
- // The context class uses this to call the concrete strategy
- interface Strategy {
- void execute();
- }
- // Implements the algorithm using the strategy interface
- class FirstStrategy implements Strategy {
- public void execute() {
- System.out.println("Called FirstStrategy.execute()");
- }
- }
- class SecondStrategy implements Strategy {
- public void execute() {
- System.out.println("Called SecondStrategy.execute()");
- }
- }
- class ThirdStrategy implements Strategy {
- public void execute() {
- System.out.println("Called ThirdStrategy.execute()");
- }
- }
- // Configured with a ConcreteStrategy object and maintains a reference to a Strategy object
- class Context {
- Strategy strategy;
- // Constructor
- public Context(Strategy strategy) {
- this.strategy = strategy;
- }
- public void execute() {
- this.strategy.execute();
- }
- }
六、java类库中使用策略模式的例子
策略简单,应用也很广泛,在java类库中就大量的使用了策略模式,举例如下:
AWT的LayoutManager就是一个使用策略模式的例子,对于GUI来说,在一个容器(Container)中对组件的放置都是按照一定算法进行排列的,在java中,这些算法就是一些layout对象,由于每个容器对其内组件的排列算法是变化的,因此需要将这些算法的实现提取出来声明为一个接口,这里这个算法接口就是LayoutManager,围绕这个接口,java提供了多个具体的实现,就是我们熟悉的GridLayout、FlowLayout等java内置的布局;对于Container类,所有的容器都需要继承这个类,每一个这个类的子类都需要有一个安排其内组件的算法实现,因此在Container超类中,定义了一个算法接口以及设置这个接口的方法。看一下Container类的部分代码:
- public class Container extends Component {
- /**
- * Layout manager for this container.
- * @see #doLayout
- * @see #setLayout
- * @see #getLayout
- */
- LayoutManager layoutMgr;//这里就是可变部分,声明为一个接口
- ......
- /**
- * Sets the layout manager for this container.
- * @param mgr the specified layout manager
- * @see #doLayout
- * @see #getLayout
- */
- public void setLayout(LayoutManager mgr) {
- layoutMgr = mgr;
- if (valid) {
- invalidate();
- }
- }
- ......
- }
LayoutManager接口,声明了一些可用的方法,如下代码所示:
- public interface LayoutManager {
- void addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp);
- void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp);
- Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container parent);
- Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container parent);
- void layoutContainer(Container parent);
- }
这样LayoutManager接口的多个实现,就可以动态的应用到每个Container子类的对象中。
AWT中容器和布局管理之间的关系图为: