一、判断功能的方法
public boolean equals (Object anObject) :将此字符串与指定对象进行比较。
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase (String anotherString) :将此字符串与指定对象进行比较,忽略大小写。
二、获取功能的方法
public int length () :返回此字符串的长度。
public String concat (String str) :将指定的字符串连接到该字符串的末尾。
public char charAt (int index) :返回指定索引处的 char值。
public int indexOf (String str) :返回指定子字符串第一次出现在该字符串内的索引。
public String substring (int beginIndex) :返回一个子字符串,从beginIndex开始截取字符串到字符串结尾。
public String substring (int beginIndex, int endIndex) :返回一个子字符串,从beginIndex到endIndex截取字符串。含beginIndex,不含endIndex。
三、转换功能的方法
public char[] toCharArray () :将此字符串转换为新的字符数组。
public byte[] getBytes () :使用平台的默认字符集将该 String编码转换为新的字节数组。
public String replace (CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) :将与target匹配的字符串使用replacement字符串替换。
四、分割功能的方法
有些特殊符号需要用 反斜杠 转义,在Java要用两个反斜杠 \
五、一些常用方法
boolean contains(CharSequence s): 判断字符串中是否包含指定字符。
一、判断功能的方法
public boolean equals (Object anObject) :将此字符串与指定对象进行比较。
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase (String anotherString) :将此字符串与指定对象进行比较,忽略大小写。
public class String_Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建字符串对象
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = "HELLO";
// boolean equals(Object obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); // false
System.out.println("-----------");
//boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); // true
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3)); // true
System.out.println("-----------");
}
}
Object 是” 对象”的意思,也是一种引用类型。作为参数类型,表示任意对象都可以传递到方法中
注意:
2个字符串使用==比较运算符,比较的是地址值,如果使用的是equals方法,比较的是字符串内容是否相等
二、获取功能的方法
public int length () :返回此字符串的长度。
String s = "helloworld"; //int length():获取字符串的长度,其实也就是字符个数 System.out.println(s.length());//10
public String concat (String str) :将指定的字符串连接到该字符串的末尾。
String s = "helloworld";
//String concat:将指定的字符串连接到该字符串的末尾
String s2 = s.concat("**hello itheima");
System.out.println(s2);//helloworld**hello itheima
public char charAt (int index) :返回指定索引处的 char值。
String s = "helloworld"; //char charAt:获取指定索引处的字符 System.out.println(s.charAt(0));//h System.out.println(s.charAt(1));//e
public int indexOf (String str) :返回指定子字符串第一次出现在该字符串内的索引。
String s = "helloworld";
// 获取子字符串第一次出现在该字符串内的索引,没有返回-1
System.out.println(s.indexOf("l"));//2
System.out.println(s.indexOf("wow"));//-1
System.out.println(s.indexOf("ak"));//-1
public String substring (int beginIndex) :返回一个子字符串,从beginIndex开始截取字符串到字符串结尾。
String s = "helloworld"; // 从beginIndex开始截取字符串到字符串结尾 System.out.println(s.substring(0));//helloworld System.out.println(s.substring(5));//world
public String substring (int beginIndex, int endIndex) :返回一个子字符串,从beginIndex到endIndex截取字符串。含beginIndex,不含endIndex。
String s = "helloworld"; // 从beginIndex到endIndex截取字符串。含beginIndex,不含endIndex。 System.out.println(s.substring(0, s.length()));//helloworld System.out.println(s.substring(3,8));//lowor
三、转换功能的方法
public char[] toCharArray () :将此字符串转换为新的字符数组。
String s = "HelloWorld!"; //char[] toCharArray:把字符串转换为字符数组 char[] chs = s.toCharArray();
public byte[] getBytes () :使用平台的默认字符集将该 String编码转换为新的字节数组。
String s = "HelloWorld!"; byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();
public String replace (CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) :将与target匹配的字符串使用replacement字符串替换。
String str = "itcast itheima";
String replace = str.replace("it","IT");
四、分割功能的方法
有些特殊符号需要用 反斜杠 转义,在Java要用两个反斜杠 \
//String分割
String s = "aa|bb|cc";
String[] strArray = s.split("\|");
for(int i = 0; i < strArray.length; i++){
System.out.print(strArray[i]);
}
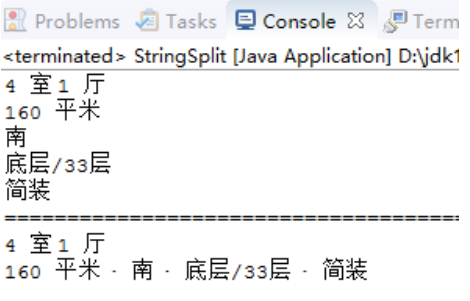
1 public class StringSplit { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 4 String info = "4 室 1 厅 · 160 平米 · 南 · 底层/33层 · 简装"; 5 ////以"· "为分隔符,截取上面的字符串。结果为五段 6 String[] s1=info.split("· "); 7 for(int i=0;i<s1.length;i++){ 8 //循环输出结果 9 System.out.println(s1[i]); 10 } 11 System.out.println("===================================================="); 12 13 //这次比上面的多了一个参数,且返回结果数组中的元素个数为2 14 s1=info.split("· ",2); 15 for(int i=0;i<s1.length;i++){ 16 //输出结果为2段 17 System.out.println(s1[i]); 18 } 19 } 20 }
五、一些常用方法
boolean contains(CharSequence s): 判断字符串中是否包含指定字符。
String s = "djlfdjksdlka";
boolean str = s.contains("g");
System.out.println("str" + str);
