142. Linked List Cycle II【easy】
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
解法一:
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * struct ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode *next; 6 * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} 7 * }; 8 */ 9 class Solution { 10 public: 11 ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { 12 if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) { 13 return NULL; 14 } 15 16 ListNode * slow = head; 17 ListNode * fast = head; 18 19 while (fast->next != NULL && fast->next->next != NULL) { 20 slow = slow->next; 21 fast = fast->next->next; 22 23 if (fast == slow) { 24 return findNode(fast, head); 25 } 26 } 27 28 return NULL; 29 } 30 31 ListNode * findNode(ListNode * fast, ListNode * head) 32 { 33 while (fast != head) { 34 fast = fast->next; 35 head = head->next; 36 } 37 38 return head; 39 } 40 41 42 };
首先先看是否有环,有环的话我们要把其中一个指针移动到链表head节点,另外一个指针不变,然后这两个指针同时往前分别走一步,直到相等为止就是环的入口点;这个问题的算法证明如下:
问题1:如何判断单链表中是否存在环(即下图中从结点E到结点R组成的环)?

设一快一慢两个指针(Node *fast, *low)同时从链表起点开始遍历,其中快指针每次移动长度为2,慢指针则为1。则若无环,开始遍历之后fast不可能与low重合,且fast或fast->next最终必然到达NULL;若有环,则fast必然不迟于low先进入环,且由于fast移动步长为2,low移动步长为1,则在low进入环后继续绕环遍历一周之前fast必然能与low重合(且必然是第一次重合)。于是函数可写如下:
1 bool hasCircle(Node* head, Node* &encounter) 2 { 3 Node *fast = head, *slow = head; 4 while(fast && fast->next) 5 { 6 fast = fast->next->next; 7 slow = slow->next; 8 if(fast == slow) 9 { 10 encounter = fast; 11 return true; 12 } 13 } 14 encounter = NULL; 15 return false; 16 }
问题2:若存在环,如何找到环的入口点(即上图中的结点E)?
解答:如图中所示,设链起点到环入口点间的距离为x,环入口点到问题1中fast与low重合点的距离为y,又设在fast与low重合时fast已绕环n周(n>0),且此时low移动总长度为s,则fast移动总长度为2s,环的长度为r。则
s + nr = 2s,n>0 ①
s = x + y ②
由①式得 s = nr
代入②式得
nr = x + y
x = nr - y ③
现让一指针p1从链表起点处开始遍历,指针p2从encounter处开始遍历,且p1和p2移动步长均为1。则当p1移动x步即到达环的入口点,由③式可知,此时p2也已移动x步即nr - y步。由于p2是从encounter处开始移动,故p2移动nr步是移回到了encounter处,再退y步则是到了环的入口点。也即,当p1移动x步第一次到达环的入口点时,p2也恰好到达了该入口点。于是函数可写如下:
1 Node* findEntry(Node* head, Node* encounter) 2 { 3 Node *p1 = head, *p2 = encounter; 4 while(p1 != p2) 5 { 6 p1 = p1->next; 7 p2 = p2->next; 8 } 9 return p1; 10 }
另外一个解释也比较好:
求解单链表环入口点的步骤:
1:使用“指针追赶”方法找到相遇点(网上资料很多,此处略)。
2:指针p1从链表头、p2从相遇点,同时出发,一次移动一个节点,再次的相遇点便是环的入口点。
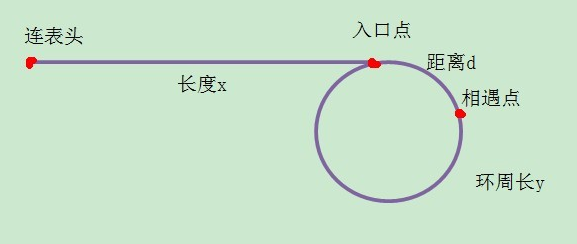
证明导向:p1从表头走,能与p2从相遇点走再次相遇,那么说明p1走到入口点时,p2可能刚好走了y-d(其中d是入口点与第一次相遇点的距离)个节点,或者走了几圈再加上y-d个节点。故就要找到y-d与x的关系。
第一次相遇:S慢:表示一次移动一个节点的指针所走的路程(即节点个数)
S快:表示一次移动两个节点的指针所走的路程(节点个数)
S慢 = x + d
S快 = 2(x + d)
S快 - S慢 = n倍y
则有:x + d = ny
x = ny - d = (n - 1)y + (y - d)
由此便说明了:x 个节点就相当于(n - 1)倍环周长加上y - d,正好是第一次相遇点到入口点的距离。
证明参考自:
http://blog.csdn.net/wuzhekai1985/article/details/6725263
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6a0e04380101a9o2.html