Strategic Game
Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 10035 Accepted Submission(s): 4691
Problem Description
Bob enjoys playing computer games, especially strategic games, but sometimes he cannot find the solution fast enough and then he is very sad. Now he has the following problem. He must defend a medieval city, the roads of which form a tree. He has to put the minimum number of soldiers on the nodes so that they can observe all the edges. Can you help him?
Your program should find the minimum number of soldiers that Bob has to put for a given tree.
The input file contains several data sets in text format. Each data set represents a tree with the following description:
the number of nodes
the description of each node in the following format
node_identifier:(number_of_roads) node_identifier1 node_identifier2 ... node_identifier
or
node_identifier:(0)
The node identifiers are integer numbers between 0 and n-1, for n nodes (0 < n <= 1500). Every edge appears only once in the input data.
For example for the tree:
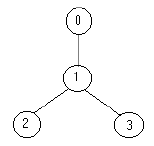
the solution is one soldier ( at the node 1).
The output should be printed on the standard output. For each given input data set, print one integer number in a single line that gives the result (the minimum number of soldiers). An example is given in the following table:
Your program should find the minimum number of soldiers that Bob has to put for a given tree.
The input file contains several data sets in text format. Each data set represents a tree with the following description:
the number of nodes
the description of each node in the following format
node_identifier:(number_of_roads) node_identifier1 node_identifier2 ... node_identifier
or
node_identifier:(0)
The node identifiers are integer numbers between 0 and n-1, for n nodes (0 < n <= 1500). Every edge appears only once in the input data.
For example for the tree:

the solution is one soldier ( at the node 1).
The output should be printed on the standard output. For each given input data set, print one integer number in a single line that gives the result (the minimum number of soldiers). An example is given in the following table:
Sample Input
4
0:(1) 1
1:(2) 2 3
2:(0)
3:(0)
5
3:(3) 1 4 2
1:(1) 0
2:(0)
0:(0)
4:(0)
Sample Output
1 2
题目大意:
给你一棵树,问你最少占几个点,就可以覆盖所有边。(占住某个点,由这点出发的所有边都称作被覆盖)
树形DP基础题。
dp[i][0]表示以i为根节点的子树,在不占i的情况下,最少需要占多少个点;
dp[i][1]表示以i为根节点的子树,在占i的情况下,最少需要占多少个点;
则状态转移方程:
dp[i][0]=∑dp[son][1];
dp[i][1]=∑min(dp[son][0],dp[son][1]);
可见是由下至上转移的,所以DFS就OK啦。

#include<cstdio> #include<queue> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn=1500; int to[maxn*2+5]; int nex[maxn*2+5]; int head[maxn*2+5]; int dp[maxn+5][2]; int vis[maxn+5]; void dfs(int x) { vis[x]=1; bool flag=0; for(int i=head[x];i!=-1;i=nex[i]) { if(!vis[to[i]]) { dfs(to[i]); flag=1; } } if(!flag) { dp[x][1]=1; return; } for(int i=head[x];i!=-1;i=nex[i]) { dp[x][0]+=dp[to[i]][1]; dp[x][1]+=min(dp[to[i]][1],dp[to[i]][0]); } dp[x][1]+=1; } int main() { int n; while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) { memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); for(int i=1,a,b,c,cnt=0;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d:(%d)",&a,&c); while(c--) { scanf("%d",&b); to[cnt]=a;nex[cnt]=head[b];head[b]=cnt++; to[cnt]=b;nex[cnt]=head[a];head[a]=cnt++; } } memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)); memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); dfs(0); printf("%d ",min(dp[0][0],dp[0][1])); } return 0; }
还有一道类似的入门题,hdu1520,附ac代码。

#include<cstdio> #include<queue> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn=6000; int weight[maxn+5]; int isson[maxn+5]; int to[maxn+5]; int nex[maxn+5]; int head[maxn+5]; int dp[maxn][2]; void dfs(int x) { if(head[x]==-1) { dp[x][0]=0; dp[x][1]=weight[x]; //printf("%d %d %d %d %d %d ",x,0,dp[x][0],x,1,dp[x][1]); return; } for(int i=head[x];i!=-1;i=nex[i]) dfs(to[i]); for(int i=head[x];i!=-1;i=nex[i]) { dp[x][0]+=max(dp[to[i]][0],dp[to[i]][1]); dp[x][1]+=dp[to[i]][0]; } dp[x][1]+=weight[x]; //printf("%d %d %d %d %d %d ",x,0,dp[x][0],x,1,dp[x][1]); } int main() { int n; while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) { for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",weight+i); memset(isson,0,sizeof(isson)); memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); for(int i=1,a,b,cnt=0;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); if(i==n) break; to[cnt]=a; nex[cnt]=head[b]; head[b]=cnt++; isson[a]=1; } int origin; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) if(!isson[i]) { origin=i; break; } //printf("%d ",origin); memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)); dfs(origin); printf("%d ",max(dp[origin][0],dp[origin][1])); } return 0; }
