文字描述
之前的链表(单链表、循环链表)的链式存储结构中只有一个指示直接后继的指针域。由此,从某个结点出发只能顺指针往后寻查其他结点。若要寻查结点的直接前驱,则需从表头指针出发。即单链表中,NextElem的执行时间为1,而PriorElem的执行时间为n。为了克服单链表这种缺点,可利用双向链表。
在双向链表中,每个节点有两个指针域,一个指向其直接后继,一个指向其直接前驱。
示意图
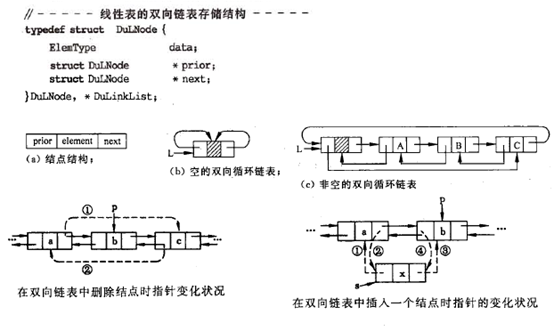
算法分析
插入、删除、查找、求后继等同单链表。但是求前驱不一样,其时间复杂度为1。
代码实现

1 // 2 // Created by lady on 19-1-31. 3 // 4 5 #include <stdlib.h> 6 #include <stdio.h> 7 #include <string.h> 8 9 //线性表的双向循环链表存储结构 10 typedef struct ElemType{ 11 char data[10]; 12 }ElemType; 13 typedef struct DuLNode{ 14 ElemType e; 15 struct DuLNode *prior; 16 struct DuLNode *next; 17 }DuLNode, *DuLinkList; 18 19 //构造一个空的双向循环链表 20 static int InitList_DuL(DuLinkList *L) 21 { 22 (*L) = (DuLinkList)malloc(sizeof(DuLNode)); 23 (*L)->prior = (*L); 24 (*L)->next = (*L); 25 memset((*L)->e.data, 0, sizeof((*L)->e.data)); 26 return 0; 27 } 28 29 //销毁L 30 static int Destory_DuL(DuLinkList *L) 31 { 32 DuLNode *p = NULL; 33 DuLNode *q = NULL; 34 p = (*L)->next; 35 while(p){ 36 q = p; 37 p = p->next; 38 free(q); 39 if(p == (*L)) 40 break; 41 } 42 free(*L); 43 (*L) = NULL; 44 return 0; 45 } 46 47 //返回双向链表L中的第i个位置的元素 48 static DuLNode *GetElemP_DuL(DuLinkList *L, int i) 49 { 50 if(L == NULL){ 51 return NULL; 52 } 53 DuLNode *p = (*L)->next; 54 int index = 1; 55 while(index<i && p){ 56 index += 1; 57 p = p->next; 58 } 59 if(index == i && p){ 60 return p; 61 }else{ 62 return NULL; 63 } 64 } 65 66 //在L的指定位置i的元素前面插入元素e 67 static int ListInsert_DuL(DuLinkList *L, int i, ElemType e) 68 { 69 DuLNode *p = NULL; 70 DuLNode *new = NULL; 71 if((p=GetElemP_DuL(L, i)) == NULL){ 72 return -1; 73 } 74 if((new = (DuLNode*)malloc(sizeof(DuLNode))) == NULL){ 75 return -1; 76 } 77 new->e = e; 78 new->prior = p->prior; 79 p->prior->next = new; 80 new->next = p; 81 p->prior = new; 82 return 0; 83 } 84 85 //删除L中的第loc个数据元素,并将被删元素的值存放在e中 86 static int ListDelete_DuL(DuLinkList *L, int i, ElemType *e) 87 { 88 DuLNode *p = NULL; 89 if((p=GetElemP_DuL(L, i)) == NULL){ 90 return -1; 91 } 92 (*e) = p->e; 93 p->prior->next = p->next; 94 p->next->prior = p->prior; 95 free(p); 96 return 0; 97 } 98 99 //依次对L的每个数据元素调用函数fun 100 static int listTraverse_DuL(DuLinkList *L, int (*fun)(ElemType,int), char note[]) 101 { 102 printf("遍历双向循环链表%s:", note); 103 DuLNode *p = NULL; 104 p = (*L)->next; 105 int i = 1; 106 while(p){ 107 fun(p->e, i); 108 i+=1; 109 p = p->next; 110 if(p == (*L)) 111 break; 112 } 113 printf(" "); 114 return 0; 115 } 116 117 static int print(ElemType e, int loc) 118 { 119 printf("%3d=%-10s", loc, e.data); 120 } 121 122 //创建一个长度为n的双向链表 123 static int CreateList_DuL(DuLinkList *L, int n, char note[]) 124 { 125 printf("创建一个长度为%d的双向循环链表%s! ", n, note); 126 InitList_DuL(L); 127 ElemType e; 128 int i = 0; 129 for(i=0; i<n; i++){ 130 printf("输入第%d个元素:", i+1); 131 scanf("%s[^\n]", e.data); 132 ListInsert_DuL(L, i+1, e); 133 } 134 return 0; 135 } 136 137 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 138 { 139 ElemType e; 140 DuLinkList L; 141 int location=0; 142 143 CreateList_DuL(&L, 5, "L"); 144 145 listTraverse_DuL(&L, print, "L"); 146 147 148 printf("输入插入元素的位置:"); 149 scanf("%d", &location); 150 printf("输入插入元素的数据:"); 151 scanf("%s[^\n]", e.data); 152 ListInsert_DuL(&L, location, e); 153 listTraverse_DuL(&L, print, "L"); 154 155 printf("输入删除元素的位置:"); 156 scanf("%d", &location); 157 ListDelete_DuL(&L, location, &e); 158 159 printf("位于%d的元素%s已经从双向循环链表中被删除! ", location, e.data); 160 listTraverse_DuL(&L, print, "L"); 161 162 Destory_DuL(&L); 163 printf("双向链表已经被销毁! "); 164 return 0; 165 }
代码运行
/home/lady/CLionProjects/untitled/cmake-build-debug/untitled 创建一个长度为5的双向循环链表L! 输入第1个元素:c 输入第2个元素:b 输入第3个元素:e 输入第4个元素:g 输入第5个元素:f 遍历双向循环链表L: 1=c 2=b 3=e 4=g 5=f 输入插入元素的位置:3 输入插入元素的数据:test 遍历双向循环链表L: 1=c 2=b 3=test 4=e 5=g 6=f 输入删除元素的位置:4 位于4的元素e已经从双向循环链表中被删除! 遍历双向循环链表L: 1=c 2=b 3=test 4=g 5=f 双向链表已经被销毁! Process finished with exit code 0
