netty 中,每一个 channel 有一个写缓冲 ChannelOutboundBuffer
ChannelOutboundBuffer 类中维持一个 Entry 链表,Entry 是链表的节点,封装了待写入的 ByteBuf,而 netty 最终写入 socket 的是 ByteBuffer,所以最终会把 ByteBuf 转为 ByteBuffer
static final class Entry { // 毫无意外,使用对象池 private static final ObjectPool<Entry> RECYCLER = ObjectPool.newPool(new ObjectCreator<Entry>() { @Override public Entry newObject(Handle<Entry> handle) { return new Entry(handle); } }); private final Handle<Entry> handle; // 下个节点 Entry next; // 消息内容,即 ByteBuf Object msg; // 一般情况,一个 ByteBuf 底层对应一个 ByteBuffer // 所以 bufs 多数时候为空,只有 buf 会被赋值 ByteBuffer[] bufs; // 真正写入 socket 的数据结构 ByteBuffer buf; // 对应写入成功的回调 ChannelPromise promise; // ByteBuf 中已写入 socket 的字节数 long progress; // ByteBuf 可读的字节数 long total; int pendingSize; int count = -1; boolean cancelled; }
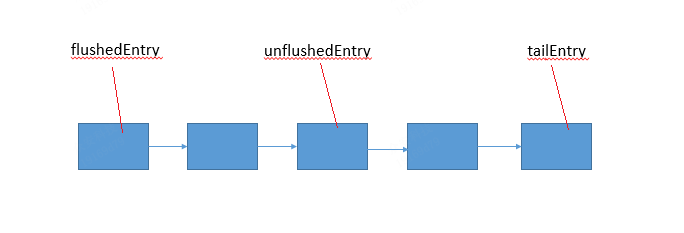
// 暂时不需要写到 socket 的 Entry 的指针 private Entry unflushedEntry; // 要写到 socket 的 Entry 的指针 private Entry flushedEntry; // 尾部 private Entry tailEntry; // 要写入 socket 的 Entry 的数量 // 等于从 flushedEntry 到 unflushedEntry 之间的 Entry 数量,不包括 unflushedEntry private int flushed;
每调用一次 HeadContext.write 最终触发 addMessage,把数据加在 tailEntry 后面
添加 Entry
public void addMessage(Object msg, int size, ChannelPromise promise) { Entry entry = Entry.newInstance(msg, size, total(msg), promise); if (tailEntry == null) { flushedEntry = null; } else { Entry tail = tailEntry; tail.next = entry; } tailEntry = entry; if (unflushedEntry == null) { unflushedEntry = entry; } incrementPendingOutboundBytes(entry.pendingSize, false); }
每调用一次 HeadContext.flush 最终触发 addFlush 和 flush
// io.netty.channel.AbstractChannel.AbstractUnsafe#flush public final void flush() { assertEventLoop(); ChannelOutboundBuffer outboundBuffer = this.outboundBuffer; if (outboundBuffer == null) { return; } // 移动 flushedEntry 和 unflushedEntry 指针 outboundBuffer.addFlush(); // 真正写 socket flush0(); }
移动 flushedEntry 和 unflushedEntry 指针。通俗地讲,flushedEntry 到 unflushedEntry 之间的 Entry 需要写入 socket,如果 unflushedEntry 是 null,则所有 Entry 写入 socket。
public void addFlush() { Entry entry = unflushedEntry; if (entry != null) { if (flushedEntry == null) { // 如果 flushedEntry 指针为空,则直接指向 unflushedEntry,最后把 unflushedEntry 置空 flushedEntry = entry; } // 如果 flushedEntry 指针不为空,则直接把 unflushedEntry 置空 do { flushed ++; if (!entry.promise.setUncancellable()) { int pending = entry.cancel(); decrementPendingOutboundBytes(pending, false, true); } entry = entry.next; } while (entry != null); // All flushed so reset unflushedEntry unflushedEntry = null; } }
需要说明的是,缓冲中只有一条链表,需要写到 socket 的是从 flushedEntry 到 unflushedEntry 之间的 Entry,不包括 unflushedEntry。
对于下面这张图,addMessage 在 tailEntry 后面增加节点,addFlush 把 unflushedEntry 置空。原则是,flushedEntry 右边的节点都要写到 socket。
我们知道
flush 之后,如果数据充足,且每次都写成功,netty 默认会持续写 16 次
// io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel#doWrite protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception { SocketChannel ch = javaChannel(); // 默认 16 次 int writeSpinCount = config().getWriteSpinCount(); do { // 当 ChannelOutboundBuffer 无可写的数据,返回 if (in.isEmpty()) { // All written so clear OP_WRITE clearOpWrite(); // Directly return here so incompleteWrite(...) is not called. return; } // Ensure the pending writes are made of ByteBufs only. int maxBytesPerGatheringWrite = ((NioSocketChannelConfig) config).getMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(); // 把 ChannelOutboundBuffer 中的 msg,转换成 ByteBuffer ByteBuffer[] nioBuffers = in.nioBuffers(1024, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite); // ByteBuffer 的数量 int nioBufferCnt = in.nioBufferCount(); switch (nioBufferCnt) { case 0: // We have something else beside ByteBuffers to write so fallback to normal writes. writeSpinCount -= doWrite0(in); break; case 1: { // 最简单的情形 ByteBuffer buffer = nioBuffers[0]; int attemptedBytes = buffer.remaining(); // 把 ByteBuffer 写入 socket final int localWrittenBytes = ch.write(buffer); if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) { // 如果 socket 不可写,则注册 OP_WRITE 事件 incompleteWrite(true); return; } // 根据写入的字节数调整下次写入的量 adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(attemptedBytes, localWrittenBytes, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite); // 删除 ChannelOutboundBuffer 中的 Entry in.removeBytes(localWrittenBytes); --writeSpinCount; break; } default: { // Zero length buffers are not added to nioBuffers by ChannelOutboundBuffer, so there is no need // to check if the total size of all the buffers is non-zero. // We limit the max amount to int above so cast is safe long attemptedBytes = in.nioBufferSize(); final long localWrittenBytes = ch.write(nioBuffers, 0, nioBufferCnt); if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) { incompleteWrite(true); return; } // Casting to int is safe because we limit the total amount of data in the nioBuffers to int above. adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite((int) attemptedBytes, (int) localWrittenBytes, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite); in.removeBytes(localWrittenBytes); --writeSpinCount; break; } } } while (writeSpinCount > 0); incompleteWrite(writeSpinCount < 0); }
把所有 flushedEntry 中的 ByteBuf 转换成 ByteBuffer
// io.netty.channel.ChannelOutboundBuffer#nioBuffers(int, long) public ByteBuffer[] nioBuffers(int maxCount, long maxBytes) { assert maxCount > 0; assert maxBytes > 0; long nioBufferSize = 0; int nioBufferCount = 0; final InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get(); ByteBuffer[] nioBuffers = NIO_BUFFERS.get(threadLocalMap); Entry entry = flushedEntry; // 遍历 flushedEntry while (isFlushedEntry(entry) && entry.msg instanceof ByteBuf) { if (!entry.cancelled) { ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) entry.msg; final int readerIndex = buf.readerIndex(); final int readableBytes = buf.writerIndex() - readerIndex; if (readableBytes > 0) { if (maxBytes - readableBytes < nioBufferSize && nioBufferCount != 0) { break; } nioBufferSize += readableBytes; int count = entry.count; if (count == -1) { entry.count = count = buf.nioBufferCount(); } int neededSpace = min(maxCount, nioBufferCount + count); if (neededSpace > nioBuffers.length) { nioBuffers = expandNioBufferArray(nioBuffers, neededSpace, nioBufferCount); NIO_BUFFERS.set(threadLocalMap, nioBuffers); } if (count == 1) { ByteBuffer nioBuf = entry.buf; if (nioBuf == null) { entry.buf = nioBuf = buf.internalNioBuffer(readerIndex, readableBytes); } nioBuffers[nioBufferCount++] = nioBuf; } else { nioBufferCount = nioBuffers(entry, buf, nioBuffers, nioBufferCount, maxCount); } if (nioBufferCount == maxCount) { break; } } } entry = entry.next; } this.nioBufferCount = nioBufferCount; this.nioBufferSize = nioBufferSize; return nioBuffers; }
删除 Entry
根据写入的字节数,删除 Entry
public void removeBytes(long writtenBytes) { for (;;) { // 当前 flushedEntry 节点 Object msg = current(); if (!(msg instanceof ByteBuf)) { assert writtenBytes == 0; break; } final ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; final int readerIndex = buf.readerIndex(); final int readableBytes = buf.writerIndex() - readerIndex; // 写入的数据大于当前 flushedEntry 的数据,即该 flushedEntry 写完 if (readableBytes <= writtenBytes) { if (writtenBytes != 0) { // 更新进度 progress(readableBytes); writtenBytes -= readableBytes; } // 删除 flushedEntry 指向的节点,向后移动 flushedEntry remove(); } else { // readableBytes > writtenBytes // 该 flushedEntry 没有写完,则只更新进度 if (writtenBytes != 0) { buf.readerIndex(readerIndex + (int) writtenBytes); progress(writtenBytes); } break; } } clearNioBuffers(); }
高水位线和低水位线
netty 统计 pending 的数据(可以认为是 unflushedEntry 的数据),超过了高水位线则改标志,注意,改了标志,也可以写入,需要用户自己判断继续写还是不写。
通过 ctx.channel().isWritable() 获取是否可写状态
// 利用 cas 设置 unwritable 的值 private static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<ChannelOutboundBuffer> UNWRITABLE_UPDATER = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(ChannelOutboundBuffer.class, "unwritable"); // 0 可写,1 不可写 private volatile int unwritable; private void incrementPendingOutboundBytes(long size, boolean invokeLater) { if (size == 0) { return; } long newWriteBufferSize = TOTAL_PENDING_SIZE_UPDATER.addAndGet(this, size); if (newWriteBufferSize > channel.config().getWriteBufferHighWaterMark()) { setUnwritable(invokeLater); } } private void setUnwritable(boolean invokeLater) { for (;;) { final int oldValue = unwritable; final int newValue = oldValue | 1; if (UNWRITABLE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, oldValue, newValue)) { if (oldValue == 0 && newValue != 0) { fireChannelWritabilityChanged(invokeLater); } break; } } }
一旦设置为不可写,只有当水位降到低水位线,标志才会重新变回可写
private void decrementPendingOutboundBytes(long size, boolean invokeLater, boolean notifyWritability) { if (size == 0) { return; } long newWriteBufferSize = TOTAL_PENDING_SIZE_UPDATER.addAndGet(this, -size); if (notifyWritability && newWriteBufferSize < channel.config().getWriteBufferLowWaterMark()) { setWritable(invokeLater); } }