http://activemq.apache.org/producer-flow-control.html
翻译:
流量控制是指:如果broker检测到destination的内存限制、temp文件限制、file store限制被超过了,就会减慢消息的流动。producer会被阻塞直到有可用资源,或者收到一个JMSException:这些行为是可以配置的。
值得一提的是:默认的<systemUsage>设置会导致producer阻塞,当达到memoryLimit或<systemUsage>的限制值时,这种阻塞行为有时被误认为是一个"挂起的producer",而事实上producer只是在等待可用空间。
同步发送的消息会自动使用按producer的流量控制;通常会应用到同步发送持久化消息,除非你开启useAsyncSend标志。
使用异步发送的producer(通常讲,发送非持久化消息的producer)不需要等待来自broker的确认;所以,当达到memory limit时,你不会被通知到。如果你想知道broker的限制值达到了,你需要配置 ProducerWindowSize 连接参数,然后异步的消息也能按producer控制流量了。
ActiveMQConnectionFactory connctionFactory = ...
connctionFactory.setProducerWindowSize(1024000);
ProducerWindowSize 是producer发送的最大字节数,在等待来自broker的消息确认前。 如果你在发送非持久化消息(默认异步发送),并且希望知道queue或topic的memory limit是否达到了。那么你需要设置connection factory 为 'alwaysSyncSend'。但是,这会降低速度,它能保证你的producer马上知道内存问题。 如果你喜欢,你可以关掉指定jms queue和topic的流量控制,例如:
<destinationPolicy> <policyMap> <policyEntries> <policyEntry topic="FOO.>" producerFlowControl="false"/> </policyEntries> </policyMap> </destinationPolicy>
注意,在ActiveMQ 5.x中引入了新的file cursor,非持久化消息会被刷到临时文件存储中来减少内存使用量。所以,你会发现queue的memoryLimit永远达不到,因为file cursor花不了多少内存,如果你真的要把所有非持久化消息保存在内存中,并且当memoryLimit达到时停止producer,你应该配置<vmQueueCursor>。
<policyEntry queue=">" producerFlowControl="true" memoryLimit="1mb"> <pendingQueuePolicy> <vmQueueCursor/> </pendingQueuePolicy> </policyEntry>
上面的片段能保证,所有的消息保存在内存中,并且每一个队列只有1Mb的限制。
How Producer Flow Control works
如果你在发送持久化消息,broker会发送一个ProducerAck消息给producer,它告知producer前一个发送窗口已经被处理了,所以producer现在可以发送下一个窗口。这和consumer的消息确认很像。当没有空间可用时,调用send()操作会无限阻塞,另一种方法是在客户端抛出异常。通过设置sendFailIfNoSpace为true,broker会导致send()抛出javax.jms.ResourceAllocationException,异常会传播到客户端。下面是配置示例:
<systemUsage> <systemUsage sendFailIfNoSpace="true"> <memoryUsage> <memoryUsage limit="20 mb"/> </memoryUsage> </systemUsage> </systemUsage>
这种做法的好处是,客户端会捕获一个javax.jms.ResourceAllocationException异常,等一会然后重试send(),而不再是无限地等待。
从5.3.1开始,加入了sendFailIfNoSpaceAfterTimeout属性,如果broker在配置的时间内仍然没有空余空间,此时send()才会失败,并且把异常传递到客户端,下面是配置:
<systemUsage> <systemUsage sendFailIfNoSpaceAfterTimeout="3000"> <memoryUsage> <memoryUsage limit="20 mb"/> </memoryUsage> </systemUsage> </systemUsage>
关闭流量控制
通常的需求是关闭流量控制,这样消息分发可以一直进行直到磁盘空间被 pending messages 耗尽。
通过配置<systemUsage>元素的某些属性,你可以降低producer的速率。
<systemUsage> <systemUsage> <memoryUsage> <memoryUsage limit="64 mb" /> </memoryUsage> <storeUsage> <storeUsage limit="100 gb" /> </storeUsage> <tempUsage> <tempUsage limit="10 gb" /> </tempUsage> </systemUsage> </systemUsage>
<memoryUsage>对应NON_PERSISTENT消息的内存容量,<storeUsage> 对应PERSITENT消息的磁盘容量,<tempUsage>对应临时文件的磁盘容量。
结合代码分析:
client-side: org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQMessageProducer.send
broker-side:从 org.apache.activemq.broker.region.Queue.send 开始
//org.apache.activemq.broker.region.Queue public void send(final ProducerBrokerExchange producerExchange, final Message message) throws Exception { final ConnectionContext context = producerExchange.getConnectionContext(); // There is delay between the client sending it and it arriving at the // destination.. it may have expired. message.setRegionDestination(this); ProducerState state = producerExchange.getProducerState(); if (state == null) { LOG.warn("Send failed for: {}, missing producer state for: {}", message, producerExchange); throw new JMSException("Cannot send message to " + getActiveMQDestination() + " with invalid (null) producer state"); } final ProducerInfo producerInfo = producerExchange.getProducerState().getInfo(); //是否发送ProducerAck final boolean sendProducerAck = !message.isResponseRequired() && producerInfo.getWindowSize() > 0 && !context.isInRecoveryMode(); if (message.isExpired()) { // message not stored - or added to stats yet - so check here broker.getRoot().messageExpired(context, message, null); if (sendProducerAck) { ProducerAck ack = new ProducerAck(producerInfo.getProducerId(), message.getSize()); context.getConnection().dispatchAsync(ack); } return; } if (memoryUsage.isFull()) { //如果内存耗尽 // 尽管这里有大段代码,但是调试没进这儿 } doMessageSend(producerExchange, message); if (sendProducerAck) { ProducerAck ack = new ProducerAck(producerInfo.getProducerId(), message.getSize()); context.getConnection().dispatchAsync(ack); } }
把消息放进 broker 的 pendingList 之前,会检查可用空间:
//org.apache.activemq.broker.region.Queue void doMessageSend(final ProducerBrokerExchange producerExchange, final Message message) throws IOException, Exception { final ConnectionContext context = producerExchange.getConnectionContext(); ListenableFuture<Object> result = null; boolean needsOrderingWithTransactions = context.isInTransaction(); producerExchange.incrementSend(); //检查使用空间 checkUsage(context, producerExchange, message); sendLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { if (store != null && message.isPersistent()) { try { message.getMessageId().setBrokerSequenceId(getDestinationSequenceId()); if (messages.isCacheEnabled()) { result = store.asyncAddQueueMessage(context, message, isOptimizeStorage()); result.addListener(new PendingMarshalUsageTracker(message)); } else { store.addMessage(context, message); } if (isReduceMemoryFootprint()) { message.clearMarshalledState(); } } catch (Exception e) { // we may have a store in inconsistent state, so reset the cursor // before restarting normal broker operations resetNeeded = true; throw e; } } // did a transaction commit beat us to the index? synchronized (orderIndexUpdates) { needsOrderingWithTransactions |= !orderIndexUpdates.isEmpty(); } if (needsOrderingWithTransactions ) { // If this is a transacted message.. increase the usage now so that // a big TX does not blow up // our memory. This increment is decremented once the tx finishes.. message.incrementReferenceCount(); registerSendSync(message, context); } else { // Add to the pending list, this takes care of incrementing the // usage manager. sendMessage(message); } } finally { sendLock.unlock(); } if (!needsOrderingWithTransactions) { messageSent(context, message); } if (result != null && message.isResponseRequired() && !result.isCancelled()) { try { result.get(); } catch (CancellationException e) { // ignore - the task has been cancelled if the message // has already been deleted } } }
对持久化消息和非持久化消息分类检查:
// org.apache.activemq.broker.region.Queue private void checkUsage(ConnectionContext context,ProducerBrokerExchange producerBrokerExchange, Message message) throws ResourceAllocationException, IOException, InterruptedException { if (message.isPersistent()) { // 持久化消息 if (store != null && systemUsage.getStoreUsage().isFull(getStoreUsageHighWaterMark())) { final String logMessage = "Persistent store is Full, " + getStoreUsageHighWaterMark() + "% of " + systemUsage.getStoreUsage().getLimit() + ". Stopping producer (" + message.getProducerId() + ") to prevent flooding " + getActiveMQDestination().getQualifiedName() + "." + " See http://activemq.apache.org/producer-flow-control.html for more info"; waitForSpace(context, producerBrokerExchange, systemUsage.getStoreUsage(), getStoreUsageHighWaterMark(), logMessage); } } else if (messages.getSystemUsage() != null && systemUsage.getTempUsage().isFull()) { // 非持久化消息 final String logMessage = "Temp Store is Full (" + systemUsage.getTempUsage().getPercentUsage() + "% of " + systemUsage.getTempUsage().getLimit() +"). Stopping producer (" + message.getProducerId() + ") to prevent flooding " + getActiveMQDestination().getQualifiedName() + "." + " See http://activemq.apache.org/producer-flow-control.html for more info"; waitForSpace(context, producerBrokerExchange, messages.getSystemUsage().getTempUsage(), logMessage); } }
最后进入具体的处理逻辑:
// org.apache.activemq.broker.region.BaseDestination protected final void waitForSpace(ConnectionContext context, ProducerBrokerExchange producerBrokerExchange, Usage<?> usage, int highWaterMark, String warning) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ResourceAllocationException { // 如果配置了sendFailIfNoSpace="true" if (!context.isNetworkConnection() && systemUsage.isSendFailIfNoSpace()) { getLog().debug("sendFailIfNoSpace, forcing exception on send, usage: {}: {}", usage, warning); throw new ResourceAllocationException(warning); } if (!context.isNetworkConnection() && systemUsage.getSendFailIfNoSpaceAfterTimeout() != 0) { if (!usage.waitForSpace(systemUsage.getSendFailIfNoSpaceAfterTimeout(), highWaterMark)) { getLog().debug("sendFailIfNoSpaceAfterTimeout expired, forcing exception on send, usage: {}: {}", usage, warning); throw new ResourceAllocationException(warning); } } else { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); long nextWarn = start; producerBrokerExchange.blockingOnFlowControl(true); destinationStatistics.getBlockedSends().increment(); while (!usage.waitForSpace(1000, highWaterMark)) { if (context.getStopping().get()) { throw new IOException("Connection closed, send aborted."); } long now = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (now >= nextWarn) { getLog().info("{}: {} (blocking for: {}s)", new Object[]{ usage, warning, new Long(((now - start) / 1000))}); nextWarn = now + blockedProducerWarningInterval; } } long finish = System.currentTimeMillis(); long totalTimeBlocked = finish - start; destinationStatistics.getBlockedTime().addTime(totalTimeBlocked); producerBrokerExchange.incrementTimeBlocked(this,totalTimeBlocked); producerBrokerExchange.blockingOnFlowControl(false); } }
如果配置了sendFailIfNoSpace="true",并且抛出异常了,处理异常的调用栈如下:
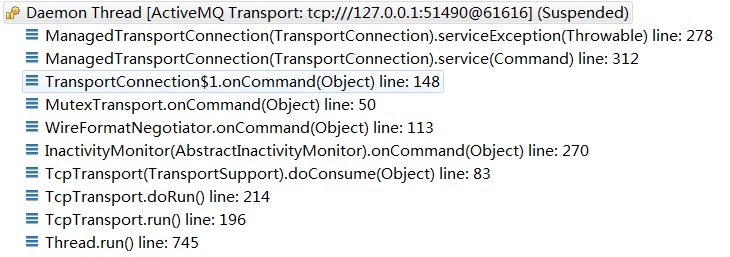
//org.apache.activemq.broker.TransportConnection public void serviceException(Throwable e) { if (...) { ... } else if (!stopping.get() && !inServiceException) { inServiceException = true; try { SERVICELOG.warn("Async error occurred: ", e); ConnectionError ce = new ConnectionError(); ce.setException(e); if (pendingStop) { dispatchSync(ce); } else { dispatchAsync(ce); } } finally { inServiceException = false; } } }
那么 producer 是如何处理 ConnectionError 消息呢?
在org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnection.onCommand(Object o) 方法中:
public Response processConnectionError(final ConnectionError error) throws Exception { executor.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { onAsyncException(error.getException()); } }); return null; }