目标:
掌握@Target注释
掌握@Document注释
掌握@inherited注释
之前定义的annotation,如果没有明确声明,可以在任何地方使用:
package 类集;
@MyDefaultAnnotationReflect(key="MLDN",value="www.mldnjava.cn") --此注释是上一节中定义的
public class SimpleBeanOne{
@MyDefaultAnnotationReflect(key="MLDN",value="www.mldnjava.cn")
public String toString(){
return "Hello LiXingHua!!!" ;
}
};
如果需要指定其使用范围,必须要使用@Target注释:
@Target
Target注释类型的必须元素如下:
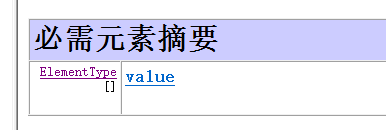
ElementType枚举常量:

现在定义一个annotation,只能在类上使用,类型是Type
import java.lang.annotation.Target ;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType ;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention ;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy ;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) // 此注释只能用在类上
@Retention(value=RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyTargetAnntation{
public String key() default "LXH" ;
public String value() default "李兴华" ;
}
此时在simpleBean的类及方法的声明上使用此annotation。
@MyTargetAnntation(key="MLDN",value="www.mldnjava.cn")
public class SimpleBean{
@MyTargetAnntation(key="MLDN",value="www.mldnjava.cn") --这里会报错,因为上面声明了只能在类中使用。
public String toString(){
return "Hello LiXingHua!!!" ;
}
};
现在如果想在类和方法都能使用,则必须设置多个范围。
import java.lang.annotation.Target ; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType ; import java.lang.annotation.Retention ; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy ; @Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD}) // 此注释只能用在类和方法上 @Retention(value=RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyTargetAnntation{ public String key() default "LXH" ; public String value() default "李兴华" ; }
@Document
@Document可以在任何的annotation上使用,所有annotation默认都是使用@Document进行注释的。
而且在生成javadoc的使用可以通过@Document设置一些说明信息。
定义一个@Document的注释:
import java.lang.annotation.Documented ;
@Documented
public @interface MyDocumentedAnntation{
public String key() default "LXH" ;
public String value() default "李兴华" ;
}
成功之后,在使用此annotation的时候就可以增加一些信息上去了。
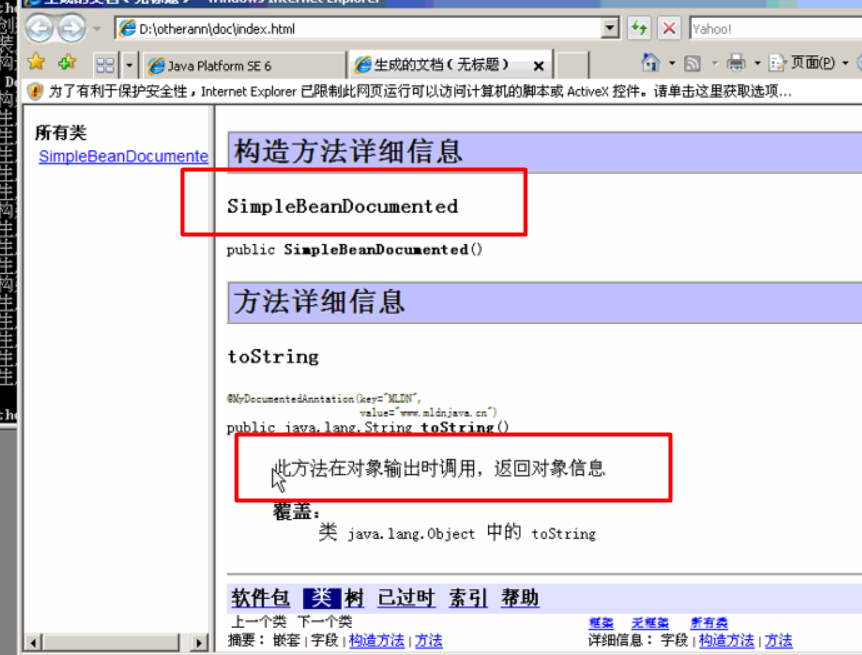
@MyDocumentedAnntation(key="MLDN",value="www.mldnjava.cn") public class SimpleBeanDocumented{ /** * 此方法在对象输出时调用,返回对象信息 */ @MyDocumentedAnntation(key="MLDN",value="www.mldnjava.cn") public String toString(){ return "Hello LiXingHua!!!" ; } };
之后通过javadoc命令,生成java.doc文档。
打开文档,发现文档的内容把刚定义的类的信息加上去了。

2,
@Inhenited注释
此注释表示一个annotation是否可以被继承下来。
package org.lxh.demo16.inheriteddemo ;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention ;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy ;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented ;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited ;
@Documented
@Inherited
@Retention(value=RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyInheritedAnnotation{
public String name() ;
}
定义一个父类,在父类使用此annotation。
package org.lxh.demo16.inheriteddemo ;
@MyInheritedAnnotation(name="李兴华")
public class Person{
};
定义子类
package org.lxh.demo16.inheriteddemo ;
public class Student extends Person{
};
按照所解释:使用的inherited声明的annotation是可以被子类继承下来的。用反射来检验一下:
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation ; import org.lxh.demo16.inheriteddemo.MyInheritedAnnotation ;//注意,要把这个annotation包也导入。 public class ReflectInheritedDemo{ public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{ Class<?> c = null ; c = Class.forName("org.lxh.demo16.inheriteddemo.Student") ; Annotation ann[] = c.getAnnotations() ; // 取得全部的Annotation for(Annotation a:ann){ // 输出 System.out.println(a) ; } // 继续取得此Annotation设置的内容,这里前面讲过 if(c.isAnnotationPresent(MyInheritedAnnotation.class)){ //是否包含这种annotation。 MyInheritedAnnotation mda = null ; mda = c.getAnnotation(MyInheritedAnnotation.class) ;//获取C这个class对象里面的这个annotation对象, String name = mda.name() ; // 取出name的内容 System.out.println("name = " + name) ; } } }
输出结果:

总结:
1,熟悉Document注释的作用。加入说明信息。
2,属性Target作用,并使用Target注释指定注释的使用位置。
3,如果一个annotation要想被子类继承下来,则使用inherited注释说明。
4,反射机制对于操作annotation是最重要的。