虽然 vue2 到 vue3 的实现大改,但在用法上变化基本不大,比较明显的一个变化就是添加了 setup(){} 函数了,
几乎所有的配置变成了以函数的方式进行定义。
即使是这样,但小改动还是很多的。
这里默认你已经熟练掌握了 vue 2.x 的使用。
一、新增composition-api
1.逻辑复用和代码组织
这是 vue 3.0 的一个核心变更了。除了改了我们定义状态的书写方式外,也为我们提供体验更棒的逻辑复用和代码组织,
新的方式可以让你把同一个业务逻辑的代码(状态,计算属性,方法等)都放到一块。
这听起来可能有点不明不白,但如果你写过比较复杂的组件,你就会发现,这个好。
2.更好的类型推断
更好的支持 TypeScript。
teleport 组件
teleport 组件它只是单纯的把定义在其内部的内容转移到目标元素中,在元素结构上不会产生多余的元素,当然也不会影响到组件树,它相关于透明的存在。为什么要有这个组件?为了有更好的代码组织体验。比如:有时,组件模板的一部分在逻辑上属于此组件,但从技术角度来看(如:样式化需求),最好将模板的这一部分移动到 DOM 中的其他位置。
比如:一些 UI 组件库的 模态窗、对话框、通知,下拉菜单等需要通知 z-index 来控制层级关系,如果都只是在不同的组件或者元素层级中,那么 z-index 的层级顺序就难以保证。可能你会说很多 UI 库不是都已经是这样的实现了的吗?至于这个 UI 库是如何实现的,我猜应该是直接操作 DOM。为什么还要提供这个 teleport 组件呢?可能是因为vue 本身的使命使然:尽量不让开发者直接操作 DOM,这些事都统一由 VUE 来完成。开发者可以把更多的时间放在业务的开发上。
<teleport to="#modals"> <div>A</div></teleport>
<teleport to="#modals"> <div>B</div></teleport>
<!-- result-->
<div id="modals"> <div>A</div> <div>B</div></div>
Suspense
加载异步组件,在异步组件加载完成成并完全渲染之前 suspense 会先显示 #fallback 插槽的内容 。
<Suspense>
<template> <Suspended-component /> </template>
<template #fallback> Loading... </template>
</Suspense>
#fallback 其实是插件 v-solt 的简写,而第一个 template 没有给,则为默认插槽。
变更
插槽 slot 语法
适用版本:Version: 2.x,Version: 3.x
未来版本的 vue 中可以说合二为一了(slot 和 slot-scope)
<!-- vue 2.x -->
<foo> <bar slot="one" slot-scope="one">
<div slot-scope="bar"> {{ one }} {{ bar }} </div> </bar>
<bar slot="two" slot-scope="two">
<div slot-scope="bar"> {{ two }} {{ bar }}
</div> </bar></foo>
<!-- vue 3.x -->
<foo> <template v-slot:one="one">
<bar v-slot="bar">
<div>{{ one }} {{ bar }}</div>
</bar></template>
<template v-slot:two="two"> <bar v-slot="bar"> <div>{{ two }} {{ bar }}
</div></bar> </template></foo>
我觉得这是好事,合二为一,不会让人有一点点的困惑。
简写
<TestComponent>
<template #one="{ name }">Hello {{ name }}</template>
</TestComponent>
指令动态参数
适用版本:Version: 2.x,Version: 3.x
<!-- v-bind with dynamic key -->
<div v-bind:[key]="value"></div>
<!-- v-bind shorthand with dynamic key -->
<div :[key]="value"></div>
<!-- v-on with dynamic event -->
<div v-on:[event]="handler"></div>
<!-- v-on shorthand with dynamic event -->
<div @[event]="handler"></div>
<!-- v-slot with dynamic name -->
<foo> <template v-slot:[name]> Hello </template></foo>
<!-- v-slot shorthand with dynamic name -->
<!-- pending #3 -->
<foo> <template #[name]> Default slot </template></foo>
简单地说就是指令名,事件名,插槽名,都可以使用变量来定义了。
Tree-shaking
适用版本:Version: 3.x
在 vue 3 中不会把所有的 api 都打包进来,只会 打包你用到的 api
<!-- vue 2.x -->
import Vue from 'vue'Vue.nextTick(() => {})const obj = Vue.observable({})<
!-- vue 3.x -->
import Vue, { nextTick, observable } from 'vue'Vue.nextTick // undefinednextTick(() => {})const obj = observable({})
即我们在项目中用什么什么,就只会打包什么,不会像 vue 2.x 那样全部 api 都打包。
.sync 大变样
适用版本: vue 3.x
<!-- vue 2.x -->
<MyComponent v-bind:title.sync="title" />
<!-- vue 3.x -->
<MyComponent v-model:title="title" />
也就是说,vue 3.0 又去掉了 .sync ,合并到了 v-model 里,而 v-model 的内部实现也有了小调整
元素
<input v-model="xxx">
<!-- would be shorthand for: -->
<input :model-value="xxx" @update:model-value="newValue => { xxx = newValue }">
组件
<input v-model="xxx">
<!-- would be shorthand for: -->
<input :model-value="xxx" @update:model-value="newValue => { xxx = newValue }">
不过好像组 alpha 版本的还不支持 v-model:aaa="xxx"
函数组件
适用版本: vue 3.x
<!-- vue 2.x -->
const FunctionalComp = { functional: true, render(h) {
return h('div', `Hello! ${props.name}`)
}
}
<!-- vue 3.x -->
import { h } from 'vue'const FunctionalComp = (props, { slots, attrs, emit }) => {
return h('div', `Hello! ${props.name}`)
}
不再需要 functional:true 选项,<template functional> 不再支付
异步组件也必需通过 api 方法创建
import { defineAsyncComponent } from 'vue'const AsyncComp = defineAsyncComponent(() => import('./Foo.vue'))
全局 api
适用版本: vue 3.x
在 vue 2.x 中
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.ignoredElements = [/^app-/]
Vue.use(/* ... */)
Vue.mixin(/* ... */)
Vue.component(/* ... */)
Vue.directive(/* ... */)
Vue.prototype.customProperty = () => {}
new Vue({ render: h => h(App)}).$mount('#app')
在 vue 3.x 中
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
const app = createApp(App)
app.config.isCustomElement = tag => tag.startsWith('app-')
app.use(/* ... */)
app.mixin(/* ... */)
app.component(/* ... */)
app.directive(/* ... */)
app.config.globalProperties.customProperty = () => {}
app.mount(App, '#app')
可以看到,创建实例的方式也改变了。一些全局的 api 方法也不在全局上了,而是放到了实例上。
v-model
适用版本:Version 3.x
1.原来的方式保留
<input v-model="foo">
2.可绑定多个 v-model
<InviteeForm v-model:name="inviteeName" v-model:email="inviteeEmail"/>
其实上面这种方式就相当于之前的 .sync 。
3.额外处理
<Comp v-model:foo.trim="text" v-model:bar.number="number" />
我们可以给这个属性添加额外的处理
指令的钩子函数
适用版本:Version 3.x
在 vue 3.x 中 指令的钩子函数仿照了组件中的钩子函数命名规则
vue 2.x 时
const MyDirective = {
bind(el, binding, vnode, prevVnode) {},
inserted() {},
update() {},
componentUpdated() {},
unbind() {}
}
vue 3.0 中
const MyDirective = { beforeMount(el, binding, vnode, prevVnode) {},
mounted() {},
beforeUpdate() {},
updated() {}
beforeUnmount() {},
// new unmounted() {}}
transition
适用版本:Version 3.x
当 <transition> 作为组件的根元素时,外部切换不会触发过渡效果
vue 2.x
<!-- modal component -->
<template> <transition> <div class="modal"><slot/></div> </transition></template>
<!-- usage -->
<modal v-if="showModal">hello</modal>
vue 3.x
<!-- modal component -->
<template> <transition> <div v-if="show" class="modal"><slot/></div> </transition></template>
<!-- usage --><
modal :show="showModal">hello</modal>
也就是说我们只能在 <sransition> 内使用切换。
transition-class
重命名两个过渡类
v-enter 重命名成.v-enter-from,v-leave重命名成 .v-enter-from。
.v-enter-from, .v-leave-to { opacity: 0;}.v-leave-from, .v-enter-to { opacity: 1}
Router
适合版本:Version: Vue (2.x / 3.x) Vue Router (3.x / 4.x)
1.router-link 添加 scoped-slot API 和 custom 属性,并移除了 tag 属性和 event 属性。
添加 scoped-slot 有什么用呢?
以前只能通知 active-class 来改变元素样式的,现在有了 scoped-slot 之后,我们就更加灵活了,可以根据 scoped-slot 回传的状态自定义,不管是样式还是类。
<router-link to="/" custom v-slot="{ href, navigate, isActive }">
<li :class="{ 'active': isActive }">
<a :href="href" @click="navigate"> <Icon>home</Icon><span class="xs-hidden">Home</span>
</a></li></router-link>
也就是说,新版本的 Router 就更加的纯粹,只提供给我们一些参数,让我们自己利用这些参数来实现不同的场景。
2.meta 合并
{ path: '/parent', meta: {
requiresAuth: true, isChild: false },
children: [ { path: 'child', meta: { isChild: true }}
]}
当访问 /parent/child 时,子路由中的 meta 如下:
{ requiresAuth: true, isChild: true }
合并策略与 Object.assign 类似
样式 scoped
适用版本:Version: 2.x, 3.x
旧版本写法
/* 深度选择器 *//*方式一:*/>>> .foo{ }/*方式二:*//deep/ .foo{ }/*方式三*/::v-deep .foo{ }
新版本写法
/* 深度选择器 */::v-deep(.foo) {}
除了上面的深度选择器外,还有下面的两个,写法也差不多
/* slot content 起作用 */::v-slotted(.foo) {}/* 全局 */::v-global(.foo) {}复制代码
属性值修正
适用版本:Version: 3.x
vue 本身会对元素的属性作相应的处理。
在旧版本的 vue 中处理如下:
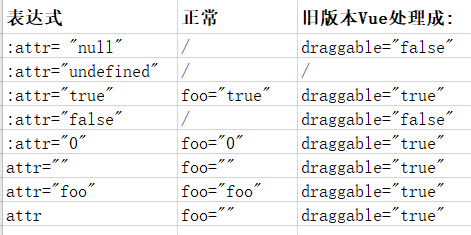
在新版本的 vue 中处理如下:
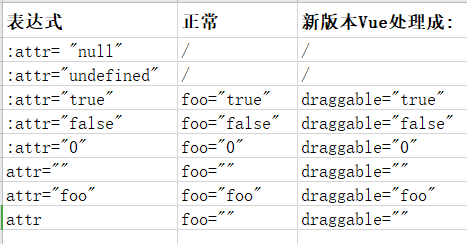
在新版本中基本保持了原样,也就是我们给元素添加什么属性值,最好 vue 处理完后还是什么属性值。
异步组件
import { defineAsyncComponent } from "vue"
// simple usageconst AsyncFoo = defineAsyncComponent(() => import("./Foo.vue"))
写法上与之前有些不一样。
动态路由
适用版本 Router 4
添加了几个方法
router.addRoute(route: RouteRecord)动态添加路由
router.removeRoute(name: string | symbol),动态删除路由
router.hasRoute(name: string | symbol): boolean ,判断路由是否存在
router.getRoutes(): RouteRecord[]获取路由列表
router.addRoute({ path: '/new-route', name: 'NewRoute', component: NewRoute})
// add to the children of an existing routerouter.addRoute('ParentRoute',
{ path: 'new-route', name: 'NewRoute', component: NewRoute})
router.removeRoute('NewRoute')
// normalized version of the records addedconst routeRecords = router.getRoutes()
emits-option
const Foo = defineComponent({
emits: { submit: (payload: { email: string; password: string }) => {
// perform runtime validation } },
methods: { onSubmit() {
this.$emit('submit', { email: 'foo@bar.com', password: 123
// Type error! })
this.$emit('non-declared-event')
// Type error! } }
})
现在的 $emit() 方法在用法上没变,但需要额外多定义 emits 对象,但要注意的是现在 alpha 版本还不支持 TypeScript
组件根元素数量
vue 3 后组件不再限制 template 中根元素的个数(旧的版本之前是只能有一个根元素)。
vue 3.x 中费弃
filters
keycode
inline-template
data-object
off 和 $once
相信你大概对 vue 3 有了一个基本的认识。
虽然不让你瞬间成为 vue 3.x 的驾驭者,
但怎么说也含蓄地体验了一把 vue 3.x 的新特性。
特别是 composition API 即使本文没有详细写出来,但通知补充的链接,你也能阅读到它的所有。我觉得 composition API 真的很棒。
原文来自 : https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1667290129402508440&wfr=spider&for=pc