Digital collectible card games have become very popular recently. So Vova decided to try one of these.
Vova has n cards in his collection. Each of these cards is characterised by its power pi, magic number ci and level li. Vova wants to build a deck with total power not less than k, but magic numbers may not allow him to do so — Vova can't place two cards in a deck if the sum of the magic numbers written on these cards is a prime number. Also Vova cannot use a card if its level is greater than the level of Vova's character.
At the moment Vova's character's level is 1. Help Vova to determine the minimum level he needs to reach in order to build a deck with the required total power.
Input
The first line contains two integers $n$ and $k$ $(1 ≤ n ≤ 100, 1 ≤ k ≤ 100000)$.
Then n lines follow, each of these lines contains three numbers that represent the corresponding card: $p_i$, $c_i$ and $l_i$ $(1 ≤ p_i ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ c_i ≤ 100000, 1 ≤ l_i ≤ n)$.
Output
If Vova won't be able to build a deck with required power, print $ - 1$. Otherwise print the minimum level Vova has to reach in order to build a deck.
题目大意
有$n$个物品,每个物品具有属性$p_i能量,c_i魔力,l_i等级$。要求选出一些物品在满足 两两魔力和为合数 且 总能量大于等于k 的情况下等级最低。
题目分析
首先可以用二分去掉等级这一维。对物品魔力的奇偶性考虑,则可以将物品分为奇偶两列,并保证了这两列物品各自是只能组成合数的(对于特殊的素数2=1+1,需要预先只保留一个能量最大且合法的1)。
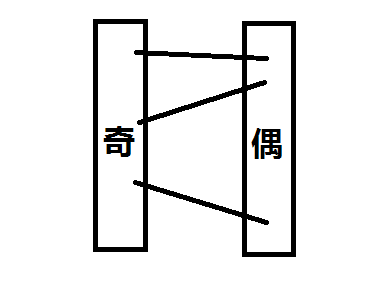
考虑以上方式的建图,直观的意义就是若选了物品i,j(各为奇偶),那么就一定会导致不合法。用边权来表示避免这种情况的代价,则是下图所示的建图方式。
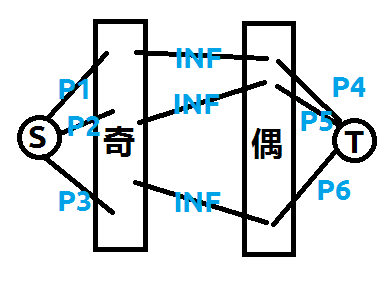
由此可见,对于一种情况的最大能量,就是该图的能量总和-最小割。
听说这是一种经典的最小割模型?
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 const int maxn = 135; 3 const int maxm = 50035; 4 const int maxNum = 200035; 5 const int INF = 2e9; 6 7 struct Edge 8 { 9 int u,v,f,c; 10 Edge(int a=0, int b=0, int c=0, int d=0):u(a),v(b),f(c),c(d) {} 11 }edges[maxm]; 12 bool pr[maxNum]; 13 int n,K,ans,L,R,mid,tag,cnt,S,T; 14 int p[maxn],c[maxn],l[maxn],sv[maxn]; 15 int edgeTot,head[maxn],nxt[maxm],lv[maxn]; 16 17 int read() 18 { 19 char ch = getchar(); 20 int num = 0, fl = 1; 21 for (; !isdigit(ch); ch = getchar()) 22 if (ch=='-') fl = -1; 23 for (; isdigit(ch); ch = getchar()) 24 num = (num<<1)+(num<<3)+ch-48; 25 return num*fl; 26 } 27 void addedge(int u, int v, int c) 28 { 29 edges[edgeTot] = Edge(u, v, 0, c), nxt[edgeTot] = head[u], head[u] = edgeTot++; 30 edges[edgeTot] = Edge(v, u, 0, 0), nxt[edgeTot] = head[v], head[v] = edgeTot++; 31 } 32 bool buildLevel() 33 { 34 memset(lv, 0, sizeof lv); 35 std::queue<int> q; 36 lv[S] = 1, q.push(S); 37 for (int tmp; q.size(); ) 38 { 39 tmp = q.front(), q.pop(); 40 for (int i=head[tmp]; i!=-1; i=nxt[i]) 41 { 42 int v = edges[i].v; 43 if (!lv[v]&&edges[i].f < edges[i].c){ 44 lv[v] = lv[tmp]+1, q.push(v); 45 if (v==T) return true; 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 return false; 50 } 51 int fndPath(int x, int lim) 52 { 53 if (x==T) return lim; 54 for (int i=head[x]; i!=-1; i=nxt[i]) 55 { 56 int v = edges[i].v, val; 57 if (lv[x]+1==lv[v]&&edges[i].f < edges[i].c){ 58 if ((val = fndPath(v, std::min(lim, edges[i].c-edges[i].f)))){ 59 edges[i].f += val, edges[i^1].f -= val; 60 return val; 61 }else lv[v] = -1; 62 } 63 } 64 return 0; 65 } 66 int dinic() 67 { 68 int ret = 0, val; 69 while (buildLevel()) 70 while ((val = fndPath(S, INF))) 71 ret += val; 72 return ret; 73 } 74 int main() 75 { 76 n = read(), K = read(); 77 for (int i=2; i<maxNum; i++) 78 if (!pr[i]) for (int j=i+i; j<maxNum; j+=i) 79 pr[j] = true; 80 for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) 81 p[i] = read(), c[i] = read(), l[i] = read(); 82 ans = -1, L = 1, R = 100, S = 0, T = n+1; 83 for (mid=(L+R)>>1; L<=R; mid=(L+R)>>1) 84 { 85 memset(head, -1, sizeof head); 86 sv[0] = tag = cnt = edgeTot = 0; 87 for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) 88 if ((c[i]==1&&p[i] > p[tag])&&(l[i] <= mid)) tag = i; 89 for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) 90 if ((c[i]!=1||i==tag)&&(l[i] <= mid)) sv[++sv[0]] = i; 91 for (int i=1; i<=sv[0]; cnt += p[sv[i]], i++) 92 if (c[sv[i]]&1) addedge(S, i, p[sv[i]]); 93 else addedge(i, T, p[sv[i]]); 94 for (int i=1; i<=sv[0]; i++) 95 if (c[sv[i]]&1) for (int j=1; j<=sv[0]; j++) 96 if ((~c[sv[j]]&1)&&(!pr[c[sv[i]]+c[sv[j]]])) 97 addedge(i, j, INF); 98 cnt -= dinic(); 99 if (cnt >= K) ans = mid, R = mid-1; 100 else L = mid+1; 101 } 102 printf("%d ",ans); 103 return 0; 104 }
END