将链表变为对象数组:public 数据类型 [] toArray()
将链表以对象数组的形式返回
任何情况下,不管是什么样的类,都不可能在类中使用输出语句,只要是想输出数据一定要将数据返回到调用处进行输出,而由于链表属于动态对象数组,最好的做法是将链表以对象数组的形式返回
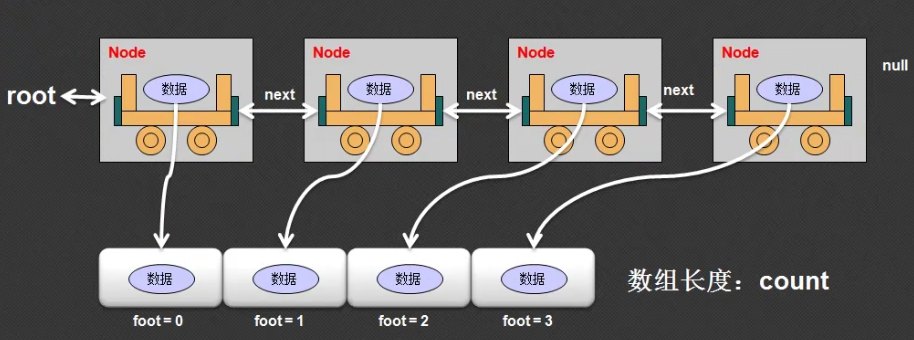
通过以上分析发现,最终Link类的toArray()方法一定要返回一个对象数组,并且这个对象数组也一定要被Node类操作,那么这个对象数组最好定义在Link类的属性里面
修改Link类的定义
增加一个返回的数组属性内容,之所以定义为属性,是因为内部类和外部类都可以访问
private String [] retArray; // 返回的数组
增加toArray()方法
public String [] toArray(){ if (this.root == null){ return null; } this.foot = 0; // 需要脚标控制 this.retArray = new String()[this.count]; //根据保存内容开辟数组 this.root.toArrayNode(); //交给Node类处理 return this.retArray; }
在Node类里面处理数组数据的保存
// 第一次调用:(Link) this = Link.root // 第二次调用:(Node) this = Link.root.next public void toArrayNode(){ Link.this.retArray[Link.this.foot ++] = this.data; if (this.next != null){ // 有后续元素 this.next.toArrayNode(); } }
实现的前提:内部类与外部类之间可以直接进行私有属性的访问
class Link{ // 链表类,外部只能看这一个类 // 定义在内部,主要为Link类服务 private class Node{ // 定义的节点类 private String data; // 保存数据 private Node next; // 引用关系 public Node(String data){ this.data = data; } public void AddNode(Node newNode){ if(this.next == null){ // 当前的下一个节点为空 this.next = newNode; }else{ // 向后继续保存 this.next.AddNode(newNode); } } public void printNode(){ // 打印Node信息 System.out.println(this.data); if( this.next != null){ this.next.printNode(); } } // 第一次调用(Link): this = Link.root // 第二次调用 (Node) : this = Link.root.next public boolean containsNode(String data){ if (data.equals(this.data)){ // 当前节点数据为要查询数据 return true; //后面不再查询了 }else{ //当前节点数据不满足查询要求 if (this.next != null){ // 有后续节点 return this.next.containsNode(data); }else{ // 没有后续节点了 return false; // 没得查了 } } } public String getNode(int index){ // 使用当前的foot内容与要查询的索引进行比较 // 随后将foot的内容自增,目的是为了下次查询方便 if (Link.this.foot++ == index){ // 如果等于,为查询的索引 return this.data; // 返回当前节点数据 }else{ // 现在应该继续向后查询 return this.next.getNode(index); } } public void setNode(int index,String data){ // 使用当前的foot内容与要修改的索引进行比较 // 随后将foot的内容自增,目的是为了下次修改方便 if(Link.this.foot++ == index){ // 如果等于,为要修改的索引 this.data = data; // 重新赋值 }else{ //继续向后查找要修改的索引 this.next.setNode(index,data); } } // 第一次调用:(Link) pervious = Link.root、this=Link.root.next // 第二次调用:(Node) pervious = this.root.next this=this.root.next.next // 要传递上一个节点以及要删除的数据 public void removeNode(Node previous,String data){ if (data.equals(this.data)){ // 当前节点为要删除节点 previous.next = this.next; // 空出当前节点 }else{ //应该向后继续查询 this.next.removeNode(this,data); } } // 第一次调用:(Link) this = Link.root // 第二次调用:(Node) this = Link.root.next public void toArrayNode(){ Link.this.retArray[Link.this.foot ++] = this.data; if (this.next != null){ // 有后续元素 this.next.toArrayNode(); } } // ===================以上为内部类============================ } private Node root; // 根结点 private int count = 0; // 保存元素的个数 private int foot = 0; private String [] retArray; // 返回的数组 public String get (int index){ if (index > this.count){ // 超过了查询的范围 return null; } this.foot = 0; // 表示从前向后查询 return this.root.getNode(index); // 查询过程交给Node类处理 } public void add(String data){ // 假设不允许有null if (data == null){ return ; } Node newNode = new Node(data); // 要保存的数据 if (this.root == null){ // 如果当前没有根节点,则设置为根节点 this.root = newNode; // 保存根节点 }else{ // 存在根节点,则到下一节点找保存数据 this.root.AddNode(newNode); } this.count ++; // 每一次保存完成后数量加一 } public int size(){ // 取得保存的数据量 return this.count; } public boolean isEmpty(){ //判断链表是否为空 return this.root == null; } public boolean contains(String data){ // 现在没有要查询的数据,要节点也不保存数据 if ( data == null || this.root == null ) { return false; //没有查询结果 } return this.root.containsNode(data); } public void set(int index,String data){ if(index > this.count){ return ; //结束方法调用 } this.foot = 0; // 重新设置foot属性的内容 this.root.setNode(index,data); //交给Node类设置数据内容 } public void remove(String data){ if(this.contains(data)){ // 一定要保证数据存在 // 要删除数据是否是根节点数据 // root是内部类的对象,此处直接访问了内部类的私有操作 if (data.equals(this.root.data)){ // 为要删除节点 this.root = this.root.next; // 突出当前根节点 }else{ // 不是根元素 // 此时根元素已经判断过了,从第二个元素开始判断 this.root.next.removeNode(this.root,data); } this.count --; } } public String [] toArray(){ if (this.root == null){ return null; } this.foot = 0; // 需要脚标控制 this.retArray = new String[this.count]; //根据保存内容开辟数组 this.root.toArrayNode(); //交给Node类处理 return this.retArray; } public void print(){ // 打印所有Node信息 this.root.printNode(); } } public class LinkDemo{ public static void main(String args[]){ Link all = new Link(); all.add("Hello"); all.add("World"); all.add("World"); all.add("World"); all.set(1,"饿了吗?"); String [] data = all.toArray(); for (int i = 0; i<data.length; i++){ System.out.println(data[i]); } } }
链表数据变为对象数组取出是最为重要的功能
这里并没有提到性能优化如,如对于大链表转换为数组的优化,这里只是基本的数据结构,为以后方便了解其它数据结构,打下基础。
如果想要提高,可以在代码的细节中再做优化