①对HashMap的整体认识
HashMap是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射。
HashMap继承于AbstractMap,实现了Map、Cloneable、java.io.Serializable接口。
HashMap的实现是不同步的,这意味着它不是线程安全的。它的key,value都可以是null。此外,HashMap中的映射不是有序的。
HashMap的实例有两个参数影响其性能:“初始容量”和“加载因子”。初始容量是哈希表在创建时的容量。加载因子是哈希表在其容量自动增加之前可以达到多满的一种尺度。通常默认加载因子是0.75,这是在时间和空间成本上寻求一种折衷。
②HashMap的构造函数
// 默认构造函数。
HashMap()
// 指定“容量大小”的构造函数
HashMap(int capacity)
// 指定“容量大小”和“加载因子”的构造函数
HashMap(int capacity, float loadFactor)
// 包含“子Map”的构造函数
HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map)
③HashMap的API
void clear()
Object clone()
boolean containsKey(Object key)
boolean containsValue(Object value)
Set<Entry<K, V>> entrySet()
V get(Object key)
boolean isEmpty()
Set<K> keySet()
V put(K key, V value)
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map)
V remove(Object key)
int size()
Collection<V> values()
④ HashMap的继承关系
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractMap<K, V>
↳ java.util.HashMap<K, V>
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable { }
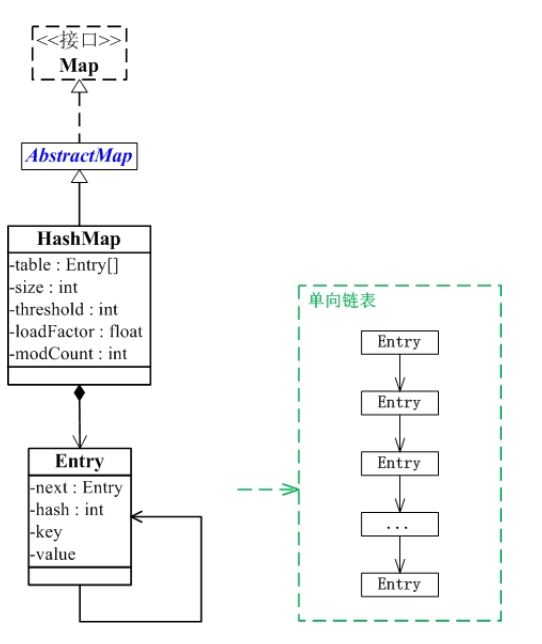
HashMap继承于AbstractMap类,实现了Map接口。Map是"key-value键值对"接口,AbstractMap实现了"键值对"的通用函数接口
HashMap是通过“拉链法”实现的哈希表。它包括几个重要的成员变量:table,size,threshold,loadFactor,modCount。
Table是一个Entry[]数组类型,Entry是一个单向链表。哈希表的key-value键值对都是存储在Entry数组中的。
Size是HashMap的大小 ,它是HashMap保存的键值对的数量。
Threshold是HashMap的阈值,用于判断是否需要调整HashMap的容量。Threshold的值=“容量*加载因子”,当HashMap中存储数据的数量达到threshold时,需要将HashMap的容量加倍。
loadFactor就是加载因子。
modCount是用来实现fail-fast机制的。
⑤HashMap遍历方式
1 遍历HashMap的键值对
第一步:根据entrySet()获取HashMap的“键值对”的Set集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。
// 假设map是HashMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
// 获取key
key = (String)entry.getKey();
// 获取value
integ = (Integer)entry.getValue();
}
2 遍历HashMap的键
第一步:根据keySet()获取HashMap的“键”的Set集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。
// 假设map是HashMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
String key = null;
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// 获取key
key = (String)iter.next();
// 根据key,获取value
integ = (Integer)map.get(key);
}
3 遍历HashMap的值
第一步:根据value()获取HashMap的“值”的集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。
// 假设map是HashMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
Integer value = null;
Collection c = map.values();
Iterator iter= c.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
value = (Integer)iter.next();
}
⑥遍历测试程序如下:
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Collection;
/*
* @desc 遍历HashMap的测试程序。
* (01) 通过entrySet()去遍历key、value,参考实现函数:
* iteratorHashMapByEntryset()
* (02) 通过keySet()去遍历key、value,参考实现函数:
* iteratorHashMapByKeyset()
* (03) 通过values()去遍历value,参考实现函数:
* iteratorHashMapJustValues()
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class HashMapIteratorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int val = 0;
String key = null;
Integer value = null;
Random r = new Random();
HashMap map = new HashMap();
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
// 随机获取一个[0,100)之间的数字
val = r.nextInt(100);
key = String.valueOf(val);
value = r.nextInt(5);
// 添加到HashMap中
map.put(key, value);
System.out.println(" key:"+key+" value:"+value);
}
// 通过entrySet()遍历HashMap的key-value
iteratorHashMapByEntryset(map) ;
// 通过keySet()遍历HashMap的key-value
iteratorHashMapByKeyset(map) ;
// 单单遍历HashMap的value
iteratorHashMapJustValues(map);
}
/*
* 通过entry set遍历HashMap
* 效率高!
*/
private static void iteratorHashMapByEntryset(HashMap map) {
if (map == null)
return ;
System.out.println("
iterator HashMap By entryset");
String key = null;
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
key = (String)entry.getKey();
integ = (Integer)entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+" -- "+integ.intValue());
}
}
/*
* 通过keyset来遍历HashMap
* 效率低!
*/
private static void iteratorHashMapByKeyset(HashMap map) {
if (map == null)
return ;
System.out.println("
iterator HashMap By keyset");
String key = null;
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
key = (String)iter.next();
integ = (Integer)map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+" -- "+integ.intValue());
}
}
/*
* 遍历HashMap的values
*/
private static void iteratorHashMapJustValues(HashMap map) {
if (map == null)
return ;
Collection c = map.values();
Iterator iter= c.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iter.next());
}
}
}
⑦通过一个实例学习如何使用HashMap
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Collection;
/*
* @desc HashMap测试程序
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testHashMapAPIs();
}
private static void testHashMapAPIs() {
// 初始化随机种子
Random r = new Random();
// 新建HashMap
HashMap map = new HashMap();
// 添加操作
map.put("one", r.nextInt(10));
map.put("two", r.nextInt(10));
map.put("three", r.nextInt(10));
// 打印出map
System.out.println("map:"+map );
// 通过Iterator遍历key-value
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
System.out.println("next : "+ entry.getKey() +" - "+entry.getValue());
}
// HashMap的键值对个数
System.out.println("size:"+map.size());
// containsKey(Object key) :是否包含键key
System.out.println("contains key two : "+map.containsKey("two"));
System.out.println("contains key five : "+map.containsKey("five"));
// containsValue(Object value) :是否包含值value
System.out.println("contains value 0 : "+map.containsValue(new Integer(0)));
// remove(Object key) : 删除键key对应的键值对
map.remove("three");
System.out.println("map:"+map );
// clear() : 清空HashMap
map.clear();
// isEmpty() : HashMap是否为空
System.out.println((map.isEmpty()?"map is empty":"map is not empty") );
}
}
运行结果
map:{two=7, one=9, three=6}
next : two - 7
next : one - 9
next : three - 6
size:3
contains key two : true
contains key five : false
contains value 0 : false
map:{two=7, one=9}
map is empty