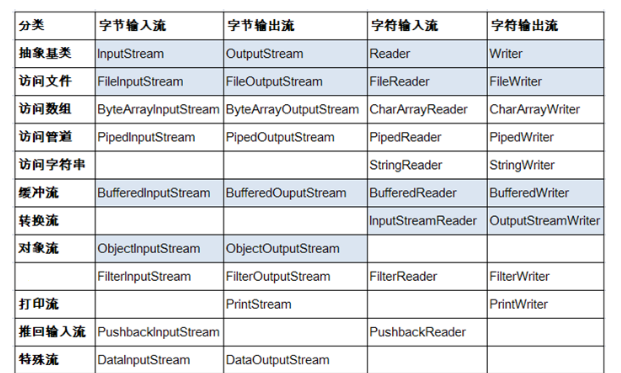
1流的分类:
按数据单位分:字节流(InputStream、OutputStream),字符流(Reader、Writer)
按流向分:输入流,输出流
按流的角色分:节电流、处理流

详细点有如下
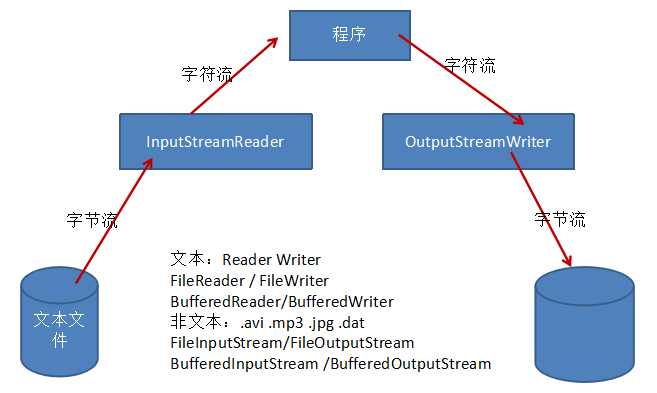
2 流的转换:InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
3 RandomAccessFile类:程序可以跳到任意位置来读写文件。
①long getFilePointer():获取文件记录指针的当前位置
②void seek(long pos):将文件记录指针定位到 pos 位置
③构造器:
public RandomAccessFile(File file, String mode)
public RandomAccessFile(String name, String mode)
关于mode:该参数指定RandomAccessFile的访问模式
如:
r: 以只读方式打开
rw:打开以便读取和写入
rwd:打开以便读取和写入;同步文件内容的更新
rws:打开以便读取和写入;同步文件内容和元数据的更
代码举例:
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.RandomAccessFile; 4 5 import org.junit.Test; 6 7 public class TestRandomAccessFile { 8 @Test 9 public void test1() throws Exception { 10 RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(new File("hello.txt"), "rw"); 11 12 // raf.seek(7); 13 // raf.write("xyz".getBytes()); 14 // 15 // raf.close(); 16 //1. 17 raf.seek(7); 18 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); 19 byte[] b = new byte[20]; 20 int len; 21 while((len = raf.read(b)) != -1){ 22 String str = new String(b,0,len); 23 sb.append(str); 24 } 25 //2. 26 raf.seek(7); 27 raf.write("xyz".getBytes()); 28 raf.write(sb.toString().getBytes()); 29 30 raf.close(); 31 } 32 }