Django 缓存
缓存的意义:
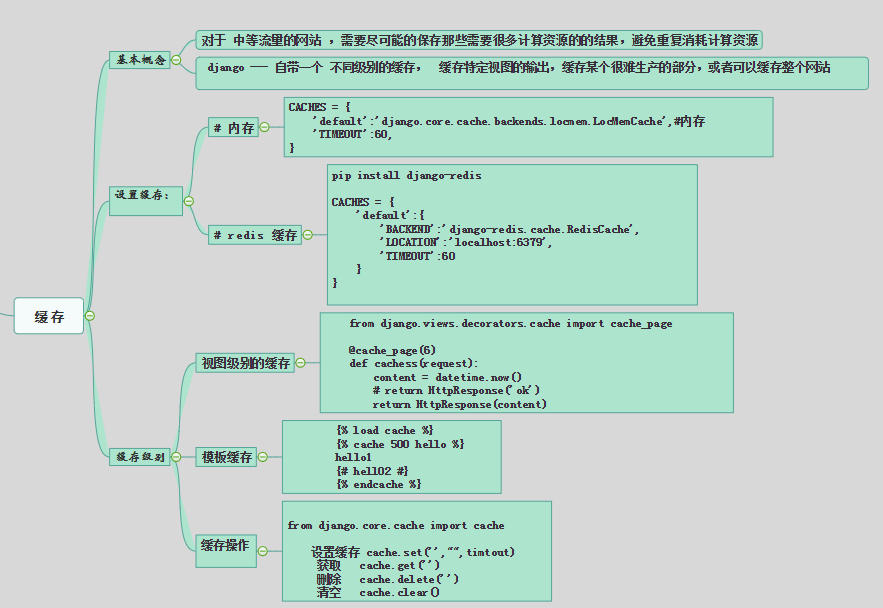
对于 中等流量的网站 ,需要尽可能的保存那些需要很多计算资源的的结果,避免重复消耗计算资源
django --- 自带一个 不同级别的缓存,
缓存特定视图的输出,缓存某个很难生产的部分,或者可以缓存整个网站
一般主页 会设置缓存
设置缓存:
数据库;
文件系统;
内存中;
settings 中 caches
内存
CACHES = {
'default':'django.core.cache.backends.locmem.LocMemCache',#内存
'TIMEOUT':60,
}
redis 缓存
pip install django-redis
CACHES = {
'default':{
'BACKEND':'django-redis.cache.RedisCache',
'LOCATION':'localhost:6379',
'TIMEOUT':60
}
}
连接数据库
默认到 0 数据库
redis-cli
select 0
keys *
视图级别的缓存
from django.views.decorators.cache import cache_page
@cache_page(6)
def cachess(request):
content = datetime.now()
# return HttpResponse('ok')
return HttpResponse(content)
模板缓存
{% load cache %}
{% cache 500 hello %}
hello1
{# hell02 #}
{% endcache %}
缓存操作
from django.core.cache import cache
设置缓存 cache.set('',"",timtout)
获取 cache.get('')
删除 cache.delete('')
清空 cache.clear()