1、HandlerMapping实现原理及源码解析
在前面讲解Spring MVC工作流程的时候我们说过,前端控制器收到请求后会调⽤处理器映射器(HandlerMapping),处理器映射器根据请求Url找到具体的处理器(Handler),生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有)一并返回给前端控制器。HandlerMapping就是处理器映射器,其作用就是根据当前请求的找到对应的 Handler,并将 Handler(执行程序)与一堆 HandlerInterceptor(拦截器)封装到HandlerExecutionChain 对象中。
HandlerMapping 具体的表现形式可以是类,也可以是⽅法。⽐如,标注了@RequestMapping的每个⽅法都可以看成是⼀个Handler。Handler负责具体实际的请求处理,在请求到达后,HandlerMapping 的作用便是找到请求相应的处理器Handler 和 Interceptor。
在 HandlerMapping 接口的内部只有一个方法:HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception; 这个方法由 AbstractHandlerMapping 实现,实现方法如下:
/** * Look up a handler for the given request, falling back to the default * handler if no specific one is found. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the corresponding handler instance, or the default handler * @see #getHandlerInternal */ @Override @Nullable public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { // 根据请求获取执行程序,具体的获取方式由子类决定 // getHandlerInternal() 是抽象方法 Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); if (handler == null) { handler = getDefaultHandler(); } if (handler == null) { return null; } // Bean name or resolved handler? if (handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } // 将 Handler 与一堆拦截器包装到 HandlerExecutionChain 对象中 HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler); } else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) { logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler()); } if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) { CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request); CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request); CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig); executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config); } return executionChain; }
可以看到在这个方法中调用了 getHandlerInternal() 方法获取到了 Handler 对象,而 Handler 对象具体内容是由它的子类去定义的。
HandlerMapping 有很多个实现类,如下图所示:
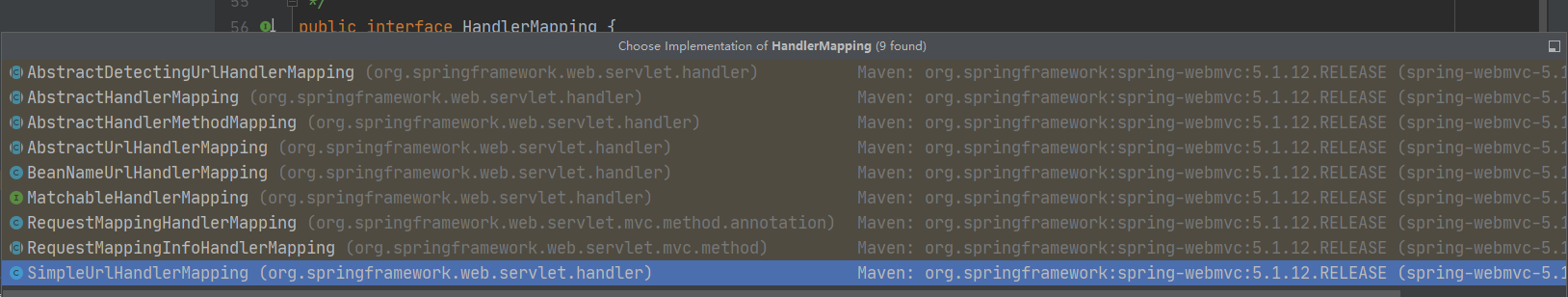
它主要有两个分支,分别继承自 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping(得到 HandlerMethod)和 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping(得到 HttpRequestHandler、Controller 或 Servlet),它们又统一继承于 AbstractHandlerMapping,如下图所示:

下面就来看一下 AbstractHandlerMapping 的两个分支子类(AbstractUrlHandlerMapping和AbstractHandlerMethodMapping)。
1.1、AbstractUrlHandlerMapping
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping 这个分支获取的 Handler 的类型实际就是一个 Controller 类,所以一个 Controller 只能对应一个请求(或者像 Struts2 那样定位到方法,使同一个业务的方法放在同一个类里).
上文中getHandler的实现方法中调用的getHandlerInternal方法(根据请求获取执行程序)就是在AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中,源码如下所示:
/** * Look up a handler for the URL path of the given request. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the handler instance, or {@code null} if none found */ @Override @Nullable protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { // 根据当前请求获取 查找路径 String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); // 根据路径获取 Handler(即Controller),先尝试直接匹配,再尝试模式匹配 Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request); if (handler == null) { // We need to care for the default handler directly, since we need to // expose the PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE for it as well. Object rawHandler = null; if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) { rawHandler = getRootHandler(); } if (rawHandler == null) { rawHandler = getDefaultHandler(); } if (rawHandler != null) { // Bean name or resolved handler? if (rawHandler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) rawHandler; rawHandler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } validateHandler(rawHandler, request); handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null); } } return handler; }
1.2、AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 这个分支获取的 Handler 的类型是 HandlerMethod,即这个 Handler 是一个方法,它保存了方法的信息(如Method),这样一个 Controller 就可以处理多个请求了,源码如下所示:
/** * Look up a handler method for the given request. */ @Override protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { // 根据当前请求获取 查找路径 String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); // 内部类对象获取锁 this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock(); try { // 获取当前请求最佳匹配的处理方法(即Controller类的方法) HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null); } finally { // 内部类对象释放锁 this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock(); } }
上述代码中 lookupHandlerMethod() 方法的主要工作是在 Map<T, HandlerMethod> handlerMethods 中找到 HandlerMethod,这里的 T 是 HandlerMappingInfo,它封装了 @RequestMapping 注解中的信息。lookupHandlerMethod的源码如下图所示:
/** * Look up the best-matching handler method for the current request. * If multiple matches are found, the best match is selected. * @param lookupPath mapping lookup path within the current servlet mapping * @param request the current request * @return the best-matching handler method, or {@code null} if no match * @see #handleMatch(Object, String, HttpServletRequest) * @see #handleNoMatch(Set, String, HttpServletRequest) */ @Nullable protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>(); List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath); if (directPathMatches != null) { addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request); } if (matches.isEmpty()) { // No choice but to go through all mappings... addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request); } if (!matches.isEmpty()) { Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request)); matches.sort(comparator); Match bestMatch = matches.get(0); if (matches.size() > 1) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches); } if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) { return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH; } Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1); if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) { Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); String uri = request.getRequestURI(); throw new IllegalStateException( "Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}"); } } request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod); handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request); return bestMatch.handlerMethod; } else { return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request); } }
那么 HandlerMethod 是怎么创建的(即怎么把 Controller 的方法变成了它)?继续看一下源码找到 initHandlerMethods() 方法,这个方法是在这个类创建后调用的,如下所示是它的源码(包含其调用的子方法的源码):
/** * Scan beans in the ApplicationContext, detect and register handler methods. * @see #getCandidateBeanNames() * @see #processCandidateBean * @see #handlerMethodsInitialized */ protected void initHandlerMethods() { for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) { if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) { processCandidateBean(beanName); } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); } /** * Determine the names of candidate beans in the application context. * @since 5.1 * @see #setDetectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts * @see BeanFactoryUtils#beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors */ protected String[] getCandidateBeanNames() { // 从容器中获取所有 Bean 的名称,detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts 默认false,不从父容器中查找 // 即默认只查找 SpringMVC 的 IOC 容器,不查找它的父容器 Spring 的 IOC 容器 return (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), Object.class) : obtainApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); } /** * Determine the type of the specified candidate bean and call * {@link #detectHandlerMethods} if identified as a handler type. * <p>This implementation avoids bean creation through checking * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory#getType} * and calling {@link #detectHandlerMethods} with the bean name. * @param beanName the name of the candidate bean * @since 5.1 * @see #isHandler * @see #detectHandlerMethods */ protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) { Class<?> beanType = null; try { beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { // An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it. if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex); } } // 这里的 isHandler()方法由子类实现,判断是否拥有 @Controller 注解或 @RequestMapping 注解 if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) { // 利用反射得到 Bean 中的 Method 并包装成 HandlerMethod,然后放入 Map 中 detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } /** * Look for handler methods in the specified handler bean. * @param handler either a bean name or an actual handler instance * @see #getMappingForMethod */ protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) { // 获取这个 Bean 的 Class 对象 Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ? obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass()); if (handlerType != null) { // 获取被代理前的原始类型 Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); // 获取 Method // 这里的 T 就是 RequestMappingInfo,它封装了 @RequestMapping 信息 Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType, (MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> { try { // 根据 Method 和它的 @RequestMapping 注解,创建 RequestMappingInfo 对象。 return getMappingForMethod(method, userType); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" + userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex); } }); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods)); } methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> { Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType); // 注册 Method 和它的映射,RequestMappingInfo 储存着映射信息 registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping); }); } }
看完上述代码后,可以知道是在 detectHandlerMethods() 方法中将 Bean 的方法转换为 HandlerMethod 对象。
最后在 registerHandlerMethod() 方法中,将 RequestMappingInfo 作为 key,把 Method 包装成 HandlerMethod 作为 value 添加到了 Map<T, HandlerMethod> handlerMethods 中。registerHandlerMethod的源码如下所示:
/** * Register a handler method and its unique mapping. Invoked at startup for * each detected handler method. * @param handler the bean name of the handler or the handler instance * @param method the method to register * @param mapping the mapping conditions associated with the handler method * @throws IllegalStateException if another method was already registered * under the same mapping */ protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) { this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method); } public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) { this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock(); try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method); assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping); this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod); List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping); for (String url : directUrls) { this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping); } String name = null; if (getNamingStrategy() != null) { name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping); addMappingName(name, handlerMethod); } CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping); if (corsConfig != null) { this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig); } this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name)); } finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock(); }
}
1.3、AbstractHandlerMapping 实现类及使用

AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> 只有一个实现类:RequestMappingHandlerMapping(下文中会介绍该类)。
2、HandlerAdapter实现原理及源码解析
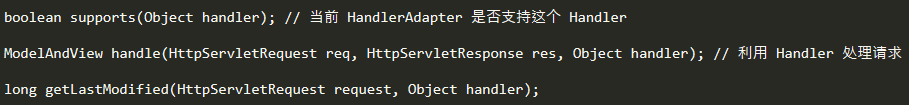
HandlerAdapter的作用是根据 Handler 来找到支持它的 HandlerAdapter,通过 HandlerAdapter 执行这个 Handler 得到 ModelAndView 对象。HandlerAdapter 接口中的方法如下:
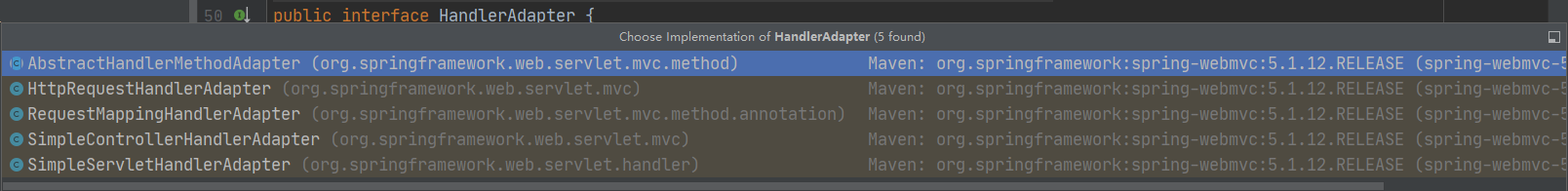
它有以下实现类:
2.1、RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
从上面的文章中可以知道,利用 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 获取的 Handler 是 HandlerMethod 类型,它代表 Controller 里要执行的方法,而 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 可以执行 HandlerMethod 对象。
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 的 handle() 方法是在它的父类 AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter 类中实现的,源码如下所示:
/** * This implementation expects the handler to be an {@link HandlerMethod}. */ @Override @Nullable public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler); }
handleInternal() 方法是由 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 自己来实现的,源码如下所示:
/** * Use the given handler method to handle the request. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @param handlerMethod handler method to use. This object must have previously been passed to the * {@link #supportsInternal(HandlerMethod)} this interface, which must have returned {@code true}. * @return a ModelAndView object with the name of the view and the required model data, * or {@code null} if the request has been handled directly * @throws Exception in case of errors */ @Override protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { ModelAndView mav; checkRequest(request); // Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.(是否需要在 synchronize 块中执行) if (this.synchronizeOnSession) { HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); if (session != null) { Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session); synchronized (mutex) { // 执行 HandlerMethod mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); } } else { // No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); } } else { // No synchronization on session demanded at all... mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); } if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) { // 是否通过 @SessionAttributes 注释声明了 session 属性 if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) { applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers); } else { prepareResponse(response); } } // 执行 HandlerMethod(invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);),得到 ModelAndView return mav; }
继续来看一下如何得到 ModelAndView,invokeHandlerMethod() 方法如下:
/** * Invoke the {@link RequestMapping} handler method preparing a {@link ModelAndView} * if view resolution is required. * @since 4.2 * @see #createInvocableHandlerMethod(HandlerMethod) */ @Nullable protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response); try { // 数据绑定 WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod); ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory); // 绑定参数,执行方法 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod); if (this.argumentResolvers != null) { invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers); } if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) { invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers); } invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory); invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer); // 创建模型和视图容器 ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer(); // 设置FlasgMap中的值 mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request)); // 初始化模型 modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod); mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect); AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response); asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor); asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors); asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors); if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) { Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult(); mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0]; asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult(); LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> { String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn); return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]"; }); invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result); } invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return null; } return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest); } finally { webRequest.requestCompleted(); } }
2.2、HttpRequestHandlerAdapter
HttpRequestHandlerAdapter 可以执行 HttpRequestHandler 类型的 Handler,源码如下:
@Override @Nullable public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { ((HttpRequestHandler) handler).handleRequest(request, response); return null; }
2.3、SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter 可以执行 Controller 类型的 Handler,源码如下:
@Override @Nullable public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response); }
2.4、SimpleServletHandlerAdapter
SimpleServletHandlerAdapter 可以执行 Servlet 类型的 Handler,源码如下:
@Override @Nullable public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { ((Servlet) handler).service(request, response); return null; }