(1)问题描述:有一批共 n 个集装箱要装上 2 艘载重量分别为 capacity1 和 capacity2 的轮船,其中集装箱 i 的重量为 wi,且装载问题要求确定是否有一个合理的装载方案可将这些集装箱装上这 2 艘轮船。如果有,找出一种装载方案。
例如:当 n = 3, capacity1 = capacity2= 50, 且 w = [10, 40, 40] 时,则可以将集装箱 1 和 2 装到第一艘轮船上,而将集装箱 3 装到第二艘轮船上;如果 w = [20, 40, 40],则无法将这 3 个集装箱都装上轮船。
(2)基本思路: 容易证明,如果一个给定装载问题有解,则采用下面的策略可得到最优装载方案。
a. 首先将第一艘轮船尽可能装满;
b. 将剩余的集装箱装上第二艘轮船。
将第一艘轮船尽可能装满等价于选取全体集装箱的一个子集,使该子集中集装箱重量之和最接近 capacity1 。由此可知,装载问题等价于以下特殊的 0-1 背包问题。
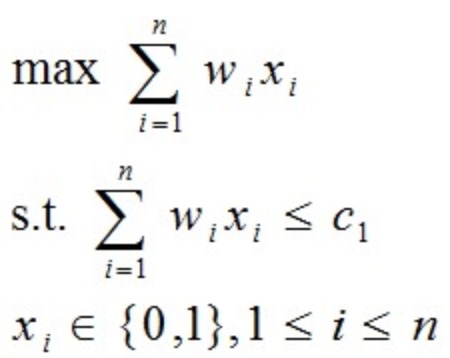
变量 Xi = 0 表示不装入集装箱 i,Xi = 1 表示装入集装箱 i;
用回溯法设计解装载问题的O(2n)计算时间算法。在某些情况下该算法优于动态规划算法。
(3)算法设计:
子集树模板算法,时间复杂度为:O(2n)
用回溯法解装载问题时,用子集树表示其解空间显然是最合适的,用可行性约束函数可剪去不满足约束条件的子树。
可以引入一个上界函数,用于剪去不含最优解的子树,从而改进算法在平均情况下的运行效率。设z是解空间树第 i 层上的当前扩展结点。currentWeight 是当前载重量;bestWeight 是当前最优载重量;indeterminacyWeight 是剩余集装箱的重。定义上界函数为 currentWeight + indeterminacyWeight。在以 z 为根的子树中任一叶结点所相应的载重量,当currentWeight + indeterminacyWeight <= bestWeight 时,可将z的右子树剪去。
(4)算法代码:

public class ExcellentLoading { /** * 物品数量 */ private static Integer num; /** * 物品重量数组 */ private static Integer[] weight; /** * 物品存储数组【0:不存放 1:存放】 */ private static Integer[] store; /** * 船的容量 */ private static Integer capacity; /** * 船的最优载重量【最优解】 */ private static Integer bestWeight = 0; /** * 未确定物品的载重量 */ private static Integer indeterminacyWeight = 0; /** * 船的当前载重量 */ private static Integer currentWeight = 0; /** * 物品最优解的下标数组 */ private static Integer[] bestIndex; /** * 初始化数据 */ private static void initData() { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入船的容量:"); capacity = input.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入物品的数量:"); num = input.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入各个物品的重量"); weight = new Integer[num]; store = new Integer[num]; bestIndex = new Integer[num]; for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { weight[i] = input.nextInt(); indeterminacyWeight += weight[i]; store[i] = 0; bestIndex[i] = i; } } /** * 装载 */ private static void loadingBacktrack(Integer i) { if (i == weight.length) { // 到达叶子结点 if (currentWeight > bestWeight) { // 当前船的装载量 > 最优解,赋值操作 for (int j = 0; j < weight.length; j++) { bestIndex[j] = store[j]; } bestWeight = currentWeight; } return; } indeterminacyWeight -= weight[i]; // 减去已被确定该讨论的物品重量 if (currentWeight + weight[i] <= capacity) { // 搜索左子树 store[i] = 1; // 物品装载 currentWeight += weight[i]; // 当前船的载重量 + 该物品重量 loadingBacktrack(i + 1); currentWeight -= weight[i]; // 当前船的载重量 - 该物品重量【回溯到上一层,讨论该物品不装】 } if (currentWeight + indeterminacyWeight > bestWeight) { // 搜索右子树 || 剪枝函数【如果船的当前载重量 + 未确定物品的重量 <= 当前船的最优值,直接剪掉】 store[i] = 0; // 该物品不装 loadingBacktrack(i + 1); } indeterminacyWeight += weight[i]; } /** * 输出 */ private static void print() { System.out.println("船装载物品最优解:"); Stream.of(bestIndex).forEach(element -> System.out.print(element + " ")); System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // 初始化数据 initData(); // 装载 loadingBacktrack(0); // 输出 print(); } }
(5)输入输出

请输入船的容量: 60 请输入物品的数量: 5 请输入各个物品的重量 10 25 30 10 5 船装载物品最优解: 0 1 1 0 1
(6)总结:最优装载诠释了回溯算法中子集树的核心思想,类似于 0 - 1 背包问题,集装 i 箱装与不装,回溯判断最优解,使用剪枝函数去除不必要的无效搜索,否则进入右子树再次进入深度搜索,直至深度搜索完整棵二叉树,搜索出所有的解,找出最优解即可;
回溯算法子集树的时间复杂度 O(2n),递归求解,不太好想,希望各位在纸上画一画,模拟我的代码走一遍流程,便于大家理解回溯算法,递归算法。
