由于用的是效率比较低的枚举,为了避免程序运行时间太长,这里就改为6*6的棋盘
你也可以将宏定义中间的X和Y改为你想要的长和宽。。
/* * author: buer * github: buer0.github.com */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define X 6 //定义棋盘的行数 #define Y 6 //定义棋盘的列数 #define SUC 1 #define ERR 0 int getNext(int chess[][Y], int *x, int *y, int count) { if(count>8) { return ERR; } switch(count) { case 1: if(*x+1>=X || *y-2<0 || chess[*x+1][*y-2] != 0) { return ERR; } *x += 1; *y -= 2; return SUC; break; case 2: if(*x+2>=X || *y-1<0 || chess[*x+2][*y-1] != 0) { return ERR; } *x += 2; *y -= 1; return SUC; break; case 3: if(*x+2>=X || *y+1>=Y || chess[*x+2][*y+1] != 0) { return ERR; } *x += 2; *y += 1; return SUC; break; case 4: if(*x+1>=X || *y+2>=Y || chess[*x+1][*y+2] != 0) { return ERR; } *x += 1; *y += 2; return SUC; break; case 5: if(*x-1<0 || *y+2>=Y || chess[*x-1][*y+2] != 0) { return ERR; } *x -= 1; *y += 2; return SUC; break; case 6: if(*x-2<0 || *y+1>=Y || chess[*x-2][*y+1] != 0) { return ERR; } *x -= 2; *y += 1; return SUC; break; case 7: if(*x-2<0 || *y-1<0 || chess[*x-2][*y-1] != 0) { return ERR; } *x -= 2; *y -= 1; return SUC; break; case 8: if(*x-1<0 || *y-2<0 || chess[*x-1][*y-2] != 0) { return ERR; } *x -= 1; *y -= 2; return SUC; break; default: return ERR; break; } } int travel(int chess[][Y], int x, int y, int tag) { int i; int x1 = x; int y1 = y; if(tag > X*Y) { return SUC; } for(i=1; i<=8; i++) { if( getNext(chess, &x1, &y1, i) ) { chess[x1][y1] = tag; if( travel(chess, x1, y1, tag+1) ) { return SUC; }else { chess[x1][y1] = 0; x1 = x; y1 = y; } } } return ERR; } void printChess(int chess[][Y]) { int i, j; for(i=0;i<X;i++) { for(j=0;j<Y;j++) { printf("%2d ", chess[i][j]); } printf(" "); } printf(" "); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int chess[X][Y]; int i,j,res; for(i=0;i<X;i++) { for(j=0;j<Y;j++) { chess[i][j] = 0; } } chess[2][0] = 1; res = travel(chess, 2, 0, 2); if(res == SUC) { printf("success "); printChess(chess); }else { printf("failed"); } return 0; }
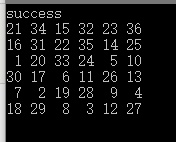
运行结果: