Executor框架最核心的类是ThreadPoolExecutor它是线程的核型类,主要由下列4个组件构成。
1.corePool:核心线程池的大小
2.maximumPool:最大线程池的大小
3.BlockingQueue:用来暂时保存任务的工作队列
4.RejectedExecutionHandler:当ThreadPoolExecutor已经关闭或ThradPoolExecutor已经饱和时(达到了最大线程池大小且工作队列已满),execute()方法将要调用Handler.
下面通过Executor框架的工具类Executors,可以创建3种类型的ThreadPoolExecutor:
1.FixedThreadPool
2.SingleThreadExecutor
3.CachedThreadPool
1.FixedThreadPool的创建方式:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
corePool 和 maximumPool 等于nThreads指定线程数。当线程池中的线程数大于corePoolsize时,keepAliveTime为多余的空闲线程等待新任务的最长时间,超过这个时间后多余的线程将被终止。
这里将keepAliveTime设置为0l,意味者将多余空闲线程将会立即终止。
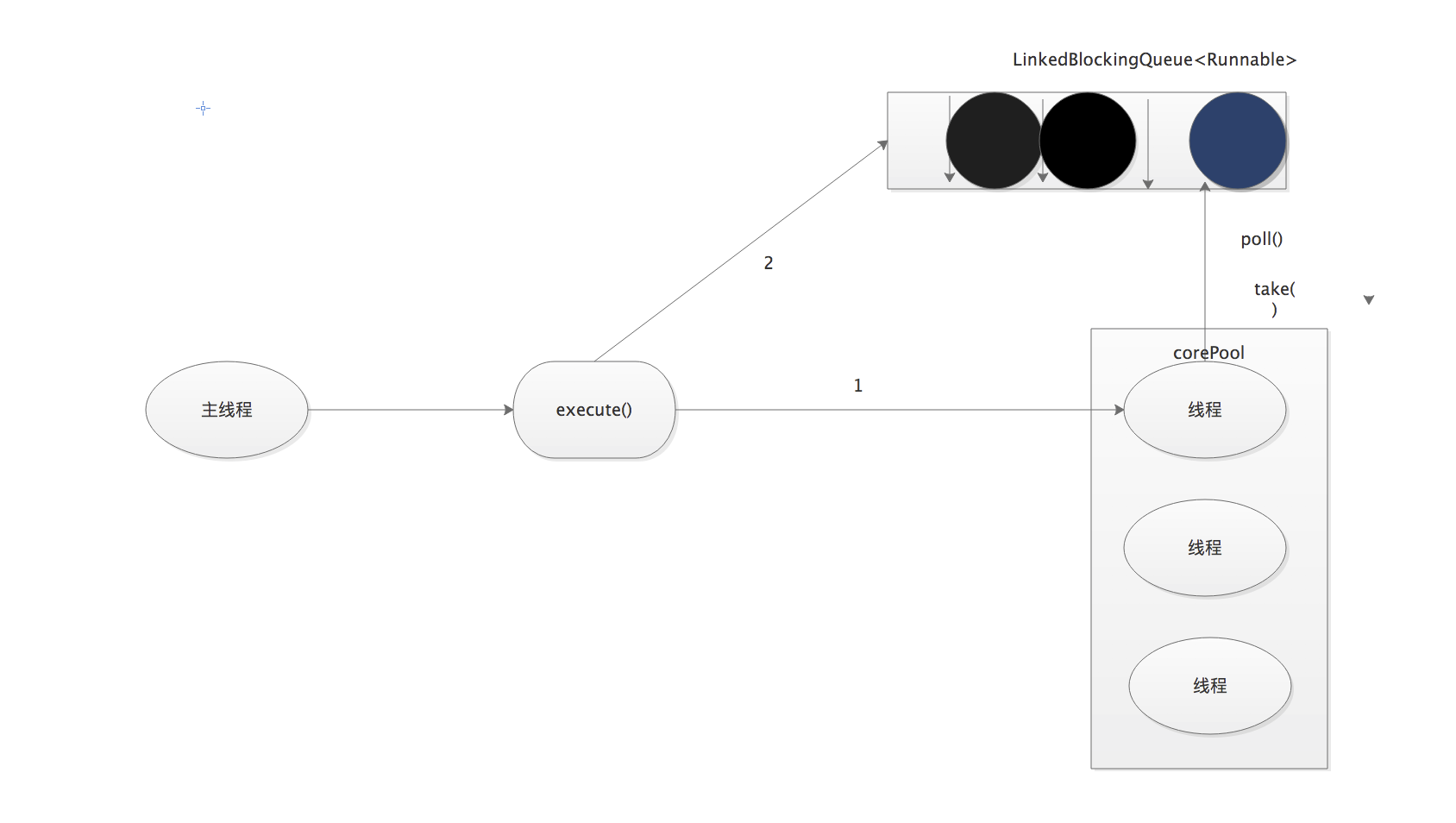
1)如果当前运行的线程数少于corePoolSize,则创建新线程来执行任务。
2)在线程池完成预热之后(当前运行的线程数等于corePoolSize),将任务加入LinkedBlockingQueue.
3) 线程执行完1中的任务后,会在循环中反复从LinkedBlockingQueue获取任务来执行
FixedThreadPool使用无界队列作为线程池中的工作队列(队列容量为Interger.MAX_VALUE).使用无界队列作为工作队列。
1)当线程池中的线程数达到corePoolSize后,新任务将在无解队列中等待,因此线程池中的线程数不会超过corePoolSize
2) 由于1,使用无界队列时maximumPoolSize将是一个无效参数
3)由于1和2,使用无界队列时keepAliveTime将是一个无效参数
4)由于使用无解队列,运行中的FixedThreadPool(未执行方法shutdown()或shutdownNow())不会拒绝任务(不会调用RejectedExecutionHandler.rejectedExecution方法)
2.SingleThreadExecutor
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
SinggleThreadExecutor的corePoolSize和maximumPoolSize被设置为1.其他参数与FixedThreadPool相同。
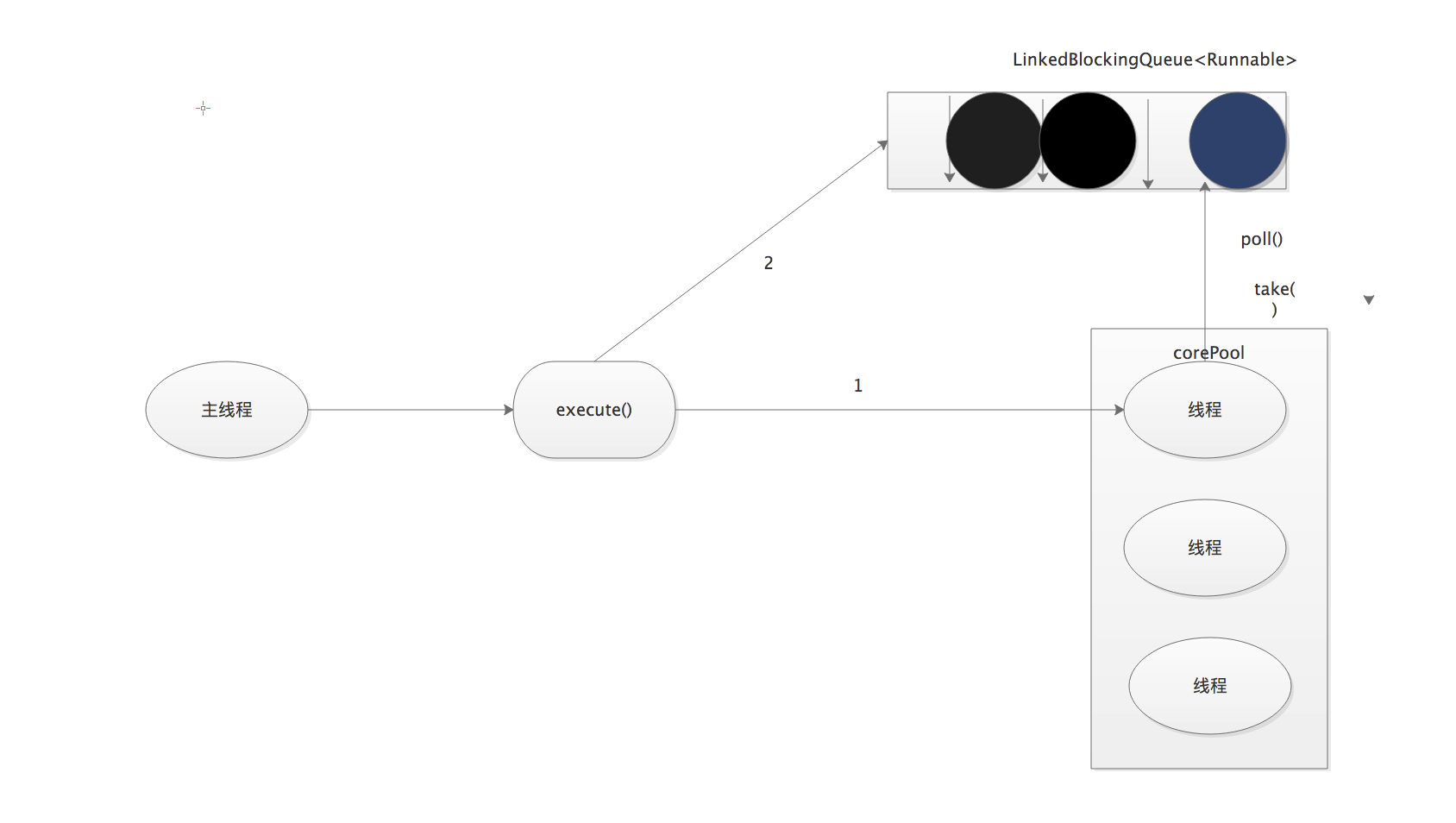
执行过程:
1)如果当前线程的线程数少于corePoolsize(即线程池中无运行的线程),则创建一个新的线程来执行任务
2) 在线程池完成预热之后(当前线程池中的一个运行线程),将任务加入LinkedBlockingQueue.
3) 线程执行完1中的任务后,会在一个无限循环中从LinkedBlockingQueue获取任务来执行。
3.CachedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
CachedThreadPool的corePoolSize被设置为0,即corePool为空;maximumPoolSize被设置为Inter.MAX_VALUE,即maximumPool是无界的。这里把keepAliveTime设置为60L,意味者CachedThreadPool中的空闲
线程等待新任务的最长时间为60秒,空闲时间超过60秒就会被终止。
FixedThreadPool和SingleThreadExecutor使用无界队列LinkedBlockingQueue作为线程池的工作队列。CachedThreadPool使用没有容量的SynchronousQueue作为线程池的工作队列,但CachedThreadPool的maximumPool
是无界的。这意味者,如果主线程提交任务的速度高于maximumPool线程处理任务的速度时,CachedThreadPool会不断创建新线程。极端情况下,CachedThreadPool会创建创建多线程而耗尽CPU和资源。
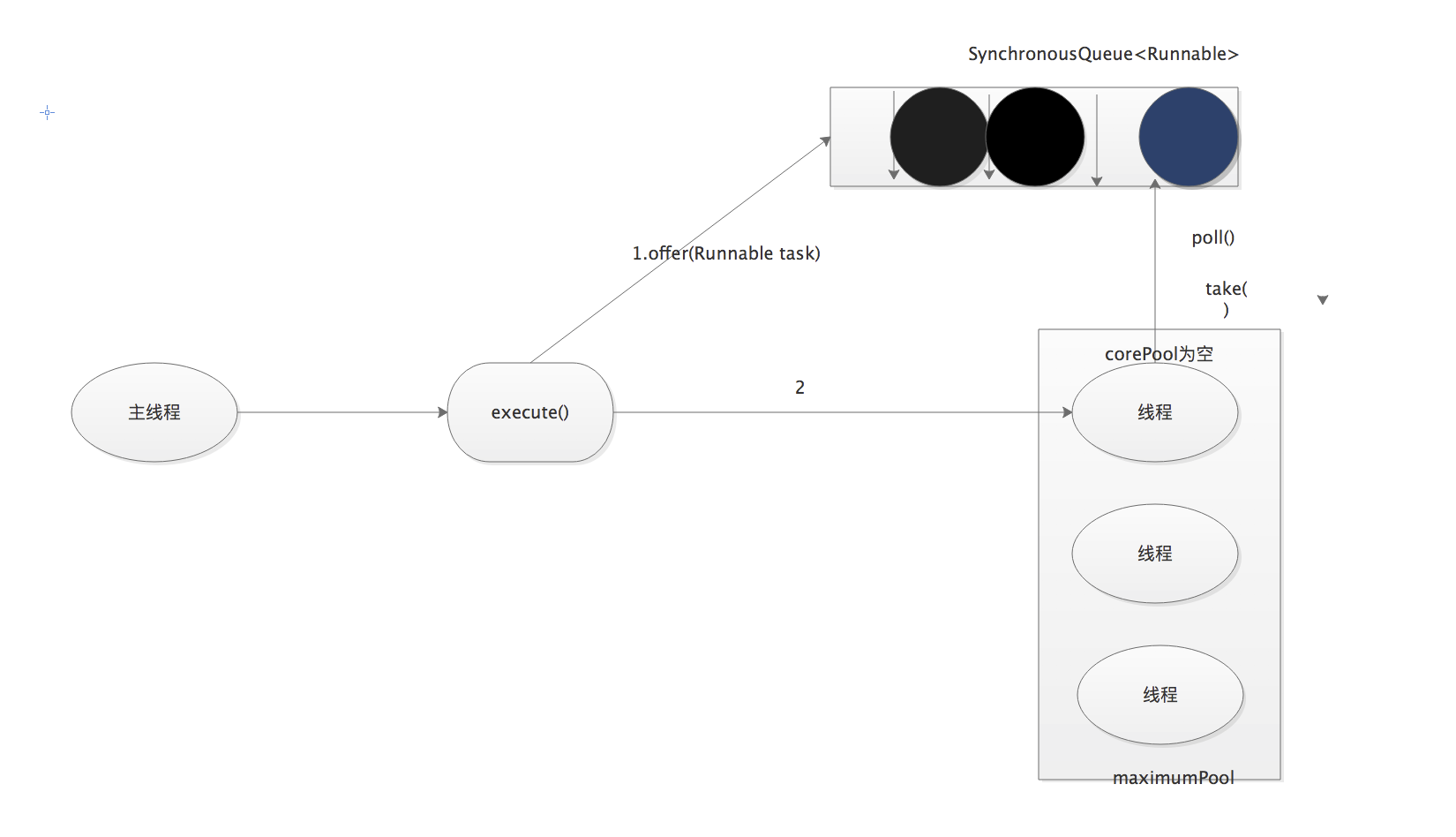
执行过程:
1)首先执行SynchronousQueue.offer(Runnable task).如果当前maximumPool中有空线程正在执行SynchronousQueue.poll(),那么主线程offer操作与空闲线程执行的poll操作配对成功,主线程把任务交给空闲线程执行,execute()方法执行完成;否则执行下面步骤2)、
2)当初始maximumPool为空,或者maximumPool中没有空闲线程时,将没有线程执行SynchronousQueue.poll.这种情况下,步骤1将失败。此时CachedThreadedPool会创建一个新线程执行任务,execute()方法执行完成
3)步骤2)中创建的线程将任务执行完成后,会执行Synchronous.poll.这个poll操作会让空闲线程最多在SynchronousQueue中等待60秒种。如果60秒内主线程提交来一个新任务,那么这个空闲线程将执行主线程提交的任务;否则,这个空闲线程将终止。由于60秒的空闲线程将会被终止,因此长时间保持空闲的CachedThreadPool不会使用任何资源。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor详解:
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor继承自ThreadPoolExecutor.它主要用来在给定的延迟之后运行任务,或者定期执行任务。ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor功能更强大、更灵活。Timer对应的是单个后台线程,而SchduledThreadPoolExecutor可以构造函数中指定多个对应的后台线程数。
接口scheduleAtFixedRate原型定义及参数说明:
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit);
command:执行线程
initialDelay:初始化延时
period:两次开始执行最小间隔时间
unit:计时单位
接口scheduleWithFixedDelay原型定义及参数说明:
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit);
command:执行线程
initialDelay:初始化延时
period:前一次执行结束到下一次执行开始的间隔时间(间隔执行延迟时间)
unit:计时单位.
这里要注意的是:
上面写的内容有不严谨的地方,比如对于scheduleAtFixedRate方法,当我们要执行的任务大于我们指定的执行间隔时会怎么样呢?
对于中文API中的注释,我们可能会被忽悠,认为无论怎么样,它都会按照我们指定的间隔进行执行,其实当执行任务的时间大于我们指定的间隔时间时,它并不会在指定间隔时开辟一个新的线程并发执行这个任务。而是等待该线程执行完毕。
* Creates and executes a periodic action that becomes enabled first
* after the given initial delay, and subsequently with the given
* period; that is executions will commence after
* {@code initialDelay} then {@code initialDelay+period}, then
* {@code initialDelay + 2 * period}, and so on.
* If any execution of the task
* encounters an exception, subsequent executions are suppressed.
* Otherwise, the task will only terminate via cancellation or
* termination of the executor. If any execution of this task
* takes longer than its period, then subsequent executions
* may start late, but will not concurrently execute.
上图插入的注解是原文注释,我们翻译黄色注释:如果任务执行遇到异常,接下来的任务执行将被阻止。因此任务仅仅终止或者取消还有执行结束。如果任务执行长于周期间隔,接下来的任务执行将会延期,不会并发执行(也就是一起执行)。
定时任务ScheduledFutureTask的3个成员变量,如下:
1. long型成员变量time,表示这个任务将要执行的具体时间。
2.long型成员变量sequenceNumber,表示这个任务被添加到ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor中的序号。
3.long型成员变量period,表示任务执行的间隔周期
DelayQueue封装了一个PriorityQueue,这个PriorityQueue会对队列中的ScheduledFutureTask进行排序。排序时,time小的排在前面(时间早的任务将被先执行)。如果两个SchduledFutureTask
的time相同,就比较sequenceNumber,sequenceNumber小的排在前面。
执行某个周期任务的过程:
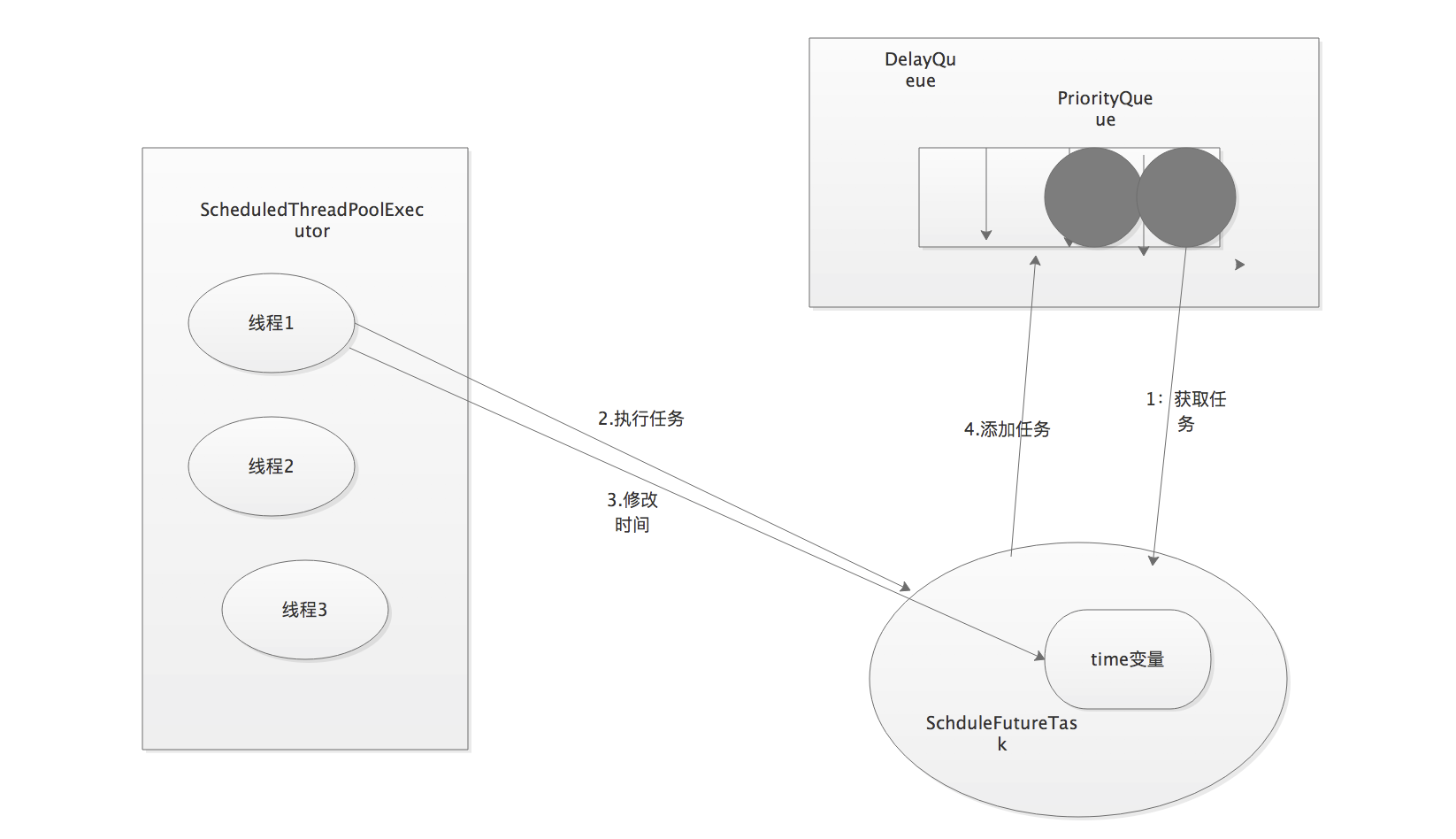
1)线程1从DelayQueue中获取已经到期的任务(time>大于当前时间)
2)线程1执行这个ScheduledFutureTask。
3)线程1修改ScheduledFutureTask的time变量为下次将要被执行的时间
4)线程1把这个修改time之后的ScheduledFutureTask放回DelayQueue中。