el表达式和jstl标签库
一:el表达式:表达式语言,jsp页面获取数据比较简单
1、el表达式的语法(掌握)
el表达式通常取值是获取作用域对象中的属性值:${属性名}=>是el表达式的简写的形式
跟jquery不一样,$(选择器)jquery对象,代码写在js的脚本块中
完整的书写形式:
四个作用域 四种取值方式获取不同作用域中的属性值
${pageScope.attrname } pageScope.属性名
${requestScope.attrname }
${sessionScope.attrname }
${applicationScope.attrname }
注:jsp2.0以上版本,对应 servlet 3.0以上版本,jsp默认忽略EL表达式,所以在使用el表达式的时候需要在 page指令中加上。isELIgnored="false" 开启EL表达式,true忽略(默认是忽略)
EL表达式取值的两种方式例子:test.jsp

1 <%@ page language="java" isELIgnored="false" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> 2 <% 3 String path = request.getContextPath(); 4 String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; 5 %> 6 7 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> 8 <html> 9 <head> 10 <base href="<%=basePath%>"> 11 12 <title>My JSP 'test.jsp' starting page</title> 13 14 <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> 15 <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> 16 <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> 17 <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> 18 <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> 19 <!-- 20 <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> 21 --> 22 23 </head> 24 25 <body> 26 <% 27 //将数据放到作用域对象中 28 29 //page域 当前页面有效 30 pageContext.setAttribute("uname", "印度阿三"); 31 32 //一次请求有效,可以是多个页面,转发页面 33 request.setAttribute("fav", "睡觉"); 34 35 //session域取值 一次会话,多个请求 36 session.setAttribute("value", "躺在床上听音乐"); 37 38 //应用域中取值一个web应用 39 application.setAttribute("小喜庆", "小云云"); 40 %> 41 <!--page域用el表达式取值 --> 42 page域用el表达式取值: 43 ${uname }  44 ${pageScope.uname }<hr> 45 46 <!--request域用el表达式取值 --> 47 request域用el表达式取值: 48 ${fav }  49 ${requestScope.fav }<hr> 50 51 <!--session域用el表达式取值 --> 52 session域用el表达式取值: 53 ${value }  54 ${sessionScope.value }<hr> 55 56 <!--application域用el表达式取值 --> 57 application域用el表达式取值: 58 ${小喜庆 }  59 ${applicationScope.小喜庆 }<hr> 60 61 </body> 62 </html>
在测试作用范围页面之前,必须先运行 test.jsp将数据放到作用域对象中
测试test.jsp四个作用域的作用范围【getTest.jsp】

1 <%@ page language="java" isELIgnored="false" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> 2 <% 3 String path = request.getContextPath(); 4 String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; 5 %> 6 7 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> 8 <html> 9 <head> 10 <base href="<%=basePath%>"> 11 12 <title>My JSP 'getTest.jsp' starting page</title> 13 14 <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> 15 <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> 16 <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> 17 <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> 18 <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> 19 <!-- 20 <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> 21 --> 22 23 </head> 24 25 <body> 26 <p>在测试 当前页面之前,必须先运行 test.jsp将数据放到作用域对象中</p><hr> 27 测试test.jsp四个作用域的作用范围 <br><hr> 28 29 <!--page 当前页面有效 --> 30 page域用el表达式取值: 31 ${uname } <br> 32 <!--request 一次请求有效,可以是多个页面,转发页面 --> 33 request域用el表达式取值: 34 ${fav } <br> 35 <!--session 一次会话,多个请求 --> 36 session域用el表达式取值: 37 ${value } <br> 38 <!--application 应用域中取值一个web应用 --> 39 application域用el表达式取值: 40 ${小喜庆 } <br> 41 </body> 42 </html>
如果不同的作用域,但是属性名相同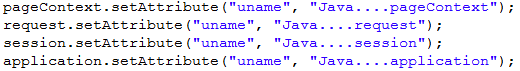
<!-- 【取值】如果不同的作用域,但是属性名相同 -->
注意:在省略 ***Scope对象的时候,取值的顺序,先从小范围获取数据 page,如果获取到了就返回,如果page获取不到,会去找request域,依次类推,找application ,如果都找不到,则返回null
2、el表达式获取不同数据类型的值(java 代码 字符串,数值,对象,list,map,数组)
①对象

注:在获取对象属性的时候,el表达式的解析的工具类,底层调用 的 get方法,不是直接调用的属性。el的解析对象用的反射,调用 get方法 Class ----getMethod("get方法")。${student.id }<=> ${student.getId }
②list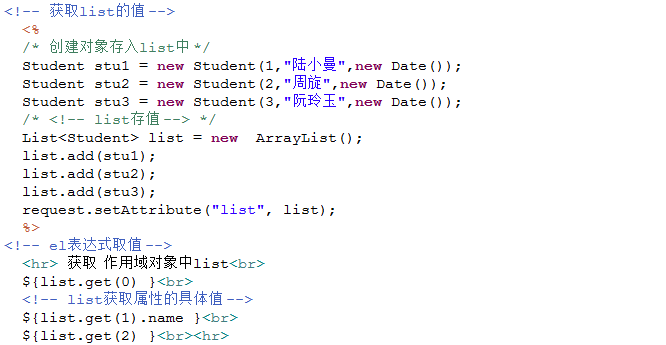

③map

注:map取值有两个:
点获取.简单【${map.fav }】
["key"] 比较灵活,可以处理特殊符号【${map.fav,ff }错误的 =>${map["fav,ff"] }】
④数组
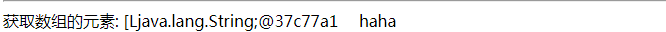
student.java

1 package boom.el.entity; 2 3 import java.util.Date; 4 5 /** 6 * 学生实体类对象 7 * @author Administrator 8 * 9 */ 10 public class Student { 11 private int id; 12 private String name; 13 private Date hiredate; 14 15 public Student() { 16 } 17 18 public Student(int id, String name, Date hiredate) { 19 super(); 20 this.id = id; 21 this.name = name; 22 this.hiredate = hiredate; 23 } 24 25 public int getId() { 26 return id; 27 } 28 29 public void setId(int id) { 30 this.id = id; 31 } 32 33 public String getName() { 34 return name; 35 } 36 37 public void setName(String name) { 38 this.name = name; 39 } 40 41 public Date getHiredate() { 42 return hiredate; 43 } 44 45 public void setHiredate(Date hiredate) { 46 this.hiredate = hiredate; 47 } 48 49 @Override 50 public String toString() { 51 return "Sutudent [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", hiredate=" 52 + hiredate + "]"; 53 } 54 55 }
test.jsp

1 <%@ page language="java" isELIgnored="false" import="java.util.* , boom.el.entity.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> 2 <% 3 String path = request.getContextPath(); 4 String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; 5 %> 6 7 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> 8 <html> 9 <head> 10 <base href="<%=basePath%>"> 11 12 <title>el表达式获取不同数据类型的值 </title> 13 14 <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> 15 <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> 16 <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> 17 <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> 18 <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> 19 <!-- 20 <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> 21 --> 22 </head> 23 <body> 24 25 <!-- 获取对象的值 --> 26 <% 27 /* 获取对象的值 【创建一个实体类 ,获取对象的属性值】*/ 28 Student student = new Student(0,"林徽因",new Date()); 29 //将 Student对象 放到作用域对象中 30 request.setAttribute("student", student); 31 %> 32 ${student }<hr> 33 ${student.id }  ${student.name }  ${student.hiredate }  34 <%-- 在获取对象属性的时候 ,el表达式的解析的工具类 底层调用 的 get方法,不是直接调用的属性 35 el的解析对象用的反射,调用 get方法 Class ----getMethod("get方法") 36 ${student.id }<=> ${student.getId } 37 --%> 38 39 <!-- 获取list的值 --> 40 <% 41 /* 创建对象存入list中 */ 42 Student stu1 = new Student(1,"陆小曼",new Date()); 43 Student stu2 = new Student(2,"周旋",new Date()); 44 Student stu3 = new Student(3,"阮玲玉",new Date()); 45 /* <!-- list存值 --> */ 46 List<Student> list = new ArrayList(); 47 list.add(stu1); 48 list.add(stu2); 49 list.add(stu3); 50 request.setAttribute("list", list); 51 %> 52 <!-- el表达式取值 --> 53 <hr> 获取 作用域对象中list<br> 54 ${list.get(0) }<br> 55 <!-- list获取属性的具体值 --> 56 ${list.get(1).name }<br> 57 ${list.get(2) }<br><hr> 58 59 <!-- 获取map的值 --> 60 <% 61 Map map = new HashMap(); 62 map.put("fav", "music"); 63 map.put("codeing", "Java"); 64 map.put("fav,ff", "run"); 65 request.setAttribute("map", map); 66 %> 67 <!-- el表达式取值 --> 68 ${map }<br> 69 ${map.fav }<br> 70 ${map["fav,ff"] }<br><hr> 71 72 <%-- map取值有两个 73 . 简单 74 ["key"] 比较灵活 ,可以处理特殊符号 75 ${map.fav,ff } 错误的 =>${map["fav,ff"] } --%> 76 77 78 <!-- 获取数组的值 --> 79 <% 80 String[] arr = {"haha" , "gaga" ,"heihei"}; 81 request.setAttribute("arr", arr); 82 %> 83 <!-- el表达式取值 --> 84 获取数组的元素: 85 ${arr }  86 ${arr[0] } 87 88 </body> 89 </html>
3、el表达式的基本运算
+ 字符串相加 非数值型字符串,在el表达式中不能直接相加,需要存放到request域中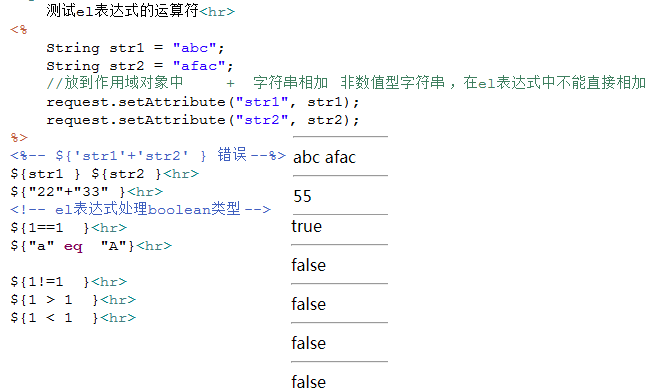
4、el表达式可以在html代码块中,javascript 的脚本块中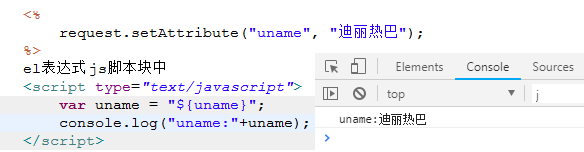
5、el表达式的内置对象11个(掌握其中的一部分)
隐含对象 描述
和作用域相关的【前4】,存取数据的隐含对象:【主要作用:获取作用域对象的数据 】

二:jstl标签库
1、jstl标签库,jsp标准标签库(只要jsp,标签库就起作用)
jstl标签库常用标签:jstl 标签库 for 循环,条件判断【for循环方法的封装 ,if 判断方法的封装】
2、jstl标签库的分类:
①核心标签库:c标签库
②常用标签:foreach 标签 遍历数据、逻辑判断标签:c:if、c:when、c:choose、c:otherwise
③格式化标签库:时间格式化标签
④函数标签库
⑤xml标签库
⑥数据库sql标签库
3、jstl标签库使用
jstl 标签,就是 java代码对 函数的封装
myeclipse创建web项目的时候,自动加载jstl
①引入相应的jstl标签库
<!-- 核心标签库 -->
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jstl/core_rt" %>
<!-- 函数标签库 -->
<%@taglib prefix="fn" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions" %>
解释:@taglib引入、uri 标签库地址、
tld 文件 将标签库底层的java实现类和 jsp连接起来的文件
②使用标签库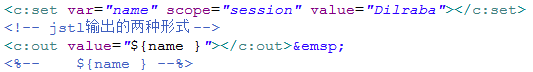
参数解释:
<c:set></c:set>:存储数据、var 存储数据的变量、scope 作用范围、value 存储的数据
<c:out value=""></c:out>:value 输出数据
<c:remove var="name"/>:移除数据
遍历:
<!--属性 :
var 遍历的变量
items 要被遍历的数据
-->
<c:forEach var="stu1" items="${list }">
${stu1.id }=>${stu1.name }<hr>
</c:forEach>
