之前学习过了阻塞队列(BiockingQueue)这里就不详细介绍了。
这里是队列的结构,他们都实现了Queue这个接口。
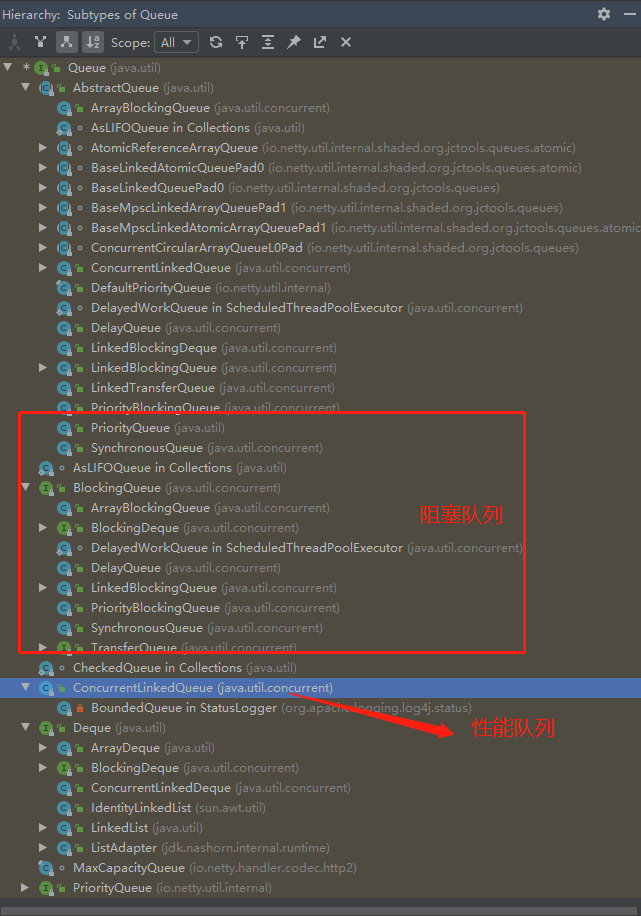
阻塞队列:阻塞队列与普通队列的区别在于,当队列是空的时,从队列中获取元素的操作将会被阻塞,或者当队列是满时,往队列里添加元素的操作会被阻塞。试图从空的阻塞队列中获取元素的线程将会被阻塞,直到其他的线程往空的队列插入新的元素。同样,试图往已满的阻塞队列中添加新元素的线程同样也会被阻塞,直到其他的线程使队列重新变得空闲起来,如从队列中移除一个或者多个元素,或者完全清空队列。
1.ArrayDeque, (数组双端队列)
2.PriorityQueue, (优先级队列)
3.ConcurrentLinkedQueue, (基于链表的并发队列)
4.DelayQueue, (延期阻塞队列)(阻塞队列实现了BlockingQueue接口)
5.ArrayBlockingQueue, (基于数组的并发阻塞队列)
6.LinkedBlockingQueue, (基于链表的FIFO阻塞队列)
7.LinkedBlockingDeque, (基于链表的FIFO双端阻塞队列)
8.PriorityBlockingQueue, (带优先级的无界阻塞队列)
9.SynchronousQueue (并发同步阻塞队列)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
今天主要讲 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 并发队列
在并发编程中我们有时候需要使用线程安全的队列。如果我们要实现一个线程安全的队列有两种实现方式一种是使用阻塞算法,另一种是使用非阻塞算法。使用阻塞算法的队列可以用一个锁(入队和出队用同一把锁)或两个锁(入队和出队用不同的锁)等方式来实现,而非阻塞的实现方式则可以使用循环CAS的方式来实现,下面我们一起来研究下Doug Lea是如何使用非阻塞的方式来实现线程安全队列ConcurrentLinkedQueue的。
ConcurrentLinkedQueue是一个基于链接节点的无界线程安全队列,它采用先进先出的规则对节点进行排序,当我们添加一个元素的时候,它会添加到队列的尾部,当我们获取一个元素时,它会返回队列头部的元素。它采用了“wait-free”算法来实现,该算法在Michael & Scott算法上进行了一些修改。
ConcurrentLinkedQueue的类图如下:

ConcurrentLinkedQueue由head节点和tail节点组成,每个节点(Node)由节点元素(item)和指向下一个节点的引用(next)组成,节点与节点之间就是通过这个next关联起来,从而组成一张链表结构的队列。
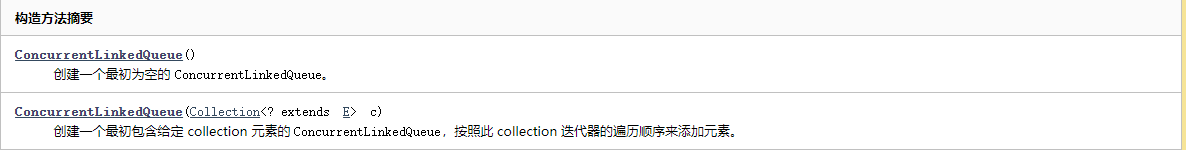
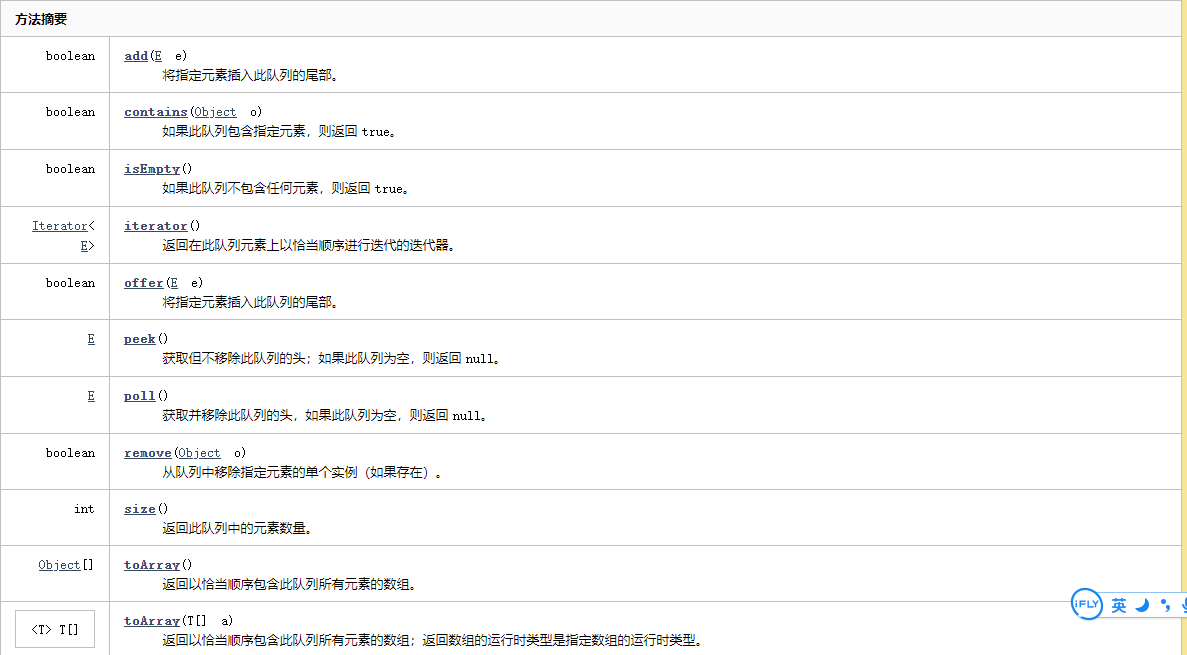
常用的方法 API
offer和poll
offer(E e) :将指定元素插入此队列的尾部。
poll():获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null。

public static void main(String[] args) { ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue(); queue.offer("哈哈哈"); System.out.println("offer后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty()); System.out.println("从队列中poll:" + queue.poll()); System.out.println("pool后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty()); }
ConcurrentLinkedQueue中的add() 和 offer() 完全一样,都是往队列尾部添加元素
peek():获取但不移除此队列的头;如果此队列为空,则返回 null

public static void main(String[] args) { ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue(); queue.offer("哈哈哈"); System.out.println("offer后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty()); System.out.println("从队列中peek:" + queue.peek()); System.out.println("从队列中peek:" + queue.peek()); System.out.println("从队列中peek:" + queue.peek()); System.out.println("pool后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty()); }
remove(Object o):从队列中移除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)

public static void main(String[] args) { ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue(); queue.offer("哈哈哈"); System.out.println("offer后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty()); System.out.println("从队列中remove已存在元素 :" + queue.remove("哈哈哈")); System.out.println("从队列中remove不存在元素:" + queue.remove("123")); System.out.println("remove后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty()); }
size or isEmpty
size(): 返回此队列中的元素数量
isEmpty(); 判断是否有数据(即可认为队列是否为空)
注意:
如果此队列包含的元素数大于 Integer.MAX_VALUE,则返回 Integer.MAX_VALUE。
需要小心的是,与大多数 collection 不同,此方法不是 一个固定时间操作。由于这些队列的异步特性,确定当前的元素数需要进行一次花费 O(n) 时间的遍历。
所以在需要判断队列是否为空时,尽量不要用 queue.size()>0,而是用 !queue.isEmpty()
比较size()和isEmpty() 效率的示例:
场景:10000个人去饭店吃饭,10张桌子供饭,分别比较size() 和 isEmpty() 的耗时

public class Test01ConcurrentLinkedQueue { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { int peopleNum = 10000;//吃饭人数 int tableNum = 10;//饭桌数量 ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>(); CountDownLatch count = new CountDownLatch(tableNum);//计数器 //将吃饭人数放入队列(吃饭的人进行排队) for(int i=1;i<=peopleNum;i++){ queue.offer("消费者_" + i); } //执行10个线程从队列取出元素(10个桌子开始供饭) System.out.println("-----------------------------------开饭了-----------------------------------"); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(tableNum); for(int i=0;i<tableNum;i++) { executorService.submit(new Dinner("00" + (i+1), queue, count)); } //计数器等待,知道队列为空(所有人吃完) count.await(); long time = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; System.out.println("-----------------------------------所有人已经吃完-----------------------------------"); System.out.println("共耗时:" + time); //停止线程池 executorService.shutdown(); } private static class Dinner implements Runnable{ private String name; private ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue; private CountDownLatch count; public Dinner(String name, ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue, CountDownLatch count) { this.name = name; this.queue = queue; this.count = count; } @Override public void run() { //while (queue.size() > 0){ while (!queue.isEmpty()){ //从队列取出一个元素 排队的人少一个 System.out.println("【" +queue.poll() + "】----已吃完..., 饭桌编号:" + name); } count.countDown();//计数器-1 } } }
执行结果:
使用size耗时:757ms
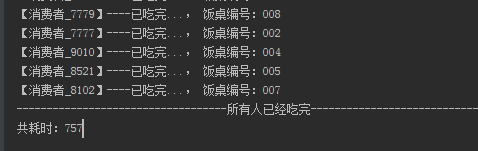
使用isEmpty耗时:210s

当数据量越大,这种耗时差距越明显。所以这种判断用isEmpty 更加合理
contains(Object o) :如果此队列包含指定元素,则返回 true

public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue(); queue.offer("123"); System.out.println(queue.contains("123")); System.out.println(queue.contains("234")); }
toArray() :返回以恰当顺序包含此队列所有元素的数组
toArray(T[] a) :返回以恰当顺序包含此队列所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型

public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String>(); queue.offer("123"); queue.offer("234"); Object[] objects = queue.toArray(); System.out.println(objects[0] + ", " + objects[1]); //将数据存储到指定数组 String[] strs = new String[2]; queue.toArray(strs); System.out.println(strs[0] + ", " + strs[1]); }
iterator() :返回在此队列元素上以恰当顺序进行迭代的迭代器

public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String>(); queue.offer("123"); queue.offer("234"); Iterator<String> iterator = queue.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } }

ConcurrentLinkedQueue文档说明: