HTTP是我们交换数据和媒体流的现代应用网络,有效利用HTTP可以使我们节省带宽和更快地加载数据,Square公司开源的OkHttp网络请求是有效率的HTTP客户端。之前的知识面仅限于框架API的调用,接触到实际的工作之后深知自己知识的不足,故而深挖框架源码尽力吸取前辈的设计经验。关于此框架的源码解析网上的教程多不胜数,此文名为源码解析,实则是炒冷饭之作,如有错误和不足之处还望各位看官指出。
拦截器
拦截器是OkHttp框架设计的精髓所在,拦截器所定义的是Request的所通过的责任链而不管Request的具体执行过程,并且可以让开发人员自定义自己的拦截器功能并且插入到责任链中
-
用户自定义的拦截器位于 OkHttpClient.addInterceptor() 添加到interceptors责任链中
-
RealCall.execute()执行的时候调用RealCall.getResponseWithInterceptorChain()将 来自 OkHttpClient的interceptors以及默认的拦截器一并加入到RealInterceptorChain责任链中并调用, 代码并没有对originalRequest进行封装, InterceptorChain和originalRequest一并流转到 RealInterceptorChain类中处理
CustomInterceptor RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor BridgeInterceptor CacheInterceptor ConnectInterceptor NetworkInterceptors CallServiceInterceptor -
RealInterceptorChain.proceed()
-
EventListener.callStart()也是在RealCall.execute()嵌入到Request调用过程, EventListener.callEnd()位于StreamAllocation中调用
-
Request.Builder
- url (String/URL/HttpUrl)
- header
- CacheControl
- Tag (Use this API to attach timing, debugging, or other application data to a request so that you may read it in interceptors, event listeners, or callbacks.)
BridgeInterceptor
Bridges from application code to network code. First it builds a network request from a user request. Then it proceeds to call the network. Finally it builds a user response from the network response.
此拦截器是应用码到网络码的桥接。它会将用户请求封装成一个网络请求并且执行请求,同时它还完成从网络响应到用户响应的转化. 最后Chain.proceed() 方法启动拦截器责任链, RealInterceptorChain中通过递归调用将网络请求以及响应的任务分别分配到各个拦截器中, 然后通过ResponseBuilder.build()方法将网络响应封装, 然后递归调用责任链模式使得调用以及Response处理的过程可以一并写入BridgeInterceptor中
public final class RealInterceptorChain implements Interceptor.Chain {
public Response proceed(Request request, StreamAllocation streamAllocation,
HttpCodec httpCodec, RealConnection connection) throws IOException {
if (index >= interceptors.size()) throw new AssertionError();
calls++;
...
// Call the next interceptor in the chain.
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors,
streamAllocation, httpCodec,connection, index + 1, request, call,
eventListener, connectTimeout, readTimeout,writeTimeout);
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index);
Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
...
return response;
}
}
CallServiceInterceptor

Interceptor的逻辑均在intercept()方法中实现, 在通过Chain实体类获取到请求主题之后,通过BufferedSink接口将请求转发到Okio接口,在拦截过程中通过EventListener接口将拦截器处理状态(主要是RequestBodyStart和RequestBodyEnd两个状态)发送出去
public final class CallServiceInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Response.Builder responseBuilder = null;
if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(request.method()) && request.body() != null) {
// If there's a "Expect: 100-continue" header on the request, wait for a "HTTP/1.1 100
// Continue" response before transmitting the request body. If we don't get that, return
// what we did get (such as a 4xx response) without ever transmitting the request body.
if ("100-continue".equalsIgnoreCase(request.header("Expect"))) {
httpCodec.flushRequest();
realChain.eventListener().responseHeadersStart(realChain.call());
responseBuilder = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(true);
}
if (responseBuilder == null) {
// Write the request body if the "Expect: 100-continue" expectation was met.
realChain.eventListener().requestBodyStart(realChain.call());
long contentLength = request.body().contentLength();
CountingSink requestBodyOut =
new CountingSink(httpCodec.createRequestBody(request, contentLength));
BufferedSink bufferedRequestBody = Okio.buffer(requestBodyOut);
request.body().writeTo(bufferedRequestBody);
bufferedRequestBody.close();
realChain.eventListener()
.requestBodyEnd(realChain.call(), requestBodyOut.successfulCount);
} else if (!connection.isMultiplexed()) {
// If the "Expect: 100-continue" expectation wasn't met, prevent the HTTP/1 connection
// from being reused. Otherwise we're still obligated to transmit the request body to
// leave the connection in a consistent state.
streamAllocation.noNewStreams();
}
}
}
}
CacheInterceptor
public final class CacheInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
CacheStrategy strategy = new CacheStrategy.Factory(now, chain.request(), cacheCandidate).get();
Request networkRequest = strategy.networkRequest;
Response cacheResponse = strategy.cacheResponse;
if (cache != null) {
/**
* Track an HTTP response being satisfied with {@code cacheStrategy}.
* 主要是跟踪networkRequest次数以及对应Cache的hitcount
*/
cache.trackResponse(strategy);
}
if (cacheCandidate != null && cacheResponse == null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body()); // The cache candidate wasn't applicable. Close it.
}
// If we're forbidden from using the network and the cache is insufficient, fail.
if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null) {
return new Response.Builder()
.request(chain.request())
.protocol(Protocol.HTTP_1_1)
.code(504)
.message("Unsatisfiable Request (only-if-cached)")
.body(Util.EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.sentRequestAtMillis(-1L)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
}
// If we don't need the network, we're done.
if (networkRequest == null) {
return cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.build();
}
//在chain.proceed()调用下一个拦截器
Response networkResponse = null;
try {
networkResponse = chain.proceed(networkRequest);
} finally {
// If we're crashing on I/O or otherwise, don't leak the cache body.
if (networkResponse == null && cacheCandidate != null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body());
}
}
//处理response并返回
...
return response;
}
}
CacheStrategy
OkHttpClient
OkHttpClient托管着所有HTTP调用, 每个Client均拥有自己的连接池和线程池
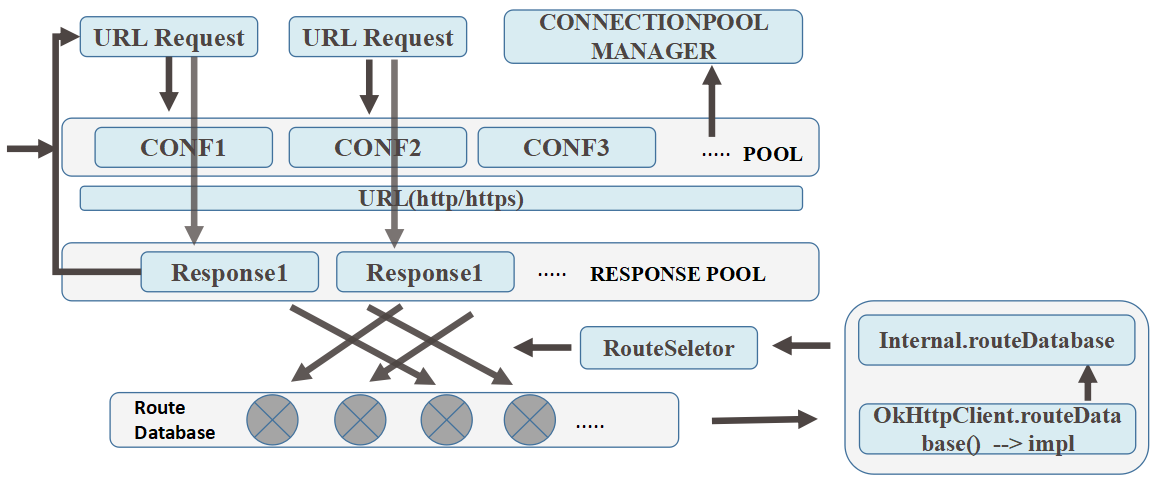
- 实现抽象类Internal的方法,这是Internel抽象类唯一的实现,方法与CacheInterceptor控制Http的Header.Lenient区域和StreamAlloction从连接池中获取连接有关
private RealConnection findConnection(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout,
int pingIntervalMillis, boolean connectionRetryEnabled) throws IOException {
...
synchronized (connectionPool) {
...
if (result == null) {
// Attempt to get a connection from the pool.
Internal.instance.get(connectionPool, address, this, null);
if (connection != null) {
foundPooledConnection = true;
result = connection;
} else {
selectedRoute = route;
}
}
}
return result;
}
- RouteDatabase && RouteSeletor
RouteDatabase是记录连接失败的连接路径的黑名单,从而OkHttp可以从失败中学习并且倾向于选择其他可用的路径,RouteSeletor通过RouteDatabase.shouldPostpone(route)方法可获知此路径是否近期曾连接失败,RouteSelector部分源码如下:
public final class RouteSelector {
/**
* Clients should invoke this method when they encounter a connectivity failure on a connection
* returned by this route selector.
* 在StreamAllocation.streamFailed()中添加了routeSelector.connectFailed()逻辑
*/
public void connectFailed(Route failedRoute, IOException failure) {
if (failedRoute.proxy().type() != Proxy.Type.DIRECT && address.proxySelector() != null) {
// Tell the proxy selector when we fail to connect on a fresh connection.
address.proxySelector().connectFailed(
address.url().uri(), failedRoute.proxy().address(), failure);
}
routeDatabase.failed(failedRoute);
}
}
Dispatcher
Dispatcher(分离器或者复用器)是异步网络请求调用时执行的策略方法, 复用器的概念十分常见,它主要的作用是输入的各路信号进行卷积运算,最大可能压榨通信的带宽,提高信息传输的效率。Dispatcher控制最大请求并发数和单个主机的最大并发数,并持有一个线程池负责执行异步请求,对同步的请求只是用作统计。OkHttp在每个分离器使用一个ExecutorService内部调用请求, Dispatcher内部主要并不涉及执行的具体。
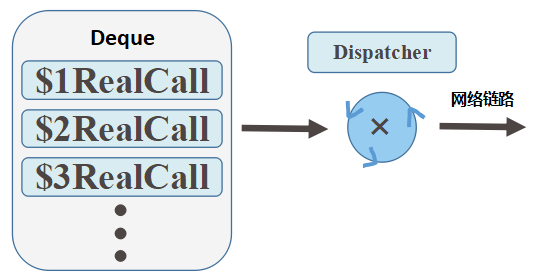
synchronized void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() < maxRequests && runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {
runningAsyncCalls.add(call);
executorService().execute(call);
} else {
readyAsyncCalls.add(call);
}
}
...
/** Used by {@code Call#execute} to signal it is in-flight. */
synchronized void executed(RealCall call) {
runningSyncCalls.add(call);
}
ExecutorSevice.execute(AsyncCall)执行代码位于AsyncCall内部复写的execute()方法, 方法内定义一些Callback回调节点运行逻辑,包括用户主动取消执行(使用retryAndFollowUpInterceptor)以及执行请求成功或者失败时的回调方法
final class AsyncCall extends NamedRunnable {
...
@Override protected void execute() {
boolean signalledCallback = false;
try {
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled"));
} else {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (signalledCallback) {
// Do not signal the callback twice!
Platform.get().log(INFO, "Callback failure for " + toLoggableString(), e);
} else {
eventListener.callFailed(RealCall.this, e);
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, e);
}
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
}
- 惰性初始模式(Created Lazily)成员
- ExecutorService()
- CacheControl
WebSocket
-
WebSocket 异步非堵塞的web socket接口 (通过Enqueue方法来实现)
-
OkHttpClient 通过实现 WebSocket.Factory.newWebSocket 接口实现工厂构造, 通常是由 OkHttpClient来构造
-
WebSocket生命周期:
- Connecting状态: 每个websocket的初始状态, 此时Message可能位于入队状态但是还没有被Dispatcher处理
- Open状态: WebSocket已经被服务器端接受并且Socket位于完全开放状态, 所有Message入队之后会即刻被处理
- Closing状态: WebSocket进入优雅的关闭状态,WebSocket继续处理已入队的Message但拒绝新的Message入队
- Closed状态: WebSocket已完成收发Message的过程, 进入完全关闭状态
WebSocket受到网络等各种因素影响, 可能会断路而提前进入关闭流程 - Canceled状态: 被动WebSocket失败连接为非优雅的过程, 而主动则是优雅短路过程
-
-
RealWebSocket
RealWebSocket管理着Request队列内容所占的空间大小以及关闭Socket之后留给优雅关闭的时间,默认为16M和60秒,在RealWebSocket.connect()方法中RealWebSocket对OkHttpClient以及Request封装成Call的形式,然后通过Call.enqueue()方法定义调用成功和失败时的Callback代码public void connect(OkHttpClient client) { client = client.newBuilder() .eventListener(EventListener.NONE) .protocols(ONLY_HTTP1) .build(); final Request request = originalRequest.newBuilder() .header("Upgrade", "websocket") .header("Connection", "Upgrade") .header("Sec-WebSocket-Key", key) .header("Sec-WebSocket-Version", "13") .build(); call = Internal.instance.newWebSocketCall(client, request); call.enqueue(new Callback() { @Override public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) { try { checkResponse(response); } catch (ProtocolException e) { failWebSocket(e, response); closeQuietly(response); return; } // Promote the HTTP streams into web socket streams. StreamAllocation streamAllocation = Internal.instance.streamAllocation(call); streamAllocation.noNewStreams(); // Prevent connection pooling! Streams streams = streamAllocation.connection().newWebSocketStreams(streamAllocation); // Process all web socket messages. try { listener.onOpen(RealWebSocket.this, response); String name = "OkHttp WebSocket " + request.url().redact(); initReaderAndWriter(name, streams); streamAllocation.connection().socket().setSoTimeout(0); loopReader(); } catch (Exception e) { failWebSocket(e, null); } } @Override public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) { failWebSocket(e, null); } }); }当Call请求被服务端响应的时候就将HTTP流导入到Web Socket流中,并且调用WebSocketListener相对应的状态方法, WebSocketListener状态如下:
onOpen()
onMessage()
onClosing()
onClosed()
onFailure()
- WebSocket -> RealWebSocket
- Connection -> RealConnection
- Interceptor -> RealInterceptorChain
- Call -> RealCall
- ResponseBody -> RealResponseBody
Gzip压缩机制
处理Gzip压缩的代码在BridgeInterceptor中,默认情况下为gzip压缩状态,可以从下面的源码片段中获知。如果header中没有Accept-Encoding,默认自动添加 ,且标记变量transparentGzip为true
// If we add an "Accept-Encoding: gzip" header field we're responsible for also decompressing
// the transfer stream.
boolean transparentGzip = false;
if (userRequest.header("Accept-Encoding") == null && userRequest.header("Range") == null) {
transparentGzip = true;
requestBuilder.header("Accept-Encoding", "gzip");
}
BridgeInterceptor解压缩的过程调用了okio.GzipSource()方法并调用Okio.buffer()缓存解压过程,源码如下
if (transparentGzip
&& "gzip".equalsIgnoreCase(networkResponse.header("Content-Encoding"))
&& HttpHeaders.hasBody(networkResponse)) {
GzipSource responseBody = new GzipSource(networkResponse.body().source());
Headers strippedHeaders = networkResponse.headers().newBuilder()
.removeAll("Content-Encoding")
.removeAll("Content-Length")
.build();
responseBuilder.headers(strippedHeaders);
String contentType = networkResponse.header("Content-Type");
responseBuilder.body(new RealResponseBody(contentType, -1L, Okio.buffer(responseBody)));
}
RealCall构造方法
在RealCall构造方法上面,早期版本的RealCall构造方法中将EventListener.Factory以及EventListenerFactory.Create()分开处理导致RealCall构造方法非线程安全. 现在版本的RealCall的构造函数使用OkHttpClient.eventListenerFactory().create()
早期版本如下:
final class RealCall implements Call {
RealCall(OkHttpClient client, Request originalRequest, boolean forWebSocket) {
...
final EventListener.Factory eventListenerFactory = client.eventListenerFactory();
this.client = client;
this.originalRequest = originalRequest;
this.forWebSocket = forWebSocket;
//重试和跟进拦截器
this.retryAndFollowUpInterceptor = new RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor(client, forWebSocket);
// TODO(jwilson): this is unsafe publication and not threadsafe.
// 这是不安全的发布,不是线程安全的。
this.eventListener = eventListenerFactory.create(this);
}
}
现在 OkHttp 3.11.0 的RealCall源代码如下
final class RealCall implements Call {
private EventListener eventListener;
...
private RealCall(OkHttpClient client, Request originalRequest, boolean forWebSocket) {
this.client = client;
this.originalRequest = originalRequest;
this.forWebSocket = forWebSocket;
this.retryAndFollowUpInterceptor = new RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor(client, forWebSocket);
}
static RealCall newRealCall(OkHttpClient client, Request originalRequest, boolean forWebSocket) {
// Safely publish the Call instance to the EventListener.
RealCall call = new RealCall(client, originalRequest, forWebSocket);
call.eventListener = client.eventListenerFactory().create(call);
return call;
}
}
ConnetionPool
连接池能够复用http连接从而减少访问相同目标主机情况下的网络延迟,此类实现管理连接开闭的策略并使用与连接池一一对应的后台线程清理过期的连接。ConnectionPool提供对Deque<RealConnection>进行操作的方法分别为put、get、connectionBecameIdle和evictAll几个操作。分别对应放入连接、获取连接、移除连接和移除所有连接操作,这里我们举例put和get操作。
public final class ConnectionPool {
...
private static final Executor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0 /* corePoolSize */,
Integer.MAX_VALUE /* maximumPoolSize */, 60L /* keepAliveTime */, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp ConnectionPool", true));
/** The maximum number of idle connections for each address. */
private final int maxIdleConnections;
private final long keepAliveDurationNs;
private final Runnable cleanupRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
while (true) {
long waitNanos = cleanup(System.nanoTime());
if (waitNanos == -1) return;
if (waitNanos > 0) {
long waitMillis = waitNanos / 1000000L;
waitNanos -= (waitMillis * 1000000L);
synchronized (ConnectionPool.this) {
try {
ConnectionPool.this.wait(waitMillis, (int) waitNanos);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
}
}
}
};
...
}
cleanUpRunnable里面是一个while(true),一个循环包括:
- 调用一次cleanUp方法进行清理并返回一个long
- 如果是-1则退出,否则调用wait方法等待这个long值的时间
okhttp是根据StreamAllocation引用计数是否为0来实现自动回收连接的。cleanUpRunnable遍历每一个RealConnection,通过引用数目确定哪些是空闲的,哪些是在使用中,同时找到空闲时间最长的RealConnection。如果空闲数目超过最大空闲数或者空闲时间超过最大空闲时间,则清理掉这个RealConnection并返回0,表示需要立刻再次清理
public final class ConnectionPool {
...
void put(RealConnection connection) {
assert (Thread.holdsLock(this));
if (!cleanupRunning) {
cleanupRunning = true;
executor.execute(cleanupRunnable);
}
connections.add(connection);
}
...
}
我们在put操作前首先要调用executor.execute(cleanupRunnable)来清理闲置的线程。
RealConnection
RealConnection是socket物理连接的包装,它里面维护了List<Reference<StreamAllocation>>的引用。List中StreamAllocation的数量也就是socket被引用的计数,如果计数为0的话,说明此连接没有被使用就是空闲的,需要被回收;如果计数不为0,则表示上层代码仍然引用,就不需要关闭连接。