1002. A+B for Polynomials (25)
This time, you are supposed to find A+B where A and B are two polynomials.
Input
Each input file contains one test case. Each case occupies 2 lines, and each line contains the information of a polynomial: K N1 aN1 N2 aN2 ... NK aNK, where K is the number of nonzero terms in the polynomial, Ni and aNi (i=1, 2, ..., K) are the exponents and coefficients, respectively. It is given that 1 <= K <= 10,0 <= NK < ... < N2 < N1 <=1000.
Output
For each test case you should output the sum of A and B in one line, with the same format as the input. Notice that there must be NO extra space at the end of each line. Please be accurate to 1 decimal place.
Sample Input2 1 2.4 0 3.2 2 2 1.5 1 0.5Sample Output
3 2 1.5 1 2.9 0 3.2
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double s[]=new double [1001];
for(int j=1000;j>=0;j--){
s[j]=0;
}
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int i=1,k;
while(i<3){
k=Integer.parseInt(in.next());
for(int j=0;j<k;j++){
int n=Integer.parseInt(in.next());
s[n]=s[n]+Double.parseDouble(in.next());
}
i++;
}
int count=0;
for(double t:s){
if(t!=0) count++;
}
System.out.print(count);
k=0;
for(int j=1000;j>=0;j--){
if(s[j]-0>0&&k<count){
System.out.printf(" %d %.1f",j,s[j]);
k++;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
提交结果部分正确
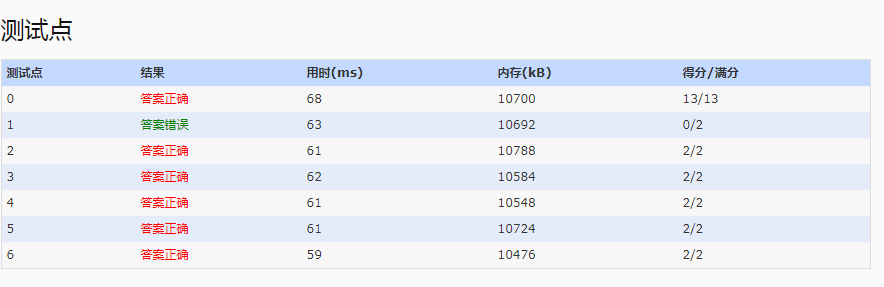
修改后
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double s[]=new double [1001];
for(int j=1000;j>=0;j--){
s[j]=0;
}
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int i=1,k;
while(i<3){
k=Integer.parseInt(in.next());
for(int j=0;j<k;j++){
int n=Integer.parseInt(in.next());
s[n]=s[n]+Double.parseDouble(in.next());
}
i++;
}
int count=0;
for(double t:s){
if(t!=0) count++;
}
System.out.print(count);
k=0;
for(int j=1000;j>=0;j--){
if(Math.abs(s[j]-0)>0&&k<count){
System.out.printf(" %d %.1f",j,s[j]);
k++;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
提交结果
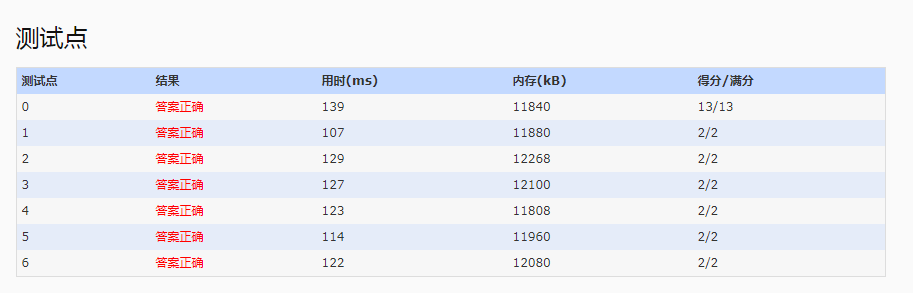
或者使用DOuble.compare(double,double)比较
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double s[]=new double [1001];
for(int j=1000;j>=0;j--){
s[j]=0;
}
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int i=1,k;
while(i<3){
k=Integer.parseInt(in.next());
for(int j=0;j<k;j++){
int n=Integer.parseInt(in.next());
s[n]=s[n]+Double.parseDouble(in.next());
}
i++;
}
int count=0;
for(double t:s){
if(t!=0) count++;
}
System.out.print(count);
k=0;
for(int j=1000;j>=0;j--){
if(Double.compare(s[j],0.0)!=0&&k<count){
System.out.printf(" %d %.1f",j,s[j]);
k++;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
其实s[j]!=0.0也可以,所以大概是要注意doubel计算中的精度问题
参考
http://blog.csdn.net/u014646950/article/details/46932525