Description
There is a right triangle with legs of length a and b. Your task is to determine whether it is possible to locate the triangle on the plane in such a way that none of its sides is parallel to the coordinate axes. All the vertices must have integer coordinates. If there exists such a location, you have to output the appropriate coordinates of vertices.
Input
The first line contains two integers a, b (1 ≤ a, b ≤ 1000), separated by a single space.
Output
In the first line print either "YES" or "NO" (without the quotes) depending on whether the required location exists. If it does, print in the next three lines three pairs of integers — the coordinates of the triangle vertices, one pair per line. The coordinates must be integers, not exceeding 109 in their absolute value.
Sample Input
1 1
NO
5 5
YES
2 1
5 5
-2 4
5 10
YES
-10 4
-2 -2
1 2
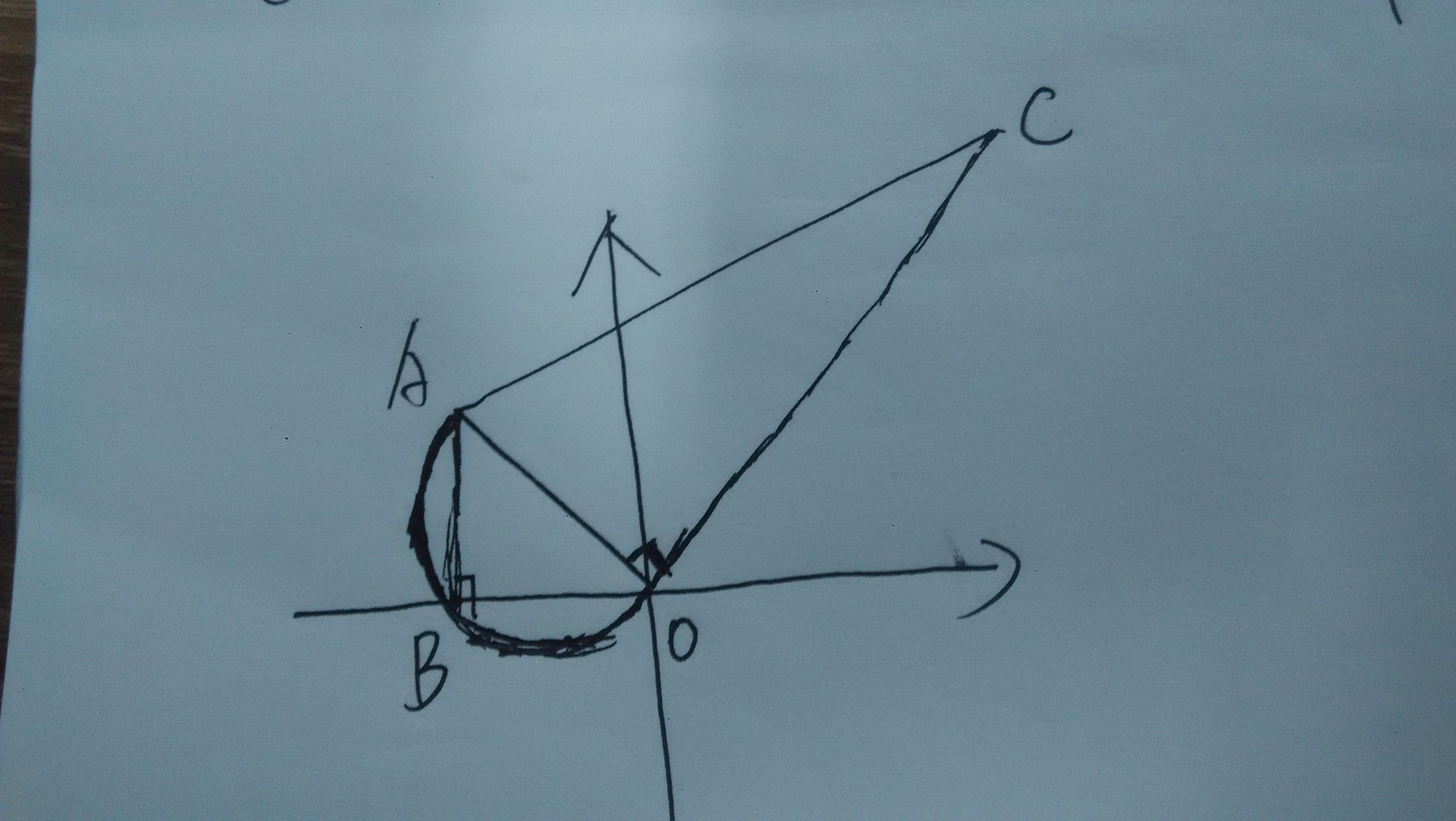
思路:取直角顶点在原点O,三角形如图AOC,以AO为直径做圆必与x轴有交点B,角AOB为直角,所以AO垂直于x轴,A的坐标为整数,所以由AO*AO=AB*BO知a^2,b^2均为两数的平方和。
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> using namespace std; int a[1005]; int gcd(int n,int m) { int i,j; for(i=n;i>=5;i--) { if(n%i==0&&m%i==0) return i; } return -1; } int main() { int i,j,n,m; int k,x,s,flag; for(i=1;i<1005;i++) a[i]=i*i; while(cin>>n>>m) { flag=0; if(n>m) { int t; t=m; m=n; n=t; } s=gcd(n,m); if(s==-1) flag=0; else { for(i=1;i<s;i++) { k=a[s]-a[i]; x=sqrt(k); if(k==x*x) { flag=1; k=i; break; } } } if(flag==1) { cout<<"YES"<<endl; if(k!=s*x) { cout<<(-1)*x*n/s<<" "<<k*n/s<<endl; cout<<m/s*k<<" "<<m/s*x<<endl; } else { cout<<n/s*k<<" "<<(-1)*x*n/s<<endl; cout<<m/s*x<<" "<<m/s*k<<endl; } cout<<"0"<<" "<<"0"<<endl; } else cout<<"NO"<<endl; } return 0; }