在 MATLAB 中,有一个非常有用的函数 reshape ,它可以将一个 m x n 矩阵重塑为另一个大小不同(r x c)的新矩阵,但保留其原始数据。
给你一个由二维数组 mat 表示的 m x n 矩阵,以及两个正整数 r 和 c ,分别表示想要的重构的矩阵的行数和列数。
重构后的矩阵需要将原始矩阵的所有元素以相同的 行遍历顺序 填充。
如果具有给定参数的 reshape 操作是可行且合理的,则输出新的重塑矩阵;否则,输出原始矩阵。
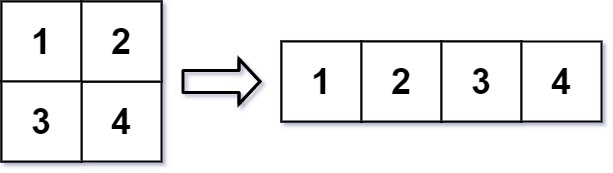
示例 1:
输入:mat = [[1,2],[3,4]], r = 1, c = 4
输出:[[1,2,3,4]]
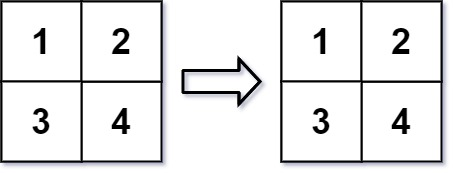
示例 2:
输入:mat = [[1,2],[3,4]], r = 2, c = 4
输出:[[1,2],[3,4]]
提示:
m == mat.length
n == mat[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 100
-1000 <= mat[i][j] <= 1000
1 <= r, c <= 300
Python解法
from typing import List class Solution: def matrixReshape(self, mat: List[List[int]], r: int, c: int) -> List[List[int]]: m,n = len(mat),len(mat[0]) #对比重构矩阵的个数和原来矩阵的个数不一致,则返回原来的矩阵 if (m * n != r * c): return mat else: templist, mat1, count = [], [], 0 #先遍历整个list 输出子list,再从子list中遍历里面的元素,放在临时的列表中, #如果列表中个数达到了列数,则把这个list放在重构list中作为一行 for childlist in mat: for item in childlist: templist.append(item) count += 1 if (count == c): mat1.append(templist) #这边如果不清空则会把前面的临时list中的数也输出出来 count=0 templist=[] return mat1 if __name__ == '__main__': a = Solution() b = a.matrixReshape([[1, 2], [3, 4]],4,1) print(b)
java解法
public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] nums,int r,int c){ int[][] res = new int[r][c]; if(nums.length ==0 || r*c != nums.length*nums[0].length) return nums; //建立队列 Queue<Integer> que = new LinkedList<>(); //将数组的元素放到队列中 for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<nums[0].length;j++){ que.add(nums[i][j]); } } //将队列中的元素放到指定的数组中 for(int i=0;i<r;i++){ for(int j=0;j<c;j++){ res[i][j] = que.remove(); } } return res; } }