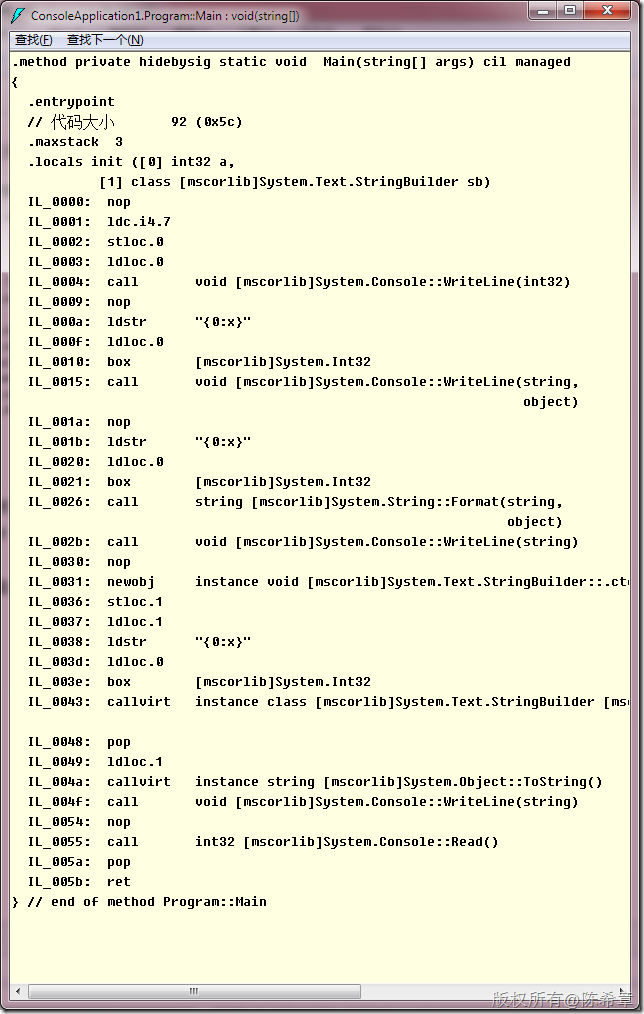
大家可以思考下面的代码
static void Main(string[] args) { int a = 7; Console.WriteLine(a); Console.WriteLine("{0:x}", a); Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0:x}", a)); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.AppendFormat("{0:x}", a); Console.WriteLine(sb.ToString()); Console.Read(); }
有几个问题:
1. 这几个方法哪些会发生装箱,哪些不会?
2. 他们有什么区别吗?
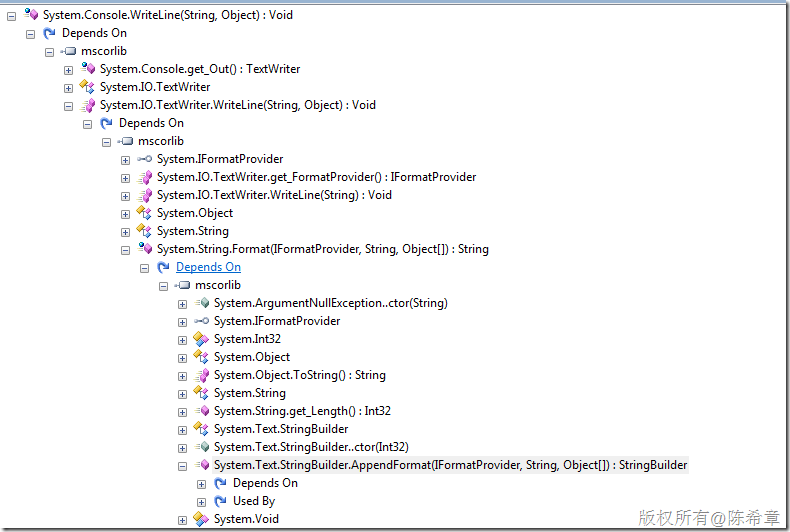
要了解这两点,可以通过下面的图形
所以,答案就是,只有第一种没有发生装箱操作。其他三种都发生了。
而后面三种,本质上有差别吗?
我们看到最后一种,是有callvirt指令的,也就是说它创建了一个stringbuilder对象,这是引用类型的。
他们真的有差别吗?
其实没有差别,如果我们通过工具查看源代码就会知道,Console.WriteLine方法,其实是调用了TextWriter.WriteLine方法,而这个又调用里的String.Format方法 ,而这个又调用了stringbuilder的AppendFormat方法
那么,为什么需要谈这些?我们的问题是:是否可以完全避免装箱呢?答案是:可以,但代价不见得小
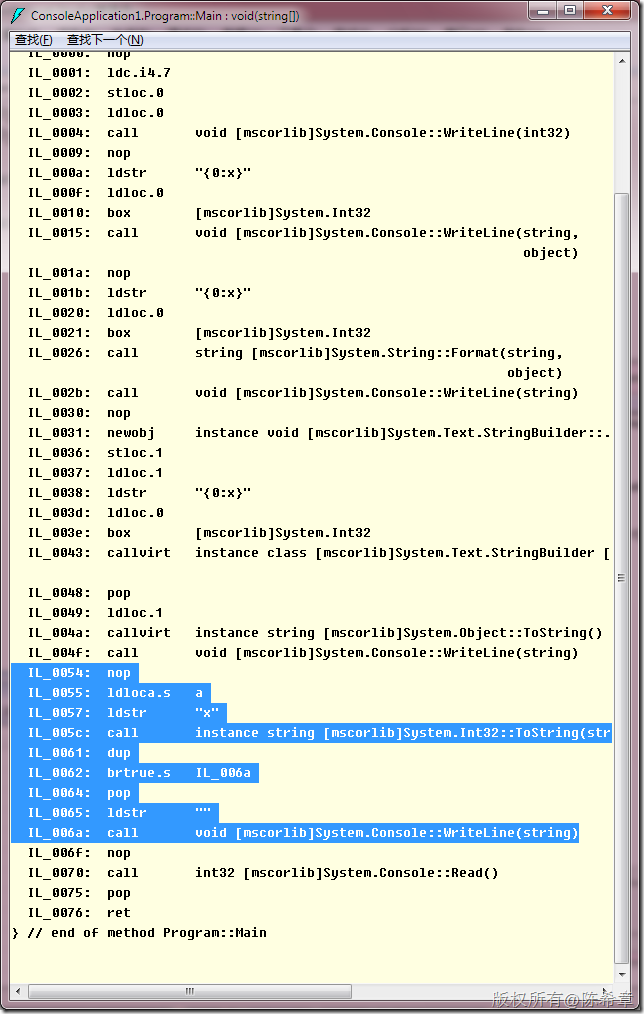
我们为什么会用strnig.Format就是因为要拼接字符串。那么能不能直接拼接呢?
Console.WriteLine("" + a.ToString("x"));
看起来确实没有了装箱对吧,但其实因为string本身不可变长,此时仍然会产生两个string
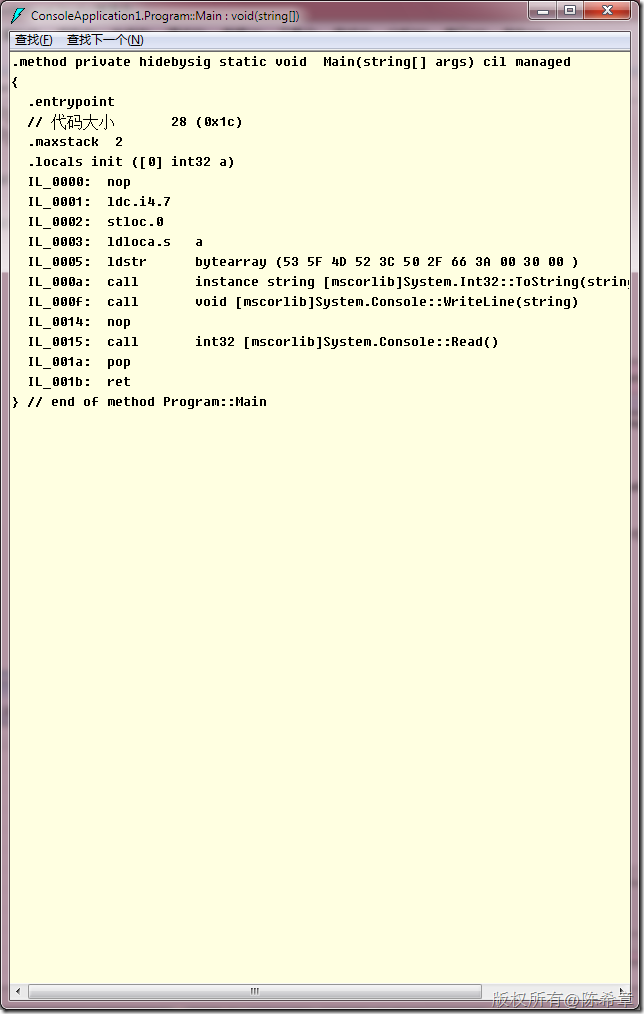
那么下面这个方式是否可行呢
Console.WriteLine(a.ToString("当前值是:0"));
如果大家有兴趣,可以看看这个AppendFormat方法
public StringBuilder AppendFormat(IFormatProvider provider, string format, params object[] args) { int num3; if ((format == null) || (args == null)) { throw new ArgumentNullException((format == null) ? "format" : "args"); } char[] chArray = format.ToCharArray(0, format.Length); int index = 0; int length = chArray.Length; char ch = '\0'; ICustomFormatter formatter = null; if (provider != null) { formatter = (ICustomFormatter) provider.GetFormat(typeof(ICustomFormatter)); } Label_004E: num3 = index; int num4 = index; while (index < length) { ch = chArray[index]; index++; if (ch == '}') { if ((index < length) && (chArray[index] == '}')) { index++; } else { FormatError(); } } if (ch == '{') { if ((index < length) && (chArray[index] == '{')) { index++; } else { index--; break; } } chArray[num4++] = ch; } if (num4 > num3) { this.Append(chArray, num3, num4 - num3); } if (index == length) { return this; } index++; if (((index == length) || ((ch = chArray[index]) < '0')) || (ch > '9')) { FormatError(); } int num5 = 0; do { num5 = ((num5 * 10) + ch) - 0x30; index++; if (index == length) { FormatError(); } ch = chArray[index]; } while (((ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9')) && (num5 < 0xf4240)); if (num5 >= args.Length) { throw new FormatException(Environment.GetResourceString("Format_IndexOutOfRange")); } while ((index < length) && ((ch = chArray[index]) == ' ')) { index++; } bool flag = false; int num6 = 0; if (ch == ',') { index++; while ((index < length) && (chArray[index] == ' ')) { index++; } if (index == length) { FormatError(); } ch = chArray[index]; if (ch == '-') { flag = true; index++; if (index == length) { FormatError(); } ch = chArray[index]; } if ((ch < '0') || (ch > '9')) { FormatError(); } do { num6 = ((num6 * 10) + ch) - 0x30; index++; if (index == length) { FormatError(); } ch = chArray[index]; } while (((ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9')) && (num6 < 0xf4240)); } while ((index < length) && ((ch = chArray[index]) == ' ')) { index++; } object arg = args[num5]; string str = null; if (ch == ':') { index++; num3 = index; num4 = index; while (true) { if (index == length) { FormatError(); } ch = chArray[index]; index++; switch (ch) { case '{': if ((index < length) && (chArray[index] == '{')) { index++; } else { FormatError(); } break; case '}': if ((index < length) && (chArray[index] == '}')) { index++; } else { index--; if (num4 > num3) { str = new string(chArray, num3, num4 - num3); } goto Label_0253; } break; } chArray[num4++] = ch; } } Label_0253: if (ch != '}') { FormatError(); } index++; string str2 = null; if (formatter != null) { str2 = formatter.Format(str, arg, provider); } if (str2 == null) { if (arg is IFormattable) { str2 = ((IFormattable) arg).ToString(str, provider); } else if (arg != null) { str2 = arg.ToString(); } } if (str2 == null) { str2 = string.Empty; } int repeatCount = num6 - str2.Length; if (!flag && (repeatCount > 0)) { this.Append(' ', repeatCount); } this.Append(str2); if (flag && (repeatCount > 0)) { this.Append(' ', repeatCount); } goto Label_004E; }