四则运算的生成
(1) 给出每个功能的重点、难点、编程收获。
public double caculate(String str)
这个函数是本程序中的主要计算函数,通过对输入的字符串进行解析然后判断操作符或是数值然后计算大致为:
重点:
1.判断string当中有没有非法字符 。
2.循环开始解析字符串,当字符串解析完,且符号栈为空时,则计算完成 。
3.用当前取得的运算符与栈顶运算符比较优先级:若高于,则因为会先运算,放入栈顶;若等于,因为出现在后面,所以会后计算,所以栈顶元素出栈,取出操作数运算; 若小于,则同理,取出栈顶元素运算,将结果入操作数栈。
4.判断当前运算符与栈顶元素优先级,取出元素,进行计算(因为优先级可能小于栈顶元素,还小于第二个元素等等,需要用循环判断。
难点:优先级比较以及栈的进出
收获:学习过逆波兰表达式,这次是实际操作,通过栈来进一步掌握
public double caculate(String str) { // 1.判断string当中有没有非法字符 String temp;// 用来临时存放读取的字符 // 2.循环开始解析字符串,当字符串解析完,且符号栈为空时,则计算完成 StringBuffer tempNum = new StringBuffer();// 用来临时存放数字字符串(当为多位数时) StringBuffer string = new StringBuffer().append(str);// 用来保存,提高效率 while (string.length() != 0) { temp = string.substring(0, 1); string.delete(0, 1); // 判断temp,当temp为操作符时 if (!isNum(temp)) { // 1.此时的tempNum内即为需要操作的数,取出数,压栈,并且清空tempNum if (!"".equals(tempNum.toString())) { // 当表达式的第一个符号为括号 double num = Integer.parseInt(tempNum.toString()); numStack.push(num); tempNum.delete(0, tempNum.length()); } // 用当前取得的运算符与栈顶运算符比较优先级:若高于,则因为会先运算,放入栈顶;若等于,因为出现在后面,所以会后计算,所以栈顶元素出栈,取出操作数运算; // 若小于,则同理,取出栈顶元素运算,将结果入操作数栈。 // 判断当前运算符与栈顶元素优先级,取出元素,进行计算(因为优先级可能小于栈顶元素,还小于第二个元素等等,需要用循环判断) while (!compare(temp.charAt(0)) && (!priStack.empty())) { double a = numStack.pop();// 第二个运算数 double b = numStack.pop();// 第一个运算数 char ope = priStack.pop(); double result = 0;// 运算结果 switch (ope) { // 如果是加号或者减号,则 case '+': result = b + a; // 将操作结果放入操作数栈 numStack.push(result); break; case '-': result = b - a; // 将操作结果放入操作数栈 numStack.push(result); break; case '*': result = b * a; // 将操作结果放入操作数栈 numStack.push(result); break; case '/': result = b/a; numStack.push(result); break; } } // 判断当前运算符与栈顶元素优先级, 如果高,或者低于平,计算完后,将当前操作符号,放入操作符栈 priStack.push(new Character(temp.charAt(0))); if (temp.charAt(0) == ')') {// 当栈顶为'(',而当前元素为')'时,则是括号内以算完,去掉括号 priStack.pop(); priStack.pop(); } } else // 当为非操作符时(数字) tempNum = tempNum.append(temp);// 将读到的这一位数接到以读出的数后(当不是个位数的时候) } return numStack.pop(); }
(二)private boolean isNum(String temp)
这个函数主要的功能就是判断传入的字符是不是0-9的数字
/** * 判断传入的字符是不是0-9的数字 * * @param str * 传入的字符串 * @return */ private boolean isNum(String temp) { return temp.matches("[0-9]"); }
(三) private boolean compare(char str)
这个函数是本程序中的比较操作符优先级的函数,大致思想如下:
重点:
1.比较当前操作符与栈顶元素操作符优先级,如果比栈顶元素优先级高,则返回true,否则返回false
2.str 需要进行比较的字符
3.比较结果 true代表比栈顶元素优先级高,false代表比栈顶元素优先级低
4. '('优先级最高, ')'优先级最低, '*/'优先级只比'+-'高
难点:设计运算符的优先级,从而对应栈内的存放顺序。
收获:对于逆波兰的理解更加深
/** * 比较当前操作符与栈顶元素操作符优先级,如果比栈顶元素优先级高,则返回true,否则返回false * * @param str 需要进行比较的字符 * @return 比较结果 true代表比栈顶元素优先级高,false代表比栈顶元素优先级低 */ private boolean compare(char str) { if (priStack.empty()) { // 当为空时,显然 当前优先级最低,返回高 return true; } char last = (char) priStack.lastElement(); // 如果栈顶为'('显然,优先级最低,')'不可能为栈顶。 if (last == '(') { return true; } switch (str) { case '#': return false;// 结束符 case '(': // '('优先级最高,显然返回true return true; case ')': // ')'优先级最低, return false; case '*': { // '*/'优先级只比'+-'高 if (last == '+' || last == '-') return true; else return false; } case '/': { if (last == '+' || last == '-') return true; else return false; } // '+-'为最低,一直返回false case '+': return false; case '-': return false; } return true; }
(四)public static void exception()
重点:
这个函数主要是为了处理异常输入时候不至于打断函数报错的异常处理函数,比如除数不能为0,当随机出题的时候遇到/0这种形式的时候就会调用exception函数并输出一个提示语句然后进行正常出题,这样可以保证在出现异常输入时候整个程序还可以继续回调执行。
难点:try catch的合理应用
收获:对于稳定程序要通过try catch尽量捕获可能出现的异常。
public static void exception() { if(w==1){ int l=0; while(l<20){ ArrayList<Object> s = new ArrayList<Object>(); Random random = new Random(); int num[] = new int[4]; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { num[i] =(int)random.nextInt(10); } char[] cs = {'+','-','*','/'}; for (int i = 0;i<num.length ; i++) { char cz = cs[(int)(Math.random()*cs.length)];//随机操作运算 s.add(num[i]); if(i<num.length-1) s.add(cz); } f4 operate = new f4(); String str = s.toString(); str=str.substring(1, str.length()-1); str+='#'; String ss = str.replaceAll(",",""); String s1 = ss.replaceAll("\s*", "");//可以替换大部分空白字符, 不限于空格 s 可以匹配空格、制表符、换页符等空白字符的其中任意一个 double t = operate.caculate(s1); System.out.println(s1.substring(0,s1.length()-1)+"="); System.out.print("?"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int read = sc.nextInt(); if(t==read){ System.out.println("答对啦,你真是个天才!"); }else{ System.out.println("再想想吧,答案似乎是"+t+"喔!"); } l++; continue;} } else if(w==2){ int l1 =0; while(l1<20){ ArrayList<Object> s = new ArrayList<Object>(); ArrayList<Object> s1 = new ArrayList<Object>(); ArrayList<Object> s2 = new ArrayList<Object>(); Random random = new Random(); int num[] = new int[4]; char[] cs = {'+','-','*','/'}; char[] kuo={'('}; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { num[i] =(int)random.nextInt(10); } for (int i = 0;i<num.length; i++) { char cz = cs[(int)(Math.random()*cs.length)];//随机操作运算 s.add(num[i]); if(i<num.length-1) s.add(cz); } for(int i = 0 ; i < s.size() ; i++) { char kuohao = kuo[(int )(Math.random()*kuo.length)]; if(s.get(i) instanceof Integer&&i<s.size()-1 ){ s1.add(kuohao); s1.add(s.get(i)); } else if(s.get(s.size()-1) instanceof Integer) s1.add(s.get(i)); } int temp=0;int p=0; int temp1=0; int temp2=0; for(int i = 0 ; i <s1.size() ; i++) { if(!(s1.get(i).equals('('))){ s2.add(s1.get(i)); } if(s1.get(i).equals('(')){ p++; if(p==2){ temp1=temp; System.out.println(p+"p"+temp1+"temp1"); } if(p==3){ temp2=temp1; } temp=i; System.out.println(temp+"temp"); s2.add(s1.get(i)); } if((temp<s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-temp-1)&&s1.get(temp).equals('('))||(temp>s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-(temp-(s1.size()/2)))&&s1.get(temp).equals('('))){ s2.add(')');} if(p==2) if((temp1<s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-temp1-1)&&s1.get(temp1).equals('('))||(temp1>s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-(temp1-(s1.size()/2)))&&s1.get(temp1).equals('('))){ s2.add(')');} if(p==3) if((temp2<s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-temp2-1)&&s1.get(temp2).equals('('))||(temp2>s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-(temp2-(s1.size()/2)))&&s1.get(temp2).equals('('))){ s2.add(')'); if((temp1<s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-temp1-1)&&s1.get(temp1).equals('('))||(temp1>s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-(temp1-(s1.size()/2)))&&s1.get(temp1).equals('('))){ s2.add(')');} } } System.out.println(" "); f4 operate = new f4(); String str = s2.toString(); str=str.substring(1, str.length()-1); str+='#'; String ss = str.replaceAll(",",""); String ss1 = ss.replaceAll("\s*", "");//可以替换大部分空白字符, 不限于空格 s 可以匹配空格、制表符、换页符等空白字符的其中任意一个 System.out.println(ss1); double t2 = operate.caculate(ss1); System.out.println(ss1.substring(0,ss1.length()-1)+"="+t2); System.out.print("?"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int read = sc.nextInt(); if(t2==read){ System.out.println("答对啦,你真是个天才!"); }else{ System.out.println("再想想吧,答案似乎是"+t2+"喔!"); } l1++; continue; } } else if(w==3){ ArrayList<Object> s = new ArrayList<Object>(); ArrayList<Object> s1 = new ArrayList<Object>(); ArrayList<Object> s2 = new ArrayList<Object>(); Random random = new Random(); int num[] = new int[4]; char[] cs = {'+','-','*','/'}; char[] kuo={'('}; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { num[i] =(int)random.nextInt(10); } for (int i = 0;i<num.length; i++) { char cz = cs[(int)(Math.random()*cs.length)];//随机操作运算 s.add(num[i]); if(i<num.length-1) s.add(cz); } for(int i = 0 ; i < s.size() ; i++) { char kuohao = kuo[(int )(Math.random()*kuo.length)]; if(s.get(i) instanceof Integer&&i<s.size()-1 ){ s1.add(kuohao); s1.add(s.get(i)); } else if(s.get(s.size()-1) instanceof Integer) s1.add(s.get(i)); } int temp=0;int p=0; int temp1=0; int temp2=0; for(int i = 0 ; i <s1.size() ; i++) { if(!(s1.get(i).equals('('))){ s2.add(s1.get(i)); } if(s1.get(i).equals('(')){ p++; if(p==2){ temp1=temp; } if(p==3){ temp2=temp1; } temp=i; s2.add(s1.get(i)); } if((temp<s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-temp-1)&&s1.get(temp).equals('('))||(temp>s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-(temp-(s1.size()/2)))&&s1.get(temp).equals('('))){ s2.add(')');} if(p==2) if((temp1<s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-temp1-1)&&s1.get(temp1).equals('('))||(temp1>s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-(temp1-(s1.size()/2)))&&s1.get(temp1).equals('('))){ s2.add(')');} if(p==3) if((temp2<s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-temp2-1)&&s1.get(temp2).equals('('))||(temp2>s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-(temp2-(s1.size()/2)))&&s1.get(temp2).equals('('))){ s2.add(')'); if((temp1<s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-temp1-1)&&s1.get(temp1).equals('('))||(temp1>s1.size()/2&&i==((int)s1.size()-(temp1-(s1.size()/2)))&&s1.get(temp1).equals('('))){ s2.add(')');} } } f4 operate = new f4(); String str = s2.toString(); str=str.substring(1, str.length()-1); str+='#'; String ss = str.replaceAll(",",""); String ss1 = ss.replaceAll("\s*", "");//可以替换大部分空白字符, 不限于空格 s 可以匹配空格、制表符、换页符等空白字符的其中任意一个 double t2 = operate.caculate(ss1); System.out.println(ss1.substring(0,ss1.length()-1)+"="+" "+t2); } }
(五)public static String doubletransint(double num)
重点:
这个函数主要是将double型输出结果(如12.0)输出时转换为int型数据(如12)。
收获:注意数值的编码类型
public static String doubletransint(double num){ if(num % 1.0 == 0){ return String.valueOf((long)num); }else{ BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(num); double f1 = b.setScale(2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue(); return String.valueOf(f1); } }
(2)给出结对编程的体会:
结对编程,因为对编程语言掌握的不同,以及掌握程度的不同,在编程思路上会有着不同,但是同样的正是因为着这样的不同,就会有着很多本来想不到的点子和看法,很利于去发现新的方法,以及解决自己没有注意到的问题。
(3) 至少5项在编码、争论、复审等活动中花费时间较长,给你较大收获的事件。 (10分)
1).编程语言,我们选择了更加成熟的java语言。这点告诉我们会什么其实非常重要
2).关于如何解觉除数为零的问题,通过一系列的争论,最后发现可以直接不随机生成零。这点告诉我们,有的时候,生活就是这样,解决实际问题的方法很有可能是换一个角度。
3).如何生成随机括号的方法,最终确定利用if判断以及折半查找来实现。
4).界面设置,最后被老师否决。告诉我们,用户的需求不能够随意的按自己的意志去改变
5).计算带括号的四则运算的方法,通过设定符号优先级,以及栈的使用。
运行截图:
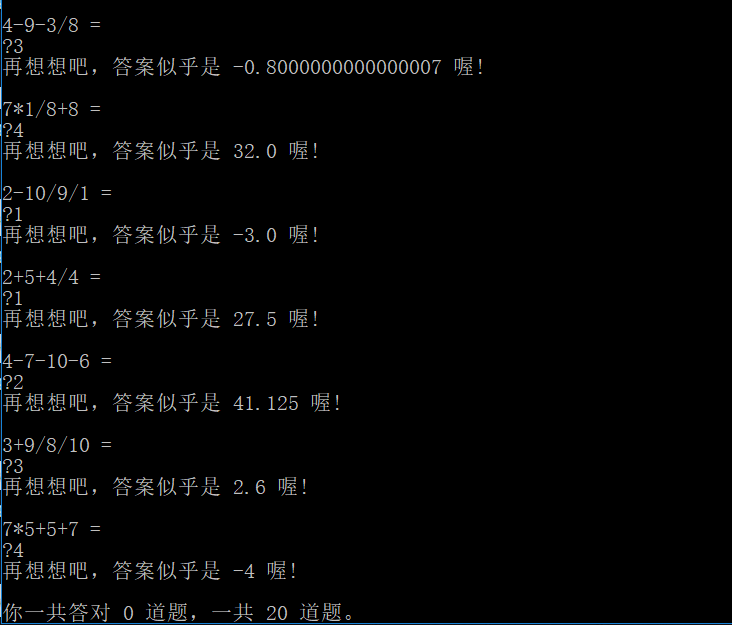

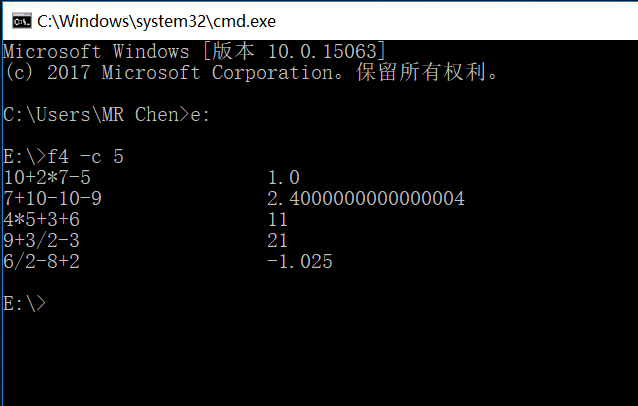
结对编程图片:

代码地址:https://git.coding.net/liuchengzhi0944/f4.git