容器基本用法:
bean 是 Spring 中最核心的东西。
我们先看一下 bean 的定义:
public class MyTestBean {
private String testStr = "testStr";
public String getTestStr() {
return testStr;
}
public void setTestStr(String testStr) {
this.testStr = testStr;
}
public MyTestBean(){}
public MyTestBean(String testStr) {
super();
this.testStr = testStr;
}
}
bean没有任何特别之处,的确,Spring的目的就是让我们的bean能成为一个纯粹的POJO。
我们接下来看一下配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myTestBean" class="zhi.hao.bean.MyTestBean"></bean>
</beans>
在上面的配置中我们看到了bean的声明方式,尽管Spring中bean的元素定义着N中属性来支撑我们业务的各种应用,但是我们只要声名成这样,基本上就已经可以满足我们的大多数应用了。
测试代码
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public class BeanFactoryTest {
@Test
public void testSimpleLoad(){
/**
* 通过当前文件的绝对路径,读取配置文件(通了)
*/
// File f = new File(this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath());
File f = new File(ServletContext.class.getResource("/").getPath());
f = new File(f.getPath()+"/../classes/beanFactoryTest.xml");
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new FileSystemResource(f));
MyTestBean bean = (MyTestBean)bf.getBean("myTestBean");
assertEquals("testStr",bean.getTestStr());
/**
* 把文件通过流的方式,读取配置文件(不通,找不到配置文件)
*/
// InputStream is = null;
// try {
// is = new FileInputStream("beanFactoryTest.xml");
// } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// Resource resource = new InputStreamResource(is);
// BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
// MyTestBean bean = (MyTestBean)bf.getBean("myTestBean");
// assertEquals("testStr",bean.getTestStr());
/**
* java项目可以使用,maven项目中找不到配置文件(不通)
*/
/*
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("classpath:beanFactoryTest.xml"));
MyTestBean bean = (MyTestBean)bf.getBean("myTestBean");
assertEquals("testStr",bean.getTestStr());
*/
}
}
以上Demo实例,github地址: https://github.com/myaq1314/learn-spring-beans
结果:
直接使用BeanFactory 作为容器对于Spring的使用来说并不多见,甚至是甚少使用,因为在企业级的应用中大多数都会使用的是ApplicationContext。
这段测试代码完成的功能:
读取配置文件beanFactoryTest.xml。
根据beanFactoryText.xml中的配置找到对应的类的配置,并实例化。
调用实例化后的实例。
最简单的Spring功能架构
如果想完成我们预想的功能,至少需要3个类
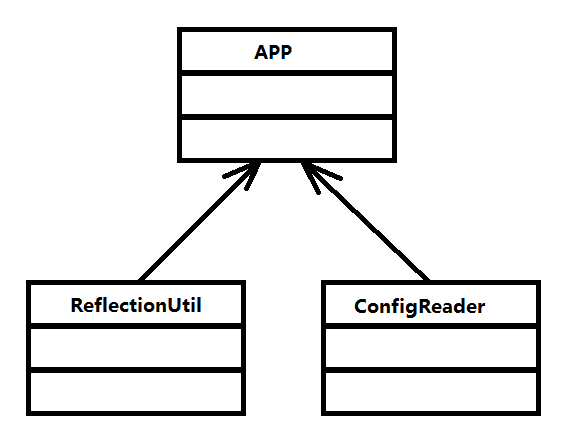
ConfigReader:用于读取及验证配置文件。
我们要用配置文件里面的东西,当然首先要做的就是读取,然后放置在内存中。
ReflectionUtil:用于根据配置文件中的配置进行反射实例化。
比如在例2.1中beanFactoryTest.xml出现的<bean id="myTestBean" class="zhi.hao.bean.MyTestBean" />,我们就可以根据bean.MyTestBean进行实例化。
APP:用于完成整个逻辑的串联。